Abstract
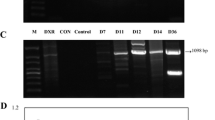
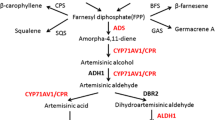
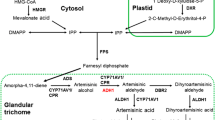
Artemisinin is widely used as an antimalarial drug, and the regulation of artemisinin metabolism is at the forefront of artemisinin research. A WRKY transcription factor, named as AaWRKY4, was cloned from high artemisinin-yielding Artemisia annua, which has similar expression pattern with the key enzymes in artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. AaWRKY4 was preferentially expressed in glandular secretory trichomes (GSTs) of young leaves and flower buds, but weakly expressed in other tissues. To further study the function of AaWRKY4, plant expression vector pHB-AaWRKY4 containing AaWRKY4 driven by CaMV 35S promoter was constructed and introduced into A. annua via Agrobacterium tumafeciens-mediated transformation. Expression analysis showed that the expression of AaWRKY4 was increased in transgenic plants. Four independent transgenic plants overexpressing AaWRKY4 were selected for further analysis. The expression levels of artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes ADS, CYP71AV1, DBR2 and ALDH1 were dramatically increased in AaWRKY4-overexpressing A. annua plants. Furthermore, the artemisinin yield was increased by 35–50% in AaWRKY4-overexpressing A. annua plants. These results indicate AaWRKY4 can upregulate artemisinin content through regulating artemisinin metabolism.
Key message
A WRKY transcription factor, named as AaWRKY4, was cloned from high artemisinin-yielding Artemisia annua. AaWRKY4 was preferentially expressed in glandular secretory trichomes (GSTs) of young leaves and flower buds. The expression levels of artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes ADS, CYP71AV1, DBR2 and ALDH1 were dramatically increased in AaWRKY4-overexpressing A. annua plants. Furthermore, the artemisinin yield was increased by 35–50% in AaWRKY4- overexpressing A. annua plants.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Gene Bank number for AaWRKY4 is MW169031. Sequence data from this article can be found in the Arabidopsis Genome Initiative or the GenBank databases.
Abbreviations
- GSTs:
-
Glandular secretory trichomes
- DMAPP:
-
Dimethylallyl diphosphate
- IPP:
-
Isopentenyl diphosphate
- MVA pathway:
-
Mevalonate pathway
- MEP pathway:
-
Nonmevalonate pathway
- ADS:
-
Amorpha-4, 11-diene synthase
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP71AV1
- DBR2:
-
Artemisinic aldehyde ∆11 (13) reductase
- ALDH1:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase
References
Bouwmeester HJ, Wallaart TE, Janssen MHA, Van Loo B, Jansen BJM, Posthumus MA, Schmidt CO, De Kraker JW, König WA, Franssen MCR (1999) Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase catalyses the first probable step in artemisinin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 52(5):843–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00206-X
Broun P (2004) Transcription factors as tools for metabolic engineering in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.01.013
Bryant L, Flatley B, Patole C, Brown G, Cramer R (2015) Proteomic analysis of Artemisia annua – towards elucidating the biosynthetic pathways of the antimalarial pro-drug artemisinin. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0565-7
Chen M, Yan T, Shen Q, Lu X, Pan Q, Huang Y, Tang Y, Fu X, Liu M, Jiang W, Zongyou L, Shi P, Ma Y-N, Hao X, Zhang L, Li L, Tang K (2016) Glandular trichome-specific WRKY 1 promotes artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 214(1):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14373
Covello PS (2008) Making artemisinin. Phytochemistry 69(17):2881–2885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.10.001
Han J, Wang H, Lundgren A, Brodelius PE (2014) Effects of overexpression of AaWRKY1 on artemisinin biosynthesis in transgenic Artemisia annua plants. Phytochemistry 102:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.02.011
Hsu E (2006) The history of qing hao in the Chinese materia medica. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 100(6):505–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.09.020
Ji Y, Xiao J, Shen Y, Ma D, Li Z, Pu G, Li X, Huang L, Liu B, Ye H, Wang H (2014) Cloning and characterization of AabHLH1, a bHLH transcription factor that positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 55(9):1592–1604. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu090
Jiang W, Lu X, Qiu B, Zhang F, Shen Q, Lv Z, Fu X, Yan T, Gao E, Zhu M, Chen L, Zhang L, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of a trichome-specific promoter of artemisinic aldehyde δ11(13) reductase (DBR2) in Artemisia annua. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32(1):82–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0603-2
Jiang W, Fu X, Pan Q, Tang Y, Shen Q, Lv Z, Yan T, Shi P, Li L, Zhang L, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2016) Overexpression of AaWRKY1 leads to an enhanced content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. Biomed Res Int 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7314971
Lu X, Jiang W, Zhang L, Zhang F, Shen Q, Wang T, Chen Y, Wu S, Lv Z, Gao E, Qiu B, Tang K (2012) Characterization of a novel ERF transcription factor in Artemisia annua and its induction kinetics after hormones and stress treatments. Mol Biol Rep 39(10):9521–9527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1816-4
Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang F, Jiang W, Shen Q, Lv Z, Wang G, Tang K (2013) AaORA, a trichome-specific AP2/ERF transcription factor of Artemisia annua, is a positive regulator in the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway and in disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol 198(4):1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12207
Ma D, Pu G, Lei C, Ma L, Wang H, Guo Y, Chen J, Du Z, Li G, Ye H, Liu B (2009) Isolation and characterization of AaWRKY1, an Artemisia annua transcription factor that regulates the amorpha-4,11-diene synthase gene, a key gene of artemisinin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 50(12):2146–2161. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp149
Matias-Hernandez L, Jiang W, Yang K, Tang K, Brodelius P, Pelaz S (2017) AaMYB1, and its orthologue AtMYB61, affect terpene metabolism and trichome development in Artemisia annua and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 90(3):520–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13509
Miller LH, Su X (2011) Artemisinin: discovery from the Chinese herbal garden. Cell 146(6):855–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.024
Picaud S, Olofsson L, Brodelius M, Brodelius PE (2005) Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant amorpha-4,11-diene synthase from Artemisia annua L. Arch Biochem Biophys 436(2):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2005.02.012
Romero MR, Efferth T, Serrano MA, Castaño B, MacIas RIR, Briz O, Marin JJG (2005) Effect of artemisinin/artesunate as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus production in an “in vitro” replicative system. Antiviral Res 68(2):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.07.005
Shen Q, Lu X, Yan T, Fu X, Zongyou L, Zhang F, Pan Q, Wang G, Sun X, Tang K (2016) The jasmonate-responsive AaMYC2 transcription factor positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 210(4):1269–1281. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13874
Shen Q, Zhang L, Liao Z, Wang S, Yan T, Shi P, Liu M, Fu X, Pan Q, Wang Y, Zongyou L, Lu X, Zhang F, Jiang W, Ma Y, Chen M, Hao X, Li L, Tang Y, Tang K (2018) The genome of Artemisia annua provides insight into the evolution of asteraceae family and artemisinin biosynthesis. Mol Plant 11(6):776–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.015
Shi P, Fu X, Shen Q, Liu M, Pan Q, Tang Y, Jiang W, Zongyou L, Yan T, Ma Y, Chen M, Hao X, Liu P, Li L, Sun X, Tang K (2017) The roles of AaMIXTA1 in regulating the initiation of glandular trichomes and cuticle biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 217(1):261–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14789
Singh NP, Lai HC (2004) Artemisinin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Anticancer Res 24(4):2277–2280
Sy LK, Brown GD (2002) The mechanism of the spontaneous autoxidation of dihydroartemisinic acid. Tetrahedron 58(5):897–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)01193-0
Tan H, Xiao L, Gao S, Li Q, Chen J, Xiao Y, Ji Q, Chen R, Chen W, Zhang L (2015) Trichome and artemisinin regulator 1 is required for trichome development and artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8(9):1396–1411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.04.002
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Nowak G, Covello PS (2006) Artemisia annua L. (Asteraceae) trichome-specific cDNAs reveal CYP71AV1, a cytochrome P450 with a key role in the biosynthesis of the antimalarial sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin. FEBS Lett 580(5):1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.065
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Covello PS (2009) Molecular cloning of an aldehyde dehydrogenase implicated in artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Botany 87(6):635–642. https://doi.org/10.1139/B09-032
Towler MJ, Weathers PJ (2007) Evidence of artemisinin production from IPP stemming from both the mevalonate and the nonmevalonate pathways. Plant Cell Rep 26(12):2129–2136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0420-x
Wallaart TE, Bouwmeester HJ, Hille J, Poppinga L, Maijers NCA (2001) Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase: cloning and functional expression of a key enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of the novel antimalarial drug artemisinin. Planta 212(3):460–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000428
Wang Y, Fu X, Xie L, Qin W, Li L, Sun X, Xing SH, Tang K (2019) Stress associated protein 1 regulates the development of glandular trichomes in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 139(2):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01677-5
Yan T, Chen M, Shen Q, Li L, Fu X, Pan Q, Tang Y, Shi P, Zongyou L, Jiang W, Ma Y-N, Hao X, Sun X, Tang K (2016) HOMEODOMAIN PROTEIN 1 is required for jasmonate-mediated glandular trichome initiation in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 213(3):1145–1155. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14205
Yan T, Li L, Xie L, Chen M, Shen Q, Pan Q, Fu X, Shi P, Tang Y, Huang H, Huang Y, Huang Y, Tang K (2018) A novel HD-ZIP IV/MIXTA complex promotes glandular trichome initiation and cuticle development in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 218(2):567–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15005
Yu ZX, Li JX, Yang CQ, Hu WL, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol Plant 5(2):353–365. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr087
Zhang Y, Teoh KH, Reed DW, Maes L, Goossens A, Olson DJH, Ross ARS, Covello PS (2008) The molecular cloning of artemisinic aldehyde Δ11(13) reductase and its role in glandular trichome-dependent biosynthesis of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. J Biol Chem 283(31):21501–21508. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M803090200
Zhang F, Fu X, Lv Z, Lu X, Shen Q, Zhang L, Zhu M, Wang G, Sun X, Liao Z, Tang K (2015) A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, aabzip1, connects abscisic acid signaling with artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8(1):163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.004
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2018JJ3008), NSF of Anhui Province (Grant No. 1908085MH268), SJTU Trans-med Awards Research (Grant No. 20190104), the Open Fund Project of Key Laboratory in Hunan Universities (Grant No. NY20K04), Science Foundation of Hengyang Normal University (Grant No. 17D14), and Science Foundation of Hengyang Normal University (Grant No. 17A03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WJ and KT conceived and designed the project. HH and XH conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. HH and WJ drafted the paper. WJ and KT reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Communicated by Maria Margarida Oliveira.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Xing, S., Tang, K. et al. AaWRKY4 upregulates artemisinin content through boosting the expressions of key enzymes in artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 146, 97–105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02049-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02049-8