Abstract
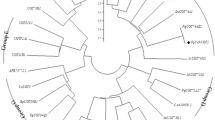
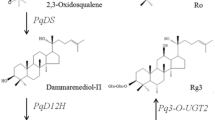
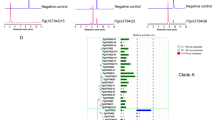
Panax quinquefolius (P. quinquefolius) has been used as medicine for thousands of years in Asia. Ginsenosides are major pharmacological active components extracted from P. quinquefolius. Glycosylation is the last and the most important step in the ginsenosides biosynthesis pathway, however, the function of glycosyltransferase has been poorly understood in the biosynthesis pathway of ginsenosides. In this study, we cloned and identified a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase gene from P. quinquefolius (Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT1) for the first time. The high similarity of amino acid sequence indicated a close evolutionary relationship and analogous function among PPT-6,20-O-UGT1 and several UDP-glycosyltransferases in P. quinquefolius or Panax ginseng. In vitro enzymatic assay confirmed that Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT1 could glycosylate the C20-OH of PPT and the C6-OH of ginsenoside F1 (F1), so that ginsenoside F1 and ginsenosides Rg1 (Rg1) were produced, respectively. Moreover, we established RNA interference (RNAi) transgenic root lines of Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT1. The expression levels of dammarenediol synthase, protopanaxadiol synthase and protopanaxatriol were up-regulated in RNAi lines. These results illustrated that Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT1 was a key enzyme for the synthesis of Rg1 and F1.
Key message
we cloned a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase gene from P. quinquefolius, enzymatic assay confirmed that this protein could glycosylate PPT and F1, thus it produced F1 and Rg1, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai L, Jialiang G, Fan W, Jing Z, Danwei W, Junping W (2018) Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides as an adjuvant treatment for diabetes. Front Pharmacol 9:423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00423
Chieh-Fu C, Wen-Fei C (2008) Comparison of the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng and Panax quinoquefolium. Acta Pharm Sin:1103–1108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00868.x
Christensen JL (2009) Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv Food Nutr Res 55(55):1–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1043-4526(08)00401-4
Cruse-Sanders JM, Hamrick JL (2004) Genetic diversity in harvested and protected populations of wild American ginseng, Panax quinquefolius L. (Araliaceae). Am J Bot 91(4):540–548. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.91.4.540
Dong GL, Lee AY, Kim KT, Cho EJ, Lee S (2015) Novel dammarane-type triterpene saponins from Panax ginseng root. Chem Pharm Bull 63(11):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c15-00302
Ha LT, Pawlicki-Jullian N, Pillon-Lequart M, Boitel-Conti M, Duong H.X. and Gontier, E., (2016). Hairy root cultures of Panax vietnamensis, a promising approach for the production of ocotillol-type ginsenosides. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 126 (1):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-0980-y
Hossen, M.J., Hong, Y.D., Baek, K.S., Yoo, S. and Cho, J.Y (2016). In vitro anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of BIOGF1K, compound K-rich fraction, prepared from Panax ginseng. J Ginseng Res 41 (1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.12.009
Jayakodi M, Choi BS, Lee SC, Kim NH, Yang TJ (2018) Ginseng genome database: an open-access platform for genomics of Panax ginseng. BMC Plant Biol 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1282-9
Ji HK, Yi YS, Kim MY, Cho JY (2016) Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J Ginseng Res 41(4):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2016.08.004
Jung SC, Kim W, Park SC, Jeong J, Sun CK (2014) Two ginseng UDP-glycosyltransferases synthesize ginsenoside Rg3 and Rd. Plant Cell Physiol 55(12):2177. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu147
Kang KB, Murukarthick J, Sun LY, Van Binh N, Hyun-Seung P, Jo KH, Young CI, Hyun KD, Jin CY, Byeol R (2018) Identification of candidate UDP-glycosyltransferases involved in protopanaxadiol-type ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. Sci Rep 8(1):11744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30262-7
Lu C, Zhao S, Wei G, Zhao H, Qu Q (2016) Functional regulation of ginsenoside biosynthesis by RNA interferences of a UDP-glycosyltransferase gene in Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius. Plant Physiol Biochem 111:67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.11.017
Lu C, Zhao S, Wang X (2017) Functional regulation of a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene (Pq3-O-UGT1) by RNA interference and overexpression in Panax quinquefolius. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 129(3):445–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1190-y
Luo JZQ, Kim JW, Luo LG (2016) Effects of ginseng and its four purifed ginsenosides (Rb2, re, Rg1, Rd) on human pancreatic islet β cell in vitro. Eur J Pharm Med Res 3(1):110–119
Nitta H, Matsumoto K, Shimizu M, Ni X, Watanabe H (1995) Panax ginseng extract improves the performance of aged fischer 344 rats in radial mazbe task but not in operant brightness discrimination task. Biol Pharm Bull 18(9):1286–1288. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.18.1286
Oh HA, Kim D, Choi HJ, Kim NJ, Kim D (2015) Anti-stress effects of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in immobilized mice. Biol Pharm Bull 38(2):331–335. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b14-00669
Patel S, Rauf A (2017) Adaptogenic herb ginseng (Panax) as medical food: status quo and future prospects. Biomed Pharm 85:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.112
Rai D, Bhatia G, Sen T, Palit G (2003) Anti-stress effects of ginkgo biloba and panax ginseng: a comparative study. J Pharmacol Sci 93(4):458–464. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.93.458
Sang HL, Jung BH, Kim SY, Lee EH, Chung BC (2006) The antistress effect of ginseng total saponin and ginsenoside Rg3 and Rb1 evaluated by brain polyamine level under immobilization stress. Pharmacol Res 54(1):46–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2006.02.001
Shergis JL, Di YM, Zhang AL, Vlahos R, Helliwell R, Ye JM, Xue CC (2014) Therapeutic potential of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Complement Ther Med 22(5):944–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2014.08.006
Sun Y, Niu Y, Xu J, Li Y (2013) Discovery of WRKY transcription factors through transcriptome analysis and characterization of a novel methyl jasmonate-induciblePqWRKY1gene from Panax quinquefolius. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 114(2):269–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0323-1
Sun H, Jiang X, Sun M, Cong H, Qiao F (2019) Evaluation of reference genes for normalizing RT-qPCR in leaves and suspension cells of Cephalotaxus hainanensis under various stimuli. Plant Methods 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0415-y
Zhang J, Cao L, Wang H, Cheng X, Wang L, Zhu L, Yan T, Xie Y, Wu Y, Zhao M (2015) Ginsenosides regulate PXR/NF-κB signaling and attenuate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Drug Metab Dispos 43(8):1181. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.063800
Zhao BS, Liu Y, Gao XY, Zhai HQ, Guo JY (2014) Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on the expression of toll-like receptor 3, 4 and their signaling transduction factors in the NG108-15 murine neuroglial cell line. Molecules 19:16925–16936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016925
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Province (20190201157JC), Major Science and Technology Project of Jilin Province-Research and demonstration of new Panax Ginseng variety selection and breeding technology (2020050400YY), Projects of National Science Foundation of China (31270337), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20120061110038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PF was responsible for the major work of isolation of Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT1 from P. quinquefolius, functional analysis, and wrote part of the manuscript. GL was responsible for writing part of the manuscript, XW, YS and YC were responsible for the data processing work. ZS designed the experiments and provided the financial support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Communicated by Goetz Hensel.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, P., Li, G., Wang, X. et al. Identification and RNAi-based gene silencing of a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase from Panax quinquefolius. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 144, 567–576 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01979-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01979-z