Abstract
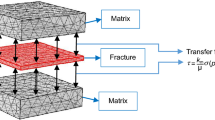
Matrix–fracture transfer functions are the backbone of any dual-porosity or dual-permeability formulation. The chief feature within them is the accurate definition of shape factors. To date, there is no completely accepted formulation of a matrix–fracture transfer function. Many formulations of shape factors for instantly-filled fractures with uniform pressure distribution have been presented and used; however, they differ by up to five times in magnitude. Based on a recently presented transfer function, time-dependent shape factors for water imbibing from fracture to matrix under pressure driven flow are proposed. Also new matrix–fracture transfer pressure-based shape factors for instantly-filled fractures with non-uniform pressure distribution are presented in this article. These are the boundary conditions for a case for porous media with clusters of parallel and disconnected fractures, for instance. These new pressure-based shape factors were obtained by solving the pressure diffusivity equation for a single phase using non-uniform boundary conditions. This leads to time-dependent shape factors because of the transient part of the solution for pressure. However, approximating the solution with an exponential function, one obtains constant shape factors that can be easily implemented in current dual-porosity reservoir simulators. The approximate shape factors provide good results for systems where the transient behavior of pressure is short (a case commonly encountered in fractured reservoirs).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin, S.: Estimation of fracture relative permeabilities from unsteady state corefloods. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 30(1), 1–14 (2001)
Akin S., Schembre J.M., Bhat S.K., Kovscek A.R.: Spontaneous imbibition characteristics of diatomite. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 25, 149–165 (2000)
Aronofsky J.S., Massé L., Natanson S.G.: A model for the mechanism of oil recovery from the porous matrix due to water invasion in fractured reservoirs. Trans. AIME 213, 17 (1958)
Bear J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. American Elsevier Publishing Co., New York (1972)
Beckner, B.L., Ishimoto, K., Yamaguchi, S. Firoozabadi, A., Aziz, K.: Imbibition dominated matrix-fracture fluid transfer in dual porosity simulators. Paper SPE 16981 in proceedings of the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Dallas, TX (1987)
Chang, M.: Deriving the shape factor of a fractured rock matrix. Technical Report NIPER-696 (DE93000170), NIPER, Bartlesville OK (1993) http://www.osti.gov/bridge/servlets/purl/10192737-T81n3D/webviewable/10192737.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2009
Crank J.: The Mathematics of Diffusion. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1975)
de Swaan, A.: Theory of waterflooding in fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 115–122 (1978)
de Swaan A.: Influence of shape and skin of matrix-rock blocks on pressure transients in fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. Form. Eval. 5, 344–352 (1990)
Gupta, A., Civan, F.: An improved model for laboratory measurement of matrix to fracture transfer function parameters in immiscible displacement. Paper SPE 28929 in proceedings of the 1994 SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, New Orleans, LA, September (1994)
Horne, R.N., Satik, C., Mahiya, G., Li, K., Ambusso, W., Tovar, R., Wang, C., Nassori, H.: Steam-water relative permeability. Paper presented at the 2000 world geothermal congress, Kyushu-Tohoku, Japan, June (2000)
Kazemi H., Merrill L.S. Jr, Porterfield K.L., Zeman P.R.: Numerical simulation of water-oil flow in naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 16(3), 317–326 (1976)
Kazemi H., Gilman J.R., El-Sharkawy A.M.: Analytical and numerical solution of oil recovery from fractured reservoirs with empirical transfer functions. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eng. 7, 219–227 (1992)
Lim K.T., Aziz K.: Matrix-fracture transfer shape factors for dual-porosity simulators. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 13, 169 (1995)
Rangel-Germán, E.: Water infiltration in fractured porous media: in-situ imaging, analytical model, and numerical study. Ph.D. Dissertation, Stanford University, Stanford, CA (2002)
Rangel-Germán E.R., Kovscek A.R.: Experimental and analytical study of multidimensional imbibition in fractured porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 36, 45–60 (2002)
Rangel-Germán, E., Kovscek, A.R.: Time-dependent matrix–fracture shape factors for partially and complete immersed fractures. SPE Paper 84411, presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Denver, USA. October (2003)
Reis J.: An analysis of oil expulsion mechanisms from matrix blocks during steam injection in naturally fractured reservoir. In Situ 16(1), 43–73 (1992)
Warren, J.E., Root, P.J.: The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 245–255 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rangel-German, E.R., Kovscek, A.R. & Akin, S. Time-Dependent Shape Factors for Uniform and Non-Uniform Pressure Boundary Conditions. Transp Porous Med 83, 591–601 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9461-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9461-7