Abstract
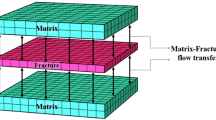
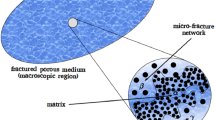
Over the past few decades, significant progress of assessing chemical transport in fractured rocks has been made in laboratory and field investigations as well as in mathematic modeling. In most of these studies, however, matrix diffusion on fracture–matrix surfaces is considered as a process of molecular diffusion only. Mathematical modeling based on this traditional concept often had problems in explaining or predicting tracer transport in fractured rock. In this article, we propose a new conceptual model of fracture-flow-enhanced matrix diffusion, which correlates with fracture-flow velocity. The proposed model incorporates an additional matrix-diffusion process, induced by rapid fluid flow along fractures. According to the boundary-layer theory, fracture-flow-enhanced matrix diffusion may dominate mass-transfer processes at fracture–matrix interfaces, where rapid flow occurs through fractures. The new conceptual model can be easily integrated with analytical solutions, as demonstrated in this article, and numerical models, as we foresee. The new conceptual model is preliminarily validated using laboratory experimental results from a series of tracer breakthrough tests with different velocities in a simple fracture system. Validating of the new model with field experiments in complicated fracture systems and numerical modeling will be explored in future research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
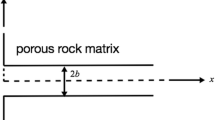
Half aperture of fractures (m)
- c :
-
Concentration (kg/m3)
- c, c i :
-
Simulated concentration (kg/m3)
- c * :
-
Measured concentration (kg/m3)
- c f :
-
(Averaged) solute concentration across fractures (kg/m3)
- c m :
-
Solute concentration of the matrix on the matrix block surface (kg/m3)
- c o :
-
Constant fracture source solute concentration (kg/m3)
- D :
-
Hydrodynamic dispersion coefficient along fractures (m2/s)
- D E :
-
Effective enhanced matrix-diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- D m :
-
Free-solution molecular diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- D * :
-
Effective molecular diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- h c :
-
Mass-transfer coefficient at the fracture–matrix interface (m/s)
- K f :
-
Distribution coefficient (m) on fracture surfaces, defined the solute mass adsorbed per unit area of fracture surface divided by solute concentration in solution
- n :
-
Exponential
- p :
-
Laplace operator
- R f :
-
Fracture-face retardation coefficient
- q c :
-
Mass-transfer flux at the fracture and matrix interface [kg/(s m2)]
- v :
-
Mean-flow velocity in fracture (m/s)
- \({\vec{v}}\) :
-
Fracture-flow velocity vector (m/s)
- w i :
-
Weighting factor
- α E :
-
Fracture-flow-enhanced dispersivity (m2-n/s1-n)
- δ c :
-
Thickness of a concentration boundary (film) layer (m)
- δ h :
-
Velocity boundary-layer thickness (m)
- \({\phi}\) :
-
Porosity of the matrix
- \({\phi}\) :
-
Objective function of Eq. 10
- λ :
-
Decay constant (1/s)
- τ :
-
Tortuosity of matrix porous media
References
Berkowitz B.: Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: A Review. Adv. Water Resour. 25, 861–884 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00042-8
Bird R.B., Steward W.E., Lightfoot E.N.: Transport Phenomena. Wiley, New York (1960)
Doherty J.: PEST Model-Independent Parameter Estimation. Watermark Numerical Computing, Australia (2004)
Fahien R.W.: Fundamentals of Transport Phenomena. McGraw-Hill, New York (1983)
Hu Q., Kneafsey T.J., Roberts J.J., Tomutsa L., Wang J.S.: Characterizing unsaturated diffusion in porous tuff gravel. Vadose Zone J. 3, 1425–1438 (2004)
Huyakorn P.S., Lester B.H., Mercer J.W.: An efficient finite element technique for modeling transport of fractured porous media, 1. Single species transport. Water Resour. Res. 19(3), 841–854 (1983). doi:10.1029/WR019i003p00841
Liu H.H., Haukwa C.B., Ahlers C.F., Bodvarsson G.S., Flint A., Guertal W.B.: Modeling flow and transport in unsaturated fractured rocks: An evaluation of the continuum approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 62–63, 173–188 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(02)00170-5
Liu H.H., Salve R., Wang J.S., Bodvarsson G.S., Hudson D.: Field investigation into unsaturated flow and transport in a fault: Model analysis. J. Contam. Hydrol. 74, 39–59 (2004a). doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2004.02.004
Liu H.H., Bodvarsson G.S., Zhang G.: The scale-dependency of the effective matrix diffusion coefficient. Vadose Zone J. 3, 312–315 (2004)
Lu G., Sonnenthal E.L., Bodvarsson G.S.: Implications of halide leaching on 36Cl studies at Yucca Mountain, Nevada. Water Resour. Res. 39(12), 3-1–3-15 (2003)
Maloszewski A., Zuber A.: Tracer experiments in fractured rocks: Matrix diffusion and validity of models. Water Resour. Res. 29(8), 2723–2735 (1993). doi:10.1029/93WR00608
Neretnieks I.: Diffusion in the rock matrix: An important factor in radionuclide Neretnieks, I. Diffusion in the rock matrix: An important factor in radionuclide retardation?. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 4379–4397 (1980). doi:10.1029/JB085iB08p04379
Neretnieks I., Eriksen T., Tahtinen P.: Tracer movement in a single fissure in granitic rock: Some experimental results and their interpretation. Water Resour. Res. 18(4), 849–858 (1982). doi:10.1029/WR018i004p00849
Ozisik M.N.: Heat Transfer: A Basic Approach. McGraw-Hill, New York (1985)
Pruess K., Narasimhan T.N.: A practical method for modeling fluid and heat flow in fractured porous media. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 25, 14–26 (1985). doi:10.2118/10509-PA
Rasmuson A., Narasimhan T.N., Neretnieks I.: Chemical transport in a fissured rock: Verification of a numerical model. Water Resour. Res. 18(3), 1479–1492 (1982). doi:10.1029/WR018i005p01479
Reimus P.W., Callahan T.J.: Matrix diffusion rates in fractured volcanic rocks at the Nevada Test Site: Evidence for a dominant influence of effective fracture aperture. Water Resour. Res. 43, W07421 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006WR005746
Starr R.C., Gillgam R.W., Sudicky E.A.: Experimental investigation of solute transport in stratified porous media, 1. The nonreactive case. Water Resour. Res. 21(7), 1035–1041 (1985). doi:10.1029/WR021i007p01043
Sudicky E.A., Frind E.O.: Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: Analytical solutions for a system of parallel fractures. Water Resour. Res. 18(6), 1634–1642 (1982). doi:10.1029/WR018i006p01634
Sudicky E.A., Gillgam R.W., Frind E.O.: Experimental investigation of solute transport in stratified porous media, vol. 2. The reactive case. Water Resour. Res. 21(7), 1043–1050 (1985). doi:10.1029/WR021i007p01035
Tang D.H., Frind E.O., Sudicky E.A.: Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: Analytical solutions for a single fractures. Water Resour. Res. 17(3), 555–564 (1981). doi:10.1029/WR017i003p00555
van Genuchten M.T., Dalton F.N.: Models for simulating salt movement in aggregated field soils. Geoderma 38, 165–183 (1986). doi:10.1016/0016-7061(86)90013-3
Warren J.E., Root P.J.: The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 3(3), 245–255 (1963). doi:10.2118/426-PA
Wu Y.S., Ahlers C.F., Fraser P., Simmons A., Pruess K.: Software Qualification of Selected TOUGH2 Modules, Report LBL-39490; UC-800. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA (1996)
Wu Y.S., Pruess K.: Numerical simulation of non-isothermal multiphase tracer transport in heterogeneous fractured porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 23, 699–723 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(00)00008-7
Wu Y.S., Liu H.H., Bodvarsson G.S.: A triple-continuum approach for modeling flow and transport processes in fractured rock. J. Contam. Hydrol. 73, 145–179 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2004.01.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, YS., Ye, M. & Sudicky, E.A. Fracture-Flow-Enhanced Matrix Diffusion in Solute Transport Through Fractured Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 81, 21–34 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9383-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9383-4