Abstract
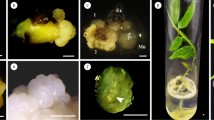
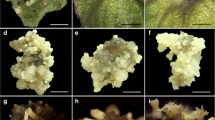
Cotyledonary segments from the germinated immature zygotic embryos were used for the somatic embryogenesis of red sandalwood (Pterocarpus santalinus). The explants were established on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 5% sucrose and the combination of 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), and α-Naphthaleneacetic acid. All the treatments responded to callus induction with a 36–97% frequency range. The maximum embryogenic frequency (69.44%) was obtained when 0.1 mg/l BAP + 2 mg/l 2,4-D and 0.1 mg/l BAP + 4 mg/l 2,4-D combinations were used. When the explants were treated with individual growth regulators, the maximum embryogenic frequency (58.33%) was produced by 4 mg/l 2,4-D. BAP was completely ineffective for somatic embryogenesis when used individually. The average number of globular-staged somatic embryos ranged between 1 and 5 (irrespective of the treatments). The maximum number of the cotyledonary-staged somatic embryos (2.85) was obtained with the treatment 0.1 mg/l BAP and 2 mg/l 2,4-D. The maximum plantlets were developed (1.30) when the cotyledonary-staged embryos from 0.1 mg/l BAP and 2 mg/l 2,4-D were transferred to MS basal medium. The plantlets obtained were acclimatized and showed 100% survival in the greenhouse condition. The embryonic cells have been histologically distinguished from non-embryonic cells with dense cytoplasm and a long suspensor. The induction, maturation, and germination of somatic embryos were challenging, suggesting the need for molecular approaches through proteomic expression for mass production and understanding of the evolution, structure, and genetic organization of the plant species.
Key message
2,4-D and NAA, individually or in combination with BAP, has a significant effect on the embryonic potential of cotyledon explant of P. santalinus.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available by the corresponding author on reasonable reason request.
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthaleneacetic acid
- PGR:
-
Plant growth regulator
References
Anuradha M, Pullaiah T (1999) Propagation studies of red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus L.f.) in vitro-an endangered taxon of Andhra Pradesh, India. Taiwania 44(3):311–324
Arockiasamy S, Ignacimuthu S, Melchias G (2000) Influence of growth regulators and explants type on in-vitro shoot propagation and rooting of red sandalwood (Pterocarpus santalinus L.). Indian J Exp Biol 38:1270–1273
Arunakumara KKIU, Walpola BC, Subasinghe S, Yoon M (2011) Pterocarpus santalinus Linn.f. (Rath handun): a review of its botany, uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 54(4):495–500. https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.076
Arunkumar AN, Joshi G (2014) Pterocarpus santalinus (Red Sanders) an endemic, endangered tree of India: current status, improvement and the future. J Trop Environ 4(2):1–10
Arya S, Kalia RK, Arya ID (2000) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in Pinus roxburghii Sarg. Plant Cell Rep 19:775–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990000197
Azamthulla M, Balasubramanian R, Kavimani S (2015) A review on Pterocarpus santalinus Linn. World J Pharm Res 4(2):282–292
Balaraju K, Agastian P, Agnacimuthu S, Park K (2011) A rapid in vitro propagation of red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus) using shoot tip explants. Acta Physiol Plant 33(6):2501–2510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0795-8
Bulle S, Reddyvari H, Nallanchakravarthula V, Vaddi DR (2016) Therapeutic potential of Pterocarpus santalinus L.: an update. Pharmacogn Rev 10(19):43–49. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.176575
Canhoto JM, Rama SC, Cruz GS (2006) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:514–519. https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2006819
Chakraborty T, Chaitanya KV, Lambardi M, Akhtar N (2022) In vitro morphogenetic responses from cotyledonary explants of immature zygotic embryos of Pterocarpus santalinus. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 150:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02320-6
Chaturani GDG, Subasinghe S, Jayatilleka MP (2006) In-vitro establishment, germination and growth performance of red sandalwood (Pterocarpus santalinus L.). Trop Agri Res Ext 9:116–130
Chen S, Li Y, Xu C, Huang X, Liu T, Peng B, Pan J, Lpn M, Liao Y (2019) Tissue culture of Red Sandalwood (Pterocarpus santalinus). Agri Biotechnol 8(5):50–54
Chitra Devi B, Narmathabai V (2011) Somatic embryogenesis in the medicinal legume Desmodium motorium (Houtt.) Merr. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 106:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9937-3
da Silva ML, Paim-Pinto DL, de Campos JMS, de Carvalho IF, Rocha DI, Batista DS, Otoni WC (2021) Repetitive somatic embryogenesis from wild passion fruit (Passifora cincinnata Mast.) anthers. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02083-6
Dunstan DI, Tautorus TE, Thorpe TA (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 471–538
Ebrahimi M, Mokhtari A, Amirian R (2018) A highly efficient method for somatic embryogenesis of Kelussia odorotissima Mozaff., an endangered medicinal plant. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 132:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1314-4
Fráterová L, Salaj T, Matušíková I, Salaj J (2013) The role of chitinases and glucanases in somatic embryogenesis of black pine and hybrid firs. Central Eur J Biol. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-013-0234-5
Guan Y, Li S-G, Fan X-F, Su Z-H (2016) Application of somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Front Plant Sci 7:938. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00938
Gulzar B, Mujib A, Malik MQ, Sayeed R, Mamgain J, Ejaz B (2020) Genes, proteins and other networks regulating somatic embryogenesis in plants. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 18:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-020-00047-5
Halim ME, Misra A (2011) The effects of the aqueous extract of Pterocarpus santalinus heartwood and vitamin E supplementation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Med Plants Res 5(3):398–409
Han KH, Park YG (1999) Somatic embryogenesis in Black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.). In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 5. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 149–161
Hasbullah NA, Taha RM, Awal A (2007) Identification of embryogenic callus and in vitro somatic embryo formation in Gerbera jamesonii Bolus ex. Hook F Catrina 2(2):113–117
Hazubska-Przybył T, Ratajczak E, Obarska A, Pers-Kamczyc E (2020) Different roles of auxins in somatic embryogenesis efficiency in two Picea species. Int J Mol Sci 21:3394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093394
Hu R, Sun Y, Wu B, Duan H, Zheng H, Hu D, Lin H, Tong Z, Xu J, Li Y (2017) Somatic embryogenesis of immature Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) hook zygotic embryos. Sci Rep 7:56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00156-1
Husain MK, Anis M, Shahzad A (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb. Trees 24:781–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-010-0448-3
Isah T (2019) Proteome study of somatic embryogenesis in Nothapodytes nimmoniana (J. Graham) Mabberly. 3 Biotech 9:119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1637-4
Jadhav J, Gonjari G, Kanase A (2011) Angiogenic effects of Pterocarpus santalinus extracts in the chick chorioallantoic membrane. Drug Invent Today 3(6):62–68
Jadhav J, Mane A, Kanase A (2012) Stimulatory effect of Pterocarpus santalinus on vasculogenesis in Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM). J Pharm Res 5(1):208–211
Kaul T, Ram B, Pandey S, Reddy CS, Reddy MK (2014) Unravelling the regulation of somatic embryogenesis by extracellular calcium and auxin efflux blockers in hypocotyl explants of Albizzia lebbeck L.: similarity in action. Int J Bioassays 3(11):3536–3542
Kendurkar SV, Nadgauda RS, Phadke CH, Jana MM, Shirke SV, Mascarenhas AF (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in some woody angiosperms. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 5. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 49–79
Keshavamurthy M, Srinath BS, Ravishankar VR (2018) Phytochemicals mediated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Pterocarpus santalinus L. (Red Sanders) bark extract and their antimicrobial properties. Partic Sci Technol 36(7):785–790. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2017.1302533
Lakshmi Sita G, Shobha J, Vaidyanathan CS (1980) Regeneration of whole plants by embryogenesis from cell suspension cultures of sandalwood. Curr Sci 49(5):196–198
Mehta R, Sharma V, Sood A, Sharma M, Sharma RK (2011) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and analysis of genetic fidelity of in vitro-derived plantlets of Bambusa nutans Wall., using AFLP markers. Eur J Forest Res 130:729–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-010-0462-4
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Navada V (2014) Ethnomedicinal value of Pterocarpus santalinus (Linn.f.), a Fabaceae member. Orient Pharm Exp Med 14:313–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0168-098
Nolan KE, Song Y, Liao S, Saeed NA, Zhang X, Rose RJ (2014) An unusual abscisic acid and gibberellic acid synergism increases somatic embryogenesis, facilitates its genetic analysis and improves transformation in Medicago truncatula. PLoS ONE 9(6):e99908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099908
Nunes S, Marum L, Farinha N, Pereira VT, Almeida T, Sousa D, Mano N, Figueiredo J, Dias MC (2018) Somatic embryogenesis of hybrid Pinus elliottii var. elliottii × P. caribaea var. hondurensis and ploidy assessment of somatic plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 132:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1311-7
Prakash E, Khan PSSV, Rao TJVS, Meru ES (2006) Micropropagation of red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus L.) using mature nodal explants. J for Res 11:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-006-0230-y
Rajeswari V, Paliwal K (2008) In-vitro plant regeneration of red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus L.f.) from cotyledonary nodes. Indian J Biotechnol 7:541–546
Rao SP, Raju AJS (2002) Pollination ecology of the red sanders Pterocarpus santalinus (Fabaceae), an endemic and endangered tree species. Curr Sci 83(9):1144–1148
Rao AM, Ashok B, Mahesh MU, Subbareddy GV, Sekhar VC, Ramanamurthy GV, Rajulu AV (2019) Antibacterial cotton fabrics with in-situ generated silver and copper bimetallic nanoparticles using red sanders powder extract as reducing agent. Int J Polymer Anal Charact 24(4):346–354. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2019.1598631
Renganayaki PR, Vijayalakshmi KP, Tamilarasan C, Nagendra MS (2020) Studies on synchronizing seed germination in red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus). J Trop Sci 32(1):66–71
Sharry S, Ponce JLC, Estrella LH, Cano RMR, Lede S, Abedini W (2006) An alternative pathway for plant in vitro regeneration of chinaberry: tree Melia azedarach L. derived from the induction of somatic embryogenesis. Electron J Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol9-issue3-fulltext-13
Shree P, Yadav D, Singh VK, Chaube R, Tripathi YB (2019) Modulation of mTOR receptor in diabetic neuropathy by santalin A of lalchandan (Pterocarpus santalinus): An in-silico assessment by molecular docking. Int J Pharm Sci Res 10(3):1115–1121
Singh AK, Chand S (2003) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cotyledon explants of a timber-yielding leguminous tree, Dalbergia sissoo Roxb. J Plant Physiol 160:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00523
Sun T, Wang Y, Zhu L, Liu X, Wang Q, Ye J (2021) Evaluation of somatic embryo production during embryogenic tissue proliferation stage using morphology, maternal genotype, proliferation rate and tissue age of Pinus thunbergii Parl. J for Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01311-1
Trigiano RN, Buckley LG, Merkle SA (1999) Somatic embryogenesis in woody legumes. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 4. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 198–208
Verma SK, Das AK, Cingoz GS, Uslu E, Gurel E (2016) Influence of nutrient media on callus induction, somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in selected Turkish crocus species. Biotechnol Rep 10:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.03.006
Vijayalakshmi KP, Renganayaki PR (2017) Effect of pre-sowing treatment on germination of red sander. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6(4):168–173
Viji M, Maheswari P, Karuppanapandian T, Manoharan K (2012) Effect of polyethylene glycol and mannitol on somatic embryogenesis of pigeonpea, Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp. Afr J Biotechnol 11(45):10340–10349. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB12.368
Wang H, Chen J, Wu S, Lin M, Chang W (2003) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryo-derived callus of Areca catechu L. (Arecaceae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:34–36. https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2002373
Warakagoda PS, Subasinghe S (2013) In-vitro propagation of Pterocarpus santalinus L. (red sandalwood) through tissue culture. J Nat Sci Found Srilanka 41(1):53–63
Weaver LA, Trigiano RN (1991) Regeneration of Cladrastis lutea (Fabaceae) via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 10:183–186
Xia X, Yang F, Ke X, Chen Y, Ye J, Zhu L (2021) Somatic embryogenesis of masson pine (Pinus massoniana): initiation, maturation and genetic stability analysis at SSR loci. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02036-z
Xu K, Wang W, Yu D, Li X, Chen J, Feng B, Zhao Y, Cheng M, Liu X, Li C (2019) NAA at a high concentration promotes efficient plant regeneration via direct somatic embryogenesis and SE-mediated transformation system in Ranunculus sceleratus. Scientific Report 9:18321. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54538-8
Yan J, Peng P, Duan G, Lin T, Bai Y (2021) Multiple analyses of various factors affecting the plantlet regeneration of Picea mongolica (H. Q. Wu) WD Xu from somatic embryos. Sci Rep 11:6694. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83948-w
Ahmedullah M, Rasingam L, Swamy J, Nagaraju S, Shankara Rao M (2019) Non-detriment findings report on the red sanders tree (Pterocarpus santalinus L.f). Botanical Survey of India (Deccan Regional Centre), MoEFCC, Hyderabad
Ahmedullah M (2021) Pterocarpus santalinus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T32104A187622484. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T32104A187622484.en
Buendía-González L, Estrada-Zúñiga ME, Orozco-Villafuerte J, Cruz-Sosa F, Vernon-Carter EJ (2012) Somatic embryogenesis of the heavy metal accumulator Prosopis laevigata. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 108:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0042-4
Hegde M, Singh BG, Krishnakumar N (2012) Non-detriment findings (NDFs) study for Pterocarpus santalinus L.f. (Red Sanders) in India, Institute of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding, Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education.
Padmalatha K, Prasad MNV (2008) In-vitro plant regeneration of Pterocarpus santalinus L.f (red sanders): an endangered medical plant and important timber tree. Tree For Sci Biotechnol 1–6.
UNEP-WCMC (2017) Technical report, report on species/country combinations selected for review by the Plants Committee following CoP16, CITES Project No.A-498.
Acknowledgements
The financial support provided by SCIENCE & ENGINEERING RESEARCH BOARD (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for the major research project under a core research grant to Dr. Nasim Akhtar (Principal Investigator) and Dr. K. Viswanatha Chaitanya (Co-investigator) (sanction order no. CRG/2018/000517 dated 24.6.2019) is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Funding was provided by Mission on Nano Science and Technology (Grant No.: CRG/2018/000517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript's concept, layout, and design are conceived by the corresponding author Dr. Nasim Akhtar. The whole manuscript, including the table and text, is developed, written and revised by the first author Tanushree Chakraborty. The manuscript was reviewed and edited several times by authors Dr. K. Viswanatha Chaitanya and Dr. Nasim Akhtar.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared that there is no conflict of interest concerning any part of the manuscript.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Paloma Moncaleán.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, T., Chaitanya, K.V. & Akhtar, N. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in red sandalwood (Pterocarpus santalinus). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 153, 547–558 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02491-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02491-w