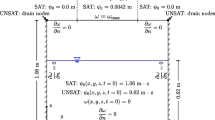
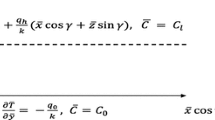Abstract
Carbon dioxide injected into saline aquifers dissolves in the resident brines increasing their density, which might lead to convective mixing. Understanding the factors that drive convection in aquifers is important for assessing geological CO2 storage sites. A hydrodynamic stability analysis is performed for non-linear, transient concentration fields in a saturated, homogenous, porous medium under various boundary conditions. The onset of convection is predicted using linear stability analysis based on the amplification of the initial perturbations. The difficulty with such stability analysis is the choice of the initial conditions used to define the imposed perturbations. We use different noises to find the fastest growing noise as initial conditions for the stability analysis. The stability equations are solved using a Galerkin technique. The resulting coupled ordinary differential equations are integrated numerically using a fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The upper and lower bounds of convection instabilities are obtained. We find that at high Rayleigh numbers, based on the fastest growing noise for all boundary conditions, both the instability time and the initial wavelength of the convective instabilities are independent of the porous layer thickness. The current analysis provides approximations that help in screening suitable candidates for homogenous geological CO2 sequestration sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachu, S., Nordbotten, J.M, Celia, M. A.: Evaluation of the spread of acid gas plumes injected in deep saline aquifers in western Canada as an analogue to CO2 injection in continental sedimentary basins. In: Rubin, E.S., Keith, D.W., Gilboy, C.F. (eds) Peer Reviewed Papers and Overviews, Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, 5–9 September 2004, Vancouver, Canada. vol. 1, pp479–487. Elsevier (2005)
Bachu, S., Carroll, J.J.: In-situ phase and thermodynamic properties of resident brine and acid gases (CO2 & H2S) injected in geological formations in western Canada. In: Rubin E.S., Keith D.W., Gilboy C.F. (eds) Peer Reviewed Papers and Overviews, Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, 5–9 September 2004, Vancouver, Canada, Vol. 1, pp449–457. Elsevier (2005)
J.L. Beck (1972) ArticleTitleConvection in a box of porous material saturated with fluid Phys. Fluids 15 IssueID8 1377–1383 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1694096
J.-P. Caltagirone (1980) ArticleTitleStability of a saturated porous media layer subject to a sudden rise in surface temperature: comparison between the linear and energy methods Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 33 47–58
Carslaw, H.S., Jaeger, J.C.: Conduction of Heat in Solids, p. 185. Oxford University Press (1959)
Ennis-King, J.P., Paterson, L.: Role of convective mixing in the long term storage of carbon dioxide in deep saline formations, SPE paper 84340, ATCE 5–8 October 2003. Denver (2003)
J.P. Ennis-King I. Preston L. Paterson (2005) ArticleTitleOnset of convection in anisotropic porous media subject to a rapid change in boundary conditions Phys. Fluids 17 084107 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.2033911
T. Foster (1965a) ArticleTitleStability of a homogenous fluid cooled from above Phys. Fluids 8 IssueID7 1249–1257 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1761393
T. Foster (1965b) ArticleTitleOnset of convection in a layer of fluid cooled from above Phys. Fluids 8 IssueID10 1770–1774 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1761108
T. Foster (1968) ArticleTitleEffect of boundary conditions on the onset of convection Phys. Fluids 11 1257–1262 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1692095
Gerald C.F., Wheatley, P.O.: Applied Numerical Analysis, 4th edn. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley (1989)
Hassanzadeh, H., Pooladi-Darvish, M., Keith, D.W.: Modeling of convective mixing in CO2 storage. J. Can. Petroleum Technol. 44(10), (2005)
Hassanzadeh, H.: Mathematical modeling of convective mixing in porous media for geological CO2 storage. Dissertation, University of Calgary (2006)
C.W. Horton F.T. Rogers SuffixJr. (1945) ArticleTitleConvection currents in porous media J. Appl. Phys. 20 367–369 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1707601
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Special report on Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage. Cambridge University Press (2005)
B.S. Jhavery G.M. Homsy (1982) ArticleTitleThe onset of convection in fluid layer heated rapidly in a time-dependent manner J. Fluid Mech. 114 251–260 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112082000135
M. Kaviany (1984) ArticleTitleOnset of thermal convection in a saturated porous medium: experiment and analysis Intern. J. Heat Mass Transfer 27 IssueID11 2101–2110 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0017-9310(84)90197-2
Y. Katto T. Masuoka (1967) ArticleTitleCriterion for the onset of convective flow in a fluid in a porous medium Intern. J. Heat Mass Transfer 10 297–309 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0017-9310(67)90147-0
M.C. Kim L.H. Kim C.K. Choi (2004) ArticleTitleThe onset of convective motion in a horizontal fluid layer heated from below and cooled from above with constant heat flux Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer 31 837–846 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0735-1933(04)00070-3
M.C. Kim S. Kim (2005) ArticleTitleOnset of convective stability in a fluid-saturated porous layer subjected to time-dependent heating Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 32 IssueID3–4 416–424
D. Kvernvold P. Tyvand (1980) ArticleTitleDispersion effects on thermal convection in porous media J. Fluid Mech. 99 IssueIDpart 4 673–686 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112080000821
E.R. Lapwood (1948) ArticleTitleConvection of a fluid in a porous medium Proc. Cambridge Phil. Soc. 44 508–521 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S030500410002452X
W. Lick (1965) ArticleTitleThe stability of a fluid layer with time-dependent heating J. Fluid Mech. 21 IssueIDpart 3 565–576 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112065000332
E.G.B Lindeberg D. Wessel-Berg (1996) ArticleTitleVertical convection in an aquifer column under a gas cap of CO2 Energy Convers. Manage. 38 229–234 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00274-9
E.G. Mahler R.S Schechter E.H. Wissler (1968) ArticleTitleStability of a fluid layer with time-dependent density gradients Phys. Fluids 11 IssueID9 1901–1912 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1692217
H.L. Morrison F.T. Rogers SuffixJr. C.W. Horton (1949) ArticleTitleConvection currents in porous media, II. Observation of conditions at onset of convection J. Appl. Phys. 20 1027–1029 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1698267
B.R. Morton (1957) ArticleTitleOn the equilibrium of a stratified layer of fluid J. Mech. Appl. Math. 10 433–447
D.A. Nield A. Bejan (1999) Convection in Porous Media EditionNumberSecond Springer-Verlag New York
Ozisik M.N.: Heat Conduction, 2nd edn, p. 48. John Wiley & Sons (1993)
A. Riaz M. Hesse A. Tchelepi F. Orr SuffixJr. (2006) ArticleTitleOnset of convection in a gravitationally unstable, diffusive boundary layer in porous media J. Fluid Mech. 548 87–111 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112005007494
H. Rubin (1974) ArticleTitleHeat dispersion effect on thermal convection in a Porous medium layer J. Hydrol. 21 173–185 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(74)90035-3
K.K. Tan R.B. Thorpe (1996) ArticleTitleThe onset of convection caused by buoyancy during transient heat conduction in deep fluids Chem. Eng. Sci. 51 4127–4136 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0009-2509(96)00255-2
P. Tyvand (1977) ArticleTitleHeat dispersion effect on thermal convection in anisotropic porous media J. Hydrol. 34 335–342 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(77)90140-8
P.C. Wankat G.M. Homsy (1977) ArticleTitleLower bounds for the onset of instability in heated layers Phys. Fluids 20 1200–1201 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.861683
J. Weber (1975) ArticleTitleDispersion effect on buoyancy-driven convection in stratified flows through porous media J. Hydrol. 25 59–70 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(75)90039-6
X. Xu S. Chen Z. Zhang (2006) ArticleTitleConvective stability analysis of the long-term storage of carbon dioxide in deep saline aquifers Advances in Water Resources 29 397–497 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.05.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassanzadeh, H., Pooladi-Darvish, M. & Keith, D.W. Stability of a fluid in a horizontal saturated porous layer: effect of non-linear concentration profile, initial, and boundary conditions. Transp Porous Med 65, 193–211 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-005-6088-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-005-6088-1