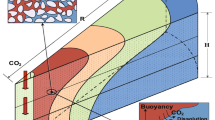
Abstract
The injection of supercritical CO2 in deep saline aquifers leads to the formation of a CO2 plume that tends to float above the formation brine. As pressure builds up, CO2 properties, i.e. density and viscosity, can vary significantly. Current analytical solutions do not account for CO2 compressibility. In this article, we investigate numerically and analytically the effect of this variability on the position of the interface between the CO2-rich phase and the formation brine. We introduce a correction to account for CO2 compressibility (density variations) and viscosity variations in current analytical solutions. We find that the error in the interface position caused by neglecting CO2 compressibility is relatively small when viscous forces dominate. However, it can become significant when gravity forces dominate, which is likely to occur at late times of injection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c r :
-
Rock compressibility
- c α :
-
Compressibility of fluid α (α = c, w)
- d :
-
Aquifer thickness
- E rel :
-
Relative error of the interface position
- g :
-
Gravity
- h w :
-
Hydraulic head of water
- k :
-
Intrinsic permeability
- \({k_{{\rm r}_\alpha}}\) :
-
α-Phase relative permeability (α = c, w)
- N :
-
Gravity number
- \({P_{{\rm t}_0}}\) :
-
Fluid pressure at the top of the aquifer prior to injection
- P DT :
-
Fluid pressure for Dentz and Tartakovsky (2009a) approach
- \({\overline{P}_{\rm DT}}\) :
-
Vertically averaged fluid pressure for Dentz and Tartakovsky (2009a) approach
- \({\overline{P}_{\rm N}}\) :
-
Vertically averaged fluid pressure for Nordbotten et al. (2005) approach
- \({\overline{P}_{0}}\) :
-
Vertically averaged fluid pressure prior to injection
- P α :
-
Fluid pressure of α-phase (α = c, w)
- Q m :
-
CO2 mass flow rate
- Q 0 :
-
CO2 volumetric flow rate
- q α :
-
Volumetric flux of α-phase (α = c, w)
- R :
-
Radius of influence
- R c :
-
CO2 plume radius at the top of the aquifer for compressible CO2
- R i :
-
CO2 plume radius at the top of the aquifer for incompressible CO2
- r :
-
Radial distance
- r 0 :
-
CO2 plume radius at the top of the aquifer
- r b :
-
CO2 plume radius at the base of the aquifer
- r c :
-
Characteristic length
- r w :
-
Injection well radius
- S s :
-
Specific storage coefficient
- \({S_{{\rm r _w}}}\) :
-
Residual saturation of the formation brine
- S α :
-
Saturation of α-phase (α = c, w)
- t :
-
Time
- z :
-
Vertical coordinate
- z 0 :
-
Depth of the top of the aquifer
- z b :
-
Depth of the base of the aquifer
- V :
-
CO2 plume volume
- α :
-
Phase index, c CO2 and w brine
- β :
-
CO2 compressibility
- \({\epsilon_{\rm v}}\) :
-
Volumetric strain
- γ cw :
-
A dimensionless parameter that measures the relative importance of viscous and gravity forces
- λ α :
-
Mobility of α-phase (α = c, w)
- μ α :
-
Viscosity of α-phase (α = c, w)
- ρ 0 :
-
CO2 density at the reference pressure \({P_{\rm t_0}}\)
- ρ 1 :
-
Constant for the CO2 density
- \({\overline{\rho}_{\rm c}}\) :
-
Mean CO2 density
- \({\overline{\rho}_{{\rm c}_{\rm DT}}}\) :
-
Mean CO2 density for Dentz and Tartakovsky (2009a) approach
- \({\overline{\rho}_{{\rm c}_{\rm N}}}\) :
-
Mean CO2 density for Nordbotten et al. (2005) approach
- ρ α :
-
Density of α-phase (α = c, w)
- σ′:
-
Effective stress
- \({\phi}\) :
-
Porosity
- ζ :
-
Interface position from the bottom of the aquifer
References
Altunin V.V., Sakhabetdinov M.A.: Viscosity of liquid and gaseous carbon dioxide at temperatures 220-1300 K and pressure up to 1200 bar. Teploenergetika, 8, 85–89 (1972)
Angus, A., Armstrong, B., Reuck, K.M. (eds): International thermodynamics tables of the fluid state. Carbon dioxide. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1976)
Aziz, K., Settari, A. (eds): Petroleum Reservoir Simulation. 2nd edn. Blitzprint Ltd., Calgary (2002)
Bachu S.: Screening and ranking of sedimentary basins for sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change. Environ. Geol. 44, 277–289 (2003)
Bachu S., Adams J.J.: Sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change: capacity of deep saline aquifers to sequester CO2 in solution. Energy Convers. Manag. 44, 3151–3175 (2003)
Bear, J. (eds): Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Elsevier, New York (1972)
Bolster, D., Barahona, M., Dentz, M., Fernandez Garcia, D., Sanchez-Vila, X., Trichero, P., Volhondo, C., Tartakovsky, D.M. : Probabilistic risk assessment applied to contamination scenarios in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 45, w06413. (2009a) doi:10.1029/2008wR007551
Bolster D., Dentz M., Carrera J.: Effective two phase flow in heterogeneous media under temporal pressure fluctuations. Water Resour. Res. 45, W05408 (2009b). doi:10.1029/2008WR007460
Cantucci B., Montegrossi G., Vaselli O., Tassi F., Quattrocchi F., Perkins E.H.: Geochemical modeling of CO2 storage in deep reservoirs: the Weyburn Project (Canada) case study. Chem. Geol. 265, 181–197 (2009)
Celia M.A., Nordbotten J.M.: Practical modeling approaches for geological storage of carbon dioxide. Ground Water 47(5), 627–638 (2009)
Chen, Z., Huan, G., Ma, Y. (eds): Computational methods for multiphase flows in porous media. SIAM, Philadelphia (2006)
Cooper H.H., Jacob C.E.: A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well field history. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 27, 526–534 (1946)
Dake, L.P. (eds): Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering. Elsevier, Oxford (1978)
Dentz M., Tartakovsky D.M.: Abrupt-interface solution for carbon dioxide injection into porous media. Trans. Porous Media 79, 15–27 (2009a)
Dentz M., Tartakovsky D.M.: Response to “Comments on abrupt-interface solution for carbon dioxide injection into porous media by Dentz and Tartakovsky (2008)” by Lu et al. Trans. Porous Media 79, 39–41 (2009b)
Ennis-King J., Paterson L.: The role of convective mixing in the long-term storage of carbon dioxide in deep saline formations. J. Soc. Pet. Eng. 10(3), 349–356 (2005)
Garcia, J.E.: Fluid Dynamics of Carbon Dioxide Disposal into Saline Aquifers. PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley (2003)
Garcia, J.E., Pruess, K.: Flow Instabilities during injection of CO2 into saline aquifers. Proceedings Tough Symposium 2003, LBNL, Berkeley (2003)
GHS: Spreadsheet with CO2 compressibility correction. http://www.h2ogeo.upc.es/publicaciones/2009/Transport%20in%20porous%20media/Effects%20of%20CO2%20Compressibility%20on%20CO2%20Storage%20in%20Deep%20Saline%20Aquifers.xls (2009)
Hesse M.A., Tchelepi H.A., Cantwell B.J., Orr F.M. Jr: Gravity currents in horizontal porous layers: Transition from early to late self-similarity. J. Fluid Mech. 577, 363–383 (2007)
Hesse M.A., Tchelepi H.A., Orr F.M. Jr: Gravity currents with residual trapping. J. Fluid Mech. 611, 35–60 (2008)
Hidalgo J.J., Carrera J.: Effect of dispersion on the onset of convection during CO2 sequestration. J. Fluid Mech. 640, 443–454 (2009)
Hitchon B., Gunter W.D., Gentzis T., Bailey R.T.: Sedimentary basins and greenhouse gases: a serendipitous association. Energy Convers. Manag. 40, 825–843 (1999)
Huppert H.E., Woods A.W.: Gravity-driven flows in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 292, 55–69 (1995)
Juanes, R., MacMinn, C.W., Szulczewski, M.L.: The footprint of the CO2 plume during carbon dioxide storage in saline aquifers: storage efficiency for capillary trapping at the basin scale. Trans. Porous Media. doi:10.1007/s11242-009-9420-3 (2009)
Katz, D.L., Lee, R.L. (eds): Natural Gas Engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York (1990)
Kopp A., Class H., Helmig R.: Investigation on CO2 storage capacity in saline aquifers Part 1. Dimensional analysis of flow processes and reservoir characteristics. J. Greenh. Gas Control 3, 263–276 (2009)
Korbol R., Kaddour A.: Sleipner vest CO2 disposal—injection of removed CO2 into the Utsira formation. Energy Convers. Manag. 36(6–9), 509–512 (1995)
Lake, L.W. (eds): Enhanced Oil Recovery. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jercey (1989)
Law D.H.S., Bachu S.: Hydrogeological and numerical analysis of CO2 disposal in deep aquifers in the Alberta sedimentary basin. Energy Convers. Manag. 37(6-8), 1167–1174 (1996)
Lu C., Lee S.-Y., Han W.S., McPherson B.J., Lichtner P.C.: Comments on “abrupt-interface solution for carbon dioxide injection into porous media” by M. Dentz and D. Tartakovsky. Trans. Porous Media 79, 29–37 (2009)
Lyle S., Huppert H.E., Hallworth M., Bickle M., Chadwick A.: Axisymmetric gravity currents in a porous medium. J Fluid Mech. 543, 293–302 (2005)
Mathias, S.A., Hardisty, P.E., Trudell, M.R., Zimmerman, R.W.: Approximate solutions for pressure buildup during CO2 injection in brine aquifers. Trans. Porous Media. doi:10.1007/s11242-008-9316-7 (2008)
McPherson B.J.O.L., Han W.S., Cole B.S.: Two equations of state assembled for basic analysis of multiphase CO2 flow and in deep sedimentary basin conditions. Comput. Geosci. 34, 427–444 (2008)
Neuweiller I., Attinger S., Kinzelbach W., King P.: Large scale mixing for immiscible displacement in heterogenous porous media. Trans. Porous Media 51, 287–314 (2003)
Neuzil C.E.: Groundwater flow in low-permeability environments. Water Resour. Res. 22(8), 1163–1195 (1986)
Nooner S.L., Eiken O., Hermanrud C., Sasagawa G.S., Stenvold T., Zumberge M.A.: Constraints on the in situ density of CO2 within the Utsira formation from time-lapse seafloor gravity measurements. J. Greenh. Gas Control 1, 198–214 (2007)
Nordbotten J.M., Celia M.A., Bachu S.: Injection and storage of CO2 in deep saline aquifers: analytical solution for CO2 plume evolution during injection. Trans. Porous Media 58, 339–360 (2005)
Nordbotten J.M., Kavetski D., Celia M.A., Bachu S.: A semi-analytical model estimating leakage associated with CO2 storage in large-scale multi-layered geological systems with multiple leaky wells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(3), 743–749 (2009). doi:10.1021/es801135v
Olivella S., Carrera J., Gens A., Alonso E.E.: Non-isothermal multiphase flow of brine and gas through saline media. Trans. Porous Media 15, 271–293 (1994)
Olivella S., Gens A., Carrera J., Alonso E.E.: Numerical formulation for a simulator (CODE_BRIGHT) for the coupled analysis of saline media. Eng. Comput. 13, 87–112 (1996)
Pruess K., Garcia J.: Multiphase flow dynamics during CO2 disposal into saline aquifers. Environ. Geol. 42, 282–295 (2002)
Pruess K., Garcia J., Kovscek T., Oldenburg C., Rutqvist J., Steelfel C., Xu T.: Code intercomparison builds confidence in numerical simulation models for geologic disposal of CO2. Energy 29, 1431–1444 (2004)
Riaz A., Hesse M., Tchelepi H., Orr F.M. Jr: Onset of convection in a gravitationally unstable diffusive boundary layer in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 548, 87–111 (2006)
Rutqvist J., Birkholzer J., Cappa F., Tsang C.-F.: Estimating maximum sustainable geological sequestration of CO2 using coupled fluid flow and geomechanical fault-slip analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 48, 1798–1807 (2007)
Saripalli P., McGrail P.: Semi-analytical approaches to modeling deep well injection of CO2 for geological sequestration. Energy Convers. Manag. 43, 185–198 (2002)
Sovova H., Prochazka J.: Calculations of compressed carbon dioxide viscosities. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 32(12), 3162–3169 (1993)
Span R., Wagner W.: A new equation of state for carbon dioxide covering the fluid region from the triple-point to 1100 K at pressures up to 88 MPa. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 25(6), 1509–1596 (1996)
Stauffer P.H., Viswanathan H.S., Pawar R.J., Guthrie G.D.: A system model for geologic sequestration of carbon dioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(3), 565–570 (2009)
Tartakovsky D.M.: (2007) Probabilistic risk analysis in subsurface hydrology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L05 404
Tchelepi, H.A., Orr, F.M. Jr.: Interaction of viscous fingering, permeability inhomogeneity and gravity segregation in three dimensions. SPE Symposium on Reservoir Simulation, New Orleans, pp. 266–271, (1994)
Thiem, G. (eds): Hydrologische Methode. Leipzig, Gebhardt (1906)
Tsang C.-F., Birkholzer J., Rutqvist J.: A comparative review of hydrologic issues involved in geologic storage of CO2 and injection disposal of liquid waste. Environ. Geol. 54, 1723–1737 (2008)
van Genuchten M.T.: A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 892–898 (1980)
Vilarrasa, V., Bolster, D., Olivella, S., Carrera, J.: Coupled hydromechanical modelling of CO2 sequestration in deep saline aquifers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control (submitted) (2010)
Zhou Q., Birkholzer J., Tsang C.-F., Rutqvist J.: A method for quick assessment of CO2 storage capacity in closed and semi-closed saline formations. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2, 626–639 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilarrasa, V., Bolster, D., Dentz, M. et al. Effects of CO2 Compressibility on CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers. Transp Porous Med 85, 619–639 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9582-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9582-z