Abstract
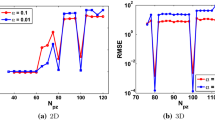
Recent developments in meshless numerical methods have led to algorithms that can be used to solve arbitrarily large problems without the support of a connected mesh, and without the computational cost and numerical ill-conditioning issues usually associated with such solution techniques. This work applies the Local Hermitian Interpolation (LHI) method, based on local interpolation with Radial Basis Functions (RBFs), to the solution of 3D unsaturated porous media problems. The proposed implementation is capable of handling real soil properties, provided either as an analytical function or as a series of pointwise measurements. The technique is implemented with implicit and explicit timestepping, and is validated against two transient Richards’ equation models, of which one has a known analytical solution. In addition, a real-world infiltration problem based on a saturated–unsaturated formulation is modelled, using a realistic variation of soil properties with water-pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear, J.: Modeling Groundwater Flow and Pollution. Reidel (1987)
Brown D.: On approximate cardinal preconditioning methods for solving PDEs with radial basis functions. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 29(4), 343–353 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.enganabound.2004.05.006
Divo E., Kassab A.: An efficient localised radial basis function meshless method for fluid flow and conjugate heat transfer. J. Heat Transfer 129, 124–136 (2007). doi:10.1115/1.2402181
Fasshauer G.E.: Solving partial differential equations by collocation with radial basis Functions. In: Le Méhautée, A., Rabut, C., Schumaker, L.L. (eds) Surface Fitting and Multiresolution Methods., Vanderbilt University Press, Tennessee (1997)
Hernandez Rosales A., Power H.: Non-overlapping domain decomposition algorithm for the Hermite radial basis function meshless collocation approach: applications to convection diffusion problems. J. Algorithms Technol. 1(1), 127–159 (2007). doi:10.1260/174830107780122685
Ingber M., Chen C., Tanski J.: A mesh free approach using radial basis functions and parallel domain decomposition for solving three-dimensional diffusion equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 60, 2183–2201 (2004). doi:10.1002/nme.1043
Kansa E.J.: Multiquadrics—a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics-I: surface approximations and partial derviatives estimates. Comput. Math. Appl. 19, 127–145 (1990a). doi:10.1016/0898-1221(90)90270-T
Kansa E.J.: Multiquadrics—a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid dynamics-II: solution to parabolic, hyperbolic and elliptic partial differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 19, 147–161 (1990b). doi:10.1016/0898-1221(90)90271-K
Lee C., Liu X., Fan S.: Local multiquadric approximation for solving boundary value problems. Comput. Mech. 30, 396–409 (2003). doi:10.1007/s00466-003-0416-5
Lehmann F.A.: P, Comparison of iterative methods for improved solution of the fluid flow equation in partially saturated porous media. Transp. Porous Media 31, 275–292 (1998). doi:10.1023/A:1006555107450
Ling L., Kansa E.J.: Preconditioning for radial basis functions with domain decomposition methods. Math. Comput. Model. 38(5), 320–327 (2004)
Ling L., Opfer R., Schaback R.: Results on meshless collocation techniques. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 30(4), 247–253 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.enganabound.2005.08.008
Madych W., Nelson S.: Multivariate interpolation and conditionally positive definite functions II. Math. Comput. 44(189), 211–230 (1990). doi:10.2307/2008691
Munoz-Gomez, J., Gonzalez-Casanova, P., Rodriguez-Gomez, G.: Domain decomposition by radial basis functions for time dependent partial differential equations. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IASTED International Conference on Advances in Computer Science and Technology. Puerto Vallarta, Mexico (2006)
Saad, Y.: SPARSKIT: a basic tool-kit for sparse matrix computations. [Cited; Available from: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~saad/software/SPARSKIT/sparskit.html] (1988–2000)
Sarler B., Vertnik R.: Meshless explicit local radial basis function collocation methods for diffusion problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 51, 1269–1282 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.camwa.2006.04.013
Schaback R.: Multivariate interpolation and approximation by translates of a basis function. In: Chui, C., Schumaker, L. (eds) Approximation Theory VIII, World Scientific Publishing, London (1995)
Schaback R.: Convergence of unsymmetric kernal-based meshless collocation methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(1), 333–351 (2007)
Serrano S.E.: Modeling infiltration with approximate solutions of Richards’ equation. J. Hydrol. Eng. 9(5), 421–432 (2004). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2004)9:5(421)
Shu C., Ding H., Yeo K.: Local radial basis function-based differential quadrature method and its application to solve two-dimensional incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192, 941–954 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(02)00618-7
Stevens, D., Power, H., Morvan, H.: An order-N complexity meshless algorithm for transport-type PDEs based on Local Hermitian Interpolation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. (2009, in Print)
Tolstykh A., Shirobokov D.: On using radial basis functions in a finite difference mode with applications to elasticity problems. Comput. Mech. 33, 68–79 (2003). doi:10.1007/s00466-003-0501-9
Tracy, F.T.: Clean two- and three-dimensional analytical solutions of Richards’ equation for testing numerical solvers. Water Resour. Res., 42(8), W08503, 1–11 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005WR004638
Vertnik R., Zaloznik M., Sarler B.: Solution of transient direct-chill aluminium billet casting problem with simultaneous material and interphase moving boundaries by a meshless method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 30, 847–855 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.enganabound.2006.05.004
Wright G., Fornberg B.: Scattered node compact finite difference-type formulas generated from radial basis functions. J. Comput. Phys. 212(1), 99–123 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.05.030
Wu Z.: Hermite-Birkhoff interpolation of scattered data by radial basis functions. Approximation Theory 8(2), 1–11 (1992)
Wu, Z.: Solving PDEs with radial basis functions and the error estimation. In: Chen, Z., et al. (eds.) Advances in Computational Mathematics (Lecture Notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics), vol. 202. CRC Press, London (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, D., Power, H., Lees, M. et al. A Meshless Solution Technique for the Solution of 3D Unsaturated Zone Problems, Based on Local Hermitian Interpolation with Radial Basis Functions. Transp Porous Med 79, 149–169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9303-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9303-z