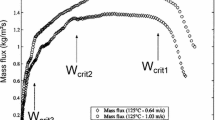
Abstract
Salt crystallisation at the surface or in a porous medium has been recognised as a major mechanism of deterioration of buildings and historical monuments. Often crystallisation occurs when the concentration of salt dissolved in the water contained in the porous medium reaches the saturation concentration as the result of evaporation. In order to predict the evolution of the ion distribution during drying, we develop a simple volume averaged model combining a semi-analytical model of drying with the numerical computation of the ions transport. The model is used to analyse the influence of the drying rate, size of the porous medium, average pore size and initial ion concentration on the ion distribution during drying and therefore the possible location of crystallisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benavente D., Garcia del Cura M.A., Garcia-Guinea J., Sanchez-Moral S., Ordenez S. (2004). Role of pore structure in salt crystallization in unsaturated porous stone. J. Crys. Growth. 260(3–4):532–544
Ben Nasrallah S., Damak O., Ben Dhia H., Arnaud G. (1991). Transfert de soluté au cours du séchage convectif. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 34:911–917
Bouhlila, R.: Ecoulements transports et réactions Géochimiques couplés dans les milieux poreux. Cas des sels et des saumures, Ph.D Thesis, ENIT, Tunis (1999)
Buenfeld, N.R., Shurafa-Daoudi, M.-T., McLoughlin, I.M.: Chloride transport due to wick action in concrete. In: Nilsson, L.O., Ollivier, J.P. (eds.) Chloride Penetration into Concrete, pp. 315–324, RILEM, Paris, (Proc. RILEM Int. Workshop on Chloride Penetration into Concrete, 1995).
Camassel B., Sghaier N., Prat M., Ben Nasrallah S. (2005). Ions transport during evaporation in capillary tubes of polygonal cross section. Chem. Eng. Sci. 60:815–826
Coussot P. (2000). Scaling approach to the convective drying of a porous medium. Eur. Phys. J. B 15:557–566
Durán J.D.G., Ontiveros A., Chibowski E., González-Caballero F. (1999). Deposition of Colloidal Zinc Sulfide on Glass Substrate. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 214:53–63
Febvre, C.: Modélisation de l’évaporation naturelle sur un salin. Mémoire Diplôme d’Ingénieur, CNAM (1982)
Finkayson B.C. (1992). Numerical Methods for Problems with Moving Fronts. Ravenna Park Publishing, Seatttle, WA
Flatt, R.J., Scherer, G.W.: Hydration and crystallization pressure of sodium sulfate: a critical review. In: Materials Issues in Art and Archaeology—Symposium 2001, vol. 712, pp. 29–34. (Boston 2002)
Huinink H.P., Pel L., Michels M.A.J. (2002a). How ions distribute in a drying porous medium: A simple model. Phys. fluids 14(4):1389–1395
Huinink H.P., Pel L.J., Michels M.A., Prat M. (2002b). Drying processes in the presence of temperature gradients. Pore –scale modelling. Eur. Phys. J. E. 9:487–498
Huinink, H. P., Pel, L., Michels, M.A.J.: Structure and transport properties of liquid clusters in a drying porous medium. Phys. Rev. E, 68, 056114 (2003)
Goudie A., Viles H. (1997). Salt Weathering Hazards. Wiley, Chichester
Laurindo J.B., Prat M. (1998). Numerical and experimental network study of evaporation in capillary porous media. Drying rates. Chem. Eng. Sci. 53(12):2257–2269
Le Bray Y., Prat M. (1999). Three dimensional pore network simulation of drying in capillary porous media. Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer 42:4207–4224
Lim P.C., Barbour S.L., Fredlund D.L. (1998). The influence of degree of saturation on the coefficient of aqueous diffusion. Can. Geotech. J. 35:811–827
Kaviany M. (1991). Principles of heat transfer in porous media mechanical engineering series. Springer-verlag, New York
Krisher, O.: Die wissenschaftlichen Grundlagen der Trocknungstechnik, 1, 298, Springer, Berlin (1963).
Masmoudi W., Prat M. (1991). Heat and mass transfer between a porous medium and a parallel external flow, application to drying of capillary porous materials. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 34(8):1975–1989
Mayer G., Wittmann F.H. (1996). Ein modell zur Beschreibung des Wasser-und Salztransports in Mauerwerk. Int. Zeitschrift für Bauinstandsetzen 2(1):67–82
Patankar, S.V.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. HPC, Washingdon, DC: Hemisspere (1980).
Pitzer K.S. (1973). Thermodynamics of electrolytes, I. Theorical basis and general equations. J Phys. Chem. 77:268–277
Prat M. (2002). Recent advances in pore-scale models for drying of porous media. Chem. Eng. J. 86(1–2):153–164
Puyate Y.T., Lawrence C.J. (1999). Effect of solute parameters on wick action in concretre. Chem. Eng. Sci. 54:4257–4265
Scherer G.W. (1999). Crystallization in pores. Cement concrete Res. 29:1347–1358
Sghaier, N., Prat, M, Ben Nasrallah, S.: On the influence of sodium chloride concentration on equilibrium contact angle. Chem. Eng. J. (2006, in press). Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse and Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieur de Monastir, in preparation.
Sghaier, N., Prat, M., Ben Nasrallah, S.: Drying processes in the presence of salt, pore scale modeling, Proceedings of ICAPM 2004, pp. 573–578, 24–27 May 2004, Évora, Portugal (2004)
Stauffer D. Aharaony A. (1992). Introduction to Percolation Theory. Taylor & Francis, London
Van Brakel J. (1980). Mass transfer in convective drying. In: Mujumdar A.S. (eds) Advances in Drying. Hemisphere, New-York, pp. 217–267
Whitaker S. (1999). The Method of Volume Averaging. Kluwer Academic publishers, Dordrecht
Yiotis A.G., Boudouvis A.G., Stubos A.K., Tsimpanogiannis I.N., Yortsos Y.C. (2004). The effect of liquid films on the drying of porous media. AiChE J. 50(11):2721–2737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sghaier, N., Prat, M. & Nasrallah, S.B. On Ions Transport during Drying in a Porous Medium. Transp Porous Med 67, 243–274 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-9007-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-9007-1