Abstract
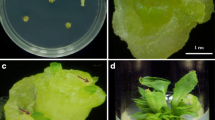
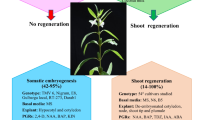
Sesamum indicum is an important oilseed crop with beneficiary nutrients such as essential fatty acids, proteins, and lignan. S. indicum crop improvement using conventional breeding methods was disastrous. Moreover, no reproducible regeneration and transformation protocol for large-scale generation of independent primary transformed plant lines of S. indicum virtually exists. Therefore, in the present study, a reproducible regeneration and transformation method was developed for S. indicum. Direct shoot regeneration (94.44%) was achieved using plumule tips as an explant source and when maintained on regeneration medium (BM11) an amalgamation of half the strength of MS macronutrients and B5 macronutrients together with MS micronutrients and vitamins. Maximum number of shoots (~ 16–19 shoots/explant) was obtained on BM11 medium supplemented with TDZ (1 mg/L) and BAP (0.1 mg/L). High root induction efficiency (~ 97%) was observed on RM4 medium consisted of half MS macronutrients, SH micronutrients and vitamins. The developed protocol was found effective for other commercially valuable genotypes such as Co 1, Phule til and Tilottama as well. Successful regeneration was subsequently extended to transformation of reporter gene (gfp: green fluorescent protein) as revealed by molecular analyses includes Southern hybridization, northern hybridization, real time PCR and histological study of the transformants developed in the present study. Based on the Southern analysis the calculated transformation frequency was found to be 1.33%. The presently developed regeneration and transformation system might facilitate any desired improvement of sesame crop.
Key message
The present study demonstrated an improved regeneration and transformation method for S. indicum, which is genotype independent and can undergo desired modifications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasim M, Khawar KM, Özcan S (2009) In vitro micropropagation from plumular apices of Turkish cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) cultivar Akkiz. Sci Hortic 122:468–471
Aasim M (2012) Micropropagation of lentil (Lens culinarisMedik.) using pulse treatment of immature plumular apices. Pak J Agric Sci 49:149–154
Aasim M, Day S, Rezaei F, Hajyzadeh M (2013) Multiple shoot regeneration of plumular apices of chickpea. Turk J Agric For 37:33–39
Al-Shafeay AF, Ibrahim AS, Nesiem MR, Tawfik MS (2011) Establishment of regeneration and transformation system in Egyptian sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cv Sohag1. GM Crops 2:182–192
Ashri A (2010) Sesame breeding. Plant breeding reviews. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 179–228
Baskaran P, Jayabalan N (2006) In vitro mass propagation and diverse callus orientation on Sesamum indicum L.-an important oil plant. J Agric Technol 2:259–269
Baque MA, Hahn E, Paek K (2010) Induction mechanism of adventitious root from leaf explants of Morindacitrifolia as affected by auxin and light quality. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 46:71–80
Belide S, Hac L, Singh SP, Green AG, Wood CC (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of safflower and the efficient recovery of transgenic plants via grafting. Plant Methods 7:12
Boszoradova E, Libantova J, Matusikova I, Poloniova Z, Jopcik M, Berenyi M, Moravcikova J (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of economically important oilseed rape cultivars. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107:317–323
Caboni E, Lauri P, Angell SD (2000) In vitro plant regeneration from callers of shoot apices in apple shoot culture. Plant Cell Rep 19:755–760
Chae SH (2014) Influence of media on in vitro root regeneration and micropropagation of Chrysanthemummorifolium Ramat cv. Hwiparam. Life Sci J 11:797–799
Chakrabarty R, Viswakarma N, Bhat SR, Kirti PB, Singh BD, Chopra VL (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cauliflower: optimization of protocol and development of Bt-transgenic cauliflower. J Biosci 27:495–502
Chakraborti P, Ghosh A (2009) Variation in callus induction and root shoot bud formation depend on seed coat of sesame genotypes. Res J Bot 5:14–19
Chandra R, Bajpai A, Gupta S, Tiwari RK (2004) Embryogenesis and plant regeneration from mesocarp of Psidium guava L. Indian J Biotechnol 3:246–248
Chattopadhyaya B, Banerjee J, Basu A, Sen SK, Maiti MK (2010) Shoot induction and regeneration using internodal transverse thin cell layer culture in Sesamum indicum L. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:173–178
Chee PP (1995) Stimulation of adventitious rooting of Taxus species by thiamine. Plant Cell Rep 14:753–757
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Chongdar S, Chhetri B, Mahato SK, Saha A (2015) Production potentials and economic feasibility of improved sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cultivars under varying dates of sowing in prevailing agro-climatic condition of North Bengal. Int J Agric Sci 7:434–439
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2014) A new high-frequency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation technique for Sesamum indicum L. using de-embryonated cotyledon as explant. Protoplasma 251:1175–1190
Chu CC, Wang CS, Sun CC, Hsu C, Yin KC, Chu CY (1975) Establishment of an efficient medium for another culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci Sinica 18:659–668
Cui X, Chakrabarty D, Lee E, Paek K (2010) Production of adventitious roots and secondary metabolites by Hypericum perforatum L. in a bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 101:4708–4716
Das DK, Reddy MK, Upadhyaya KC, Sopory SK (2002) An efficient leaf-disk culture method for the regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and transformation of grape (Vitisvinifera L.). Plant cell Rep 20:999–1005
Day DC, Lee E, Kobayashi J, Holappa DL, Albert H, Ow DW (2000) Transgene integration into the same chromosome location can produce alleles that express at a predictable level, or alleles that are differentially silenced. Genes Dev 14:2869–2880
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
George EF, Hall MA, Klerk GD (2008) The components of plant tissue culture media I: macro- and micro-nutrients. In: George EF, Hall MA, De Klerk GJ (eds) Plant propagation by tissue culture, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 65–113
Gerszberg A, Hnatuszko-Konka K, Kowalczyk T, Kononowicz AK (2016) Efficient in vitro callus induction and plant regeneration protocol for different polish tomato cultivars. NotulaeBotanicaeHortiAgrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 44:452–458
Głowacka K, Jeżowski S, Kaczmarek Z (2010) The effects of genotype, inflorescence developmental stage and induction medium on callus induction and plant regeneration in two Miscanthus species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 102:79–86
Hansen G (2000) Evidence for Agrobacterium-induced apoptosis in maize cells. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:649–657
Hasnat R, Abbasi NA, Hafiz IA, Ahmad T, Chudhary Z (2008) Effect of different bacterial dilutions on transformation efficiency of hot chilli (Capsicumfrutescens L.) varieties. Pak J Bot 40:2655–2662
Hirose N, Inoue T, Nishihara K, Sugano M, Akimoto K, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1991) Inhibition of cholesterol absorption and synthesis in rats by sesamin. J Lipid Res 32:629–638
Honnale H, Rao S (2013) Direct somatic embryogenesis in Sesamum indicum (L.) Cv-E8 from cotyledon and hypocotyl explants. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol 4:120–127
Jeyamary R, Jayabalan N (1997) Influence of growth regulators on somatic embryogenesis in Sesamum indicum L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 46:67–70
Kapoor S, Parmer SS, Yadav M, Chaudhary D, Sainger M, Jaiwal R, Jaiwal PK (2015) Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium protocols. Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 37–45
Karami O (2008) Factors affecting Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plants. Transgenic Plant J 2:127–137
Khemkladngoen N, Cartagena J, Shibagaki N, Fukui K (2011) Adventitious shoot regeneration from juvenile cotyledons of a biodiesel producing Plant, Jatropha curcas L. J Biosci Bioeng 111:67–70
Kouakou TH (2003) Contribution à l’étude de l’embryogenèsesomatique chez le cotonnier: évolution de quelquesparamètresbiochimiques au cours de la callogenèse et de la culture de suspension cellulaires. Thèse de doctorat N° 023/2003, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
Kulkarni VV, Ranganatha CN, Shankergoud I (2017) Interspecific crossing barriers in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6:4894–4900
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lokesha R, Rahaminsab J, Ranganatha ARG, Dharmaraj PS (2012) Whole plant regeneration via adventitious shoot formation from de-embryonated cotyledon explants of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). World J Sci Technol 2:47–51
Ma XH, Wu TL (2008) Rapid and efficient regeneration in soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill) from whole cotyledonary node explants. Acta Physiologiae Plant 30:209–216
Malaghan SV, Lokesha R, Savitha R, Ranganatha ARG (2013) Adventitious shoot regeneration in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) (Pedaliaceae) via deembryonatedcotyledonary explants. Res J Biol 1:31–35
Martin KP (2002) Rapid propagation of Holostemmaada-kodienSchult., a rare medicinal plant, through axillary bud multiplication and indirect organogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 21:112–117
Matzke AJ, Matzke MA (1998) Position effects and epigenetic silencing of plant transgenes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:142–148
Michel Z, Hilaire KT, Mongomaké K, Georges AN, Justin KY (2008) Effect of genotype, explants, growth regulators and sugars on callus induction in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Aust J Crop Sci 2:1–9
Miyahara Y, Hibasami H, Katsuzaki H, Imai K, Komiya T (2001) Sesamolin from sesame seed inhibits proliferation by inducing apoptosis in human lymphoid leukemiaMolt 4b cells. Int J Mol Med 7:369–371
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plant 15:473–497
Nakai M, Harada M, Nakahara K, Akimoto K, Shibata H, Miki W, Kiso Y (2003) Novel antioxidative metabolites in rat liver with ingested sesamin. J Agric Food Chem 51:1666–1670
Nakano D, Kurumazuka D, Nagai Y, Nishiyama A, Kiso Y, Matsumura Y (2008) Dietary sesamin suppresses aortic NADPH oxidase in DOCA salt hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35:324–326
Nandagopal S, Kumari BDR (2006) Adenine sulphate induced high frequency shoot organogenesis in callus and in vitro flowering of Cichoriumintybus L. cv. Focus - a potent medicinal plant. Acta agriculturaeSlovenica 87:415–425
Nzikou JM, Matos L, Bouanga-Kalou G, Ndangui CB, Pambou-Tobi NPG, Kimbonguila A, Silou Th, Linder M, Desobry S (2009) Chemical composition on the seeds and oil of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) grown in Congo-Brazzaville. Adv J Food Sci Technol 1:6–11
Opabode JT (2006) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plants: emerging factors that influence efficiency. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 1:12–20
Oplinger ES, Putnam DH, Kaminski AR, Hanson CV, Oelke EA, Schult EE, Doll JD (1990) Sesame, Alternative field crops manual. www.hort.purdue.edu/sesame.html
Osman NI, Sidik NJ, Awa A (2016) Effects of variations in culture media and hormonal treatments upon callus induction potential in endosperm explant of Barringtoniaracemosa L. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 6:143–147
Pathak N, Rai AK, Saha S, Walia S, Sen SK, Bhat KV (2014) Quantitative dissection of antioxidative bioactive components in cultivated and wild sesame germplasm reveals potentially exploitable wide genetic variability. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 17:127–139
Perera D, Barnes DJ, Baldwin B, Reichert N (2015) Direct and indirect in vitro regeneration of Miscanthus × giganteus cultivar Freedom: effects of explant type and medium on regeneration efficiency. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 51:294–302
Pusadkar PP, Kokiladevi E, Aishwarya V, Gnanam R, Sudhakar D, Balasubramanian P (2015) Efficacy of growth hormone for callus induction in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). J Cell Tissue Res 15:5067–5071
Pusadkar P, Kokiladevi E, Shilpa B (2016) Efficacy of plant growth hormones for shoot induction and regeneration in Sesame (Sesamum indicumL.). Res J Biotechnol 11:27–30
Raja A, Jayabalan N (2010) Callus induction and plantlet regeneration from leaf explant of sesame (Sesamum indicum L. cv. SVPR-1). J Swamy Bot Club 27:93–98
Ramage CM, Williams RR (2002) Mineral nutrition and plant morphogenesis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:116–124
Rao S, Honnale HN (2011) Callus induction and organogenesis in Sesamum indicum L. Cv. E 8. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm 5:1462–1468
Richter TE, Ronald PC (2000) The evolution of disease resistance genes. Plant Mol Biol 42:195–204
Sagar R, Ganesh C (2004) Frontline demonstration on sesame in West Bengal. Agric Ext Rev 16:7–10
Sankar D, Sambandam G, Ramakrishna RM, Pugalendi KV (2005) Modulation of blood pressure, lipid profiles and redox status in hypertensive patients taking different edible oils. Clin Chemica Acta 355:97–104
Saravanan S, Nadarajan N (2005) Effect of media supplements on in vitro response of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes. Res J Agric Biol Sci 1:98–100
Schenk RU, Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can J Bot 50:199–204
Seo HY, Kim YJ, Park TI, Kim HS, Yun HS (2007) High-frequency plant regeneration via adventitious shoot formation from deembryonated cotyledon explants of Sesamum indicum L. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:209–214
Sepahvand S, Ebadi A, Kamali K, Ghaemmaghami SA (2012) Effect of myo-inositol and thiamine on micropropagation of GF677 (Peach × Almond hybrid). J Agric Sci 4:275–280
Shashidhara N, Ravikumar H, Ashoka N, Santosh DT, Pawar P, Lokesha R, Janagoudar BS (2011a) Callus induction and subculturing in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): a basic strategy. Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol 4:153–156
Shashidhara N, Ravikumar H, Ashoka N, Santosh DT, Pawar P, Lokesha R, Janagoudar BS (2011b) Thidiazuron (TDZ) induced shoot regeneration in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol 4:41–44
Shilpa KS, Kumar VD, Sujatha M (2010) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of safflower (Carthamustinctorius L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:387–401
Siao AC, Hou CW, Kao YH, Jeng KC (2015) Effect of sesamin on apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:3779–3783
Singh S, Hazra S (2009) Somatic embryogenesis from the axillary meristems of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Biotech Rep 3:333–340
Sujatha M, Vijay S, Vasavi S, Reddy PV, Rao SC (2012) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cotyledons of mature seeds of multiple genotypes of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 110:275–287
Sun Q, Zhao Y, Sun H, Hammond RW, Davis RE, Xin L (2011) High efficiency and stable genetic transformation of pear (Pyrus communis L.) leaf segments and regeneration of transgenic plants. Acta Physiologiae Plant 33:383–390
Surekha C, Arundhati A, Seshagiri Rao G (2007) Differential response of Cajanus cajan varieties to transformation with different strains of Agrobacterium. J Biol Sci 7:176–181
Taskin KM, Ercan AG, Turgut K (1999) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Turk J Bot 23:291–295
Tilkat E, Onay A, Yıldırım H, Ayaz E (2009) Direct plant regeneration from mature leaf explants of pistachio, Pistacia vera L. Sci Hortic 121:361–365
Tiwari S, Kumar S, Gontia I (2011) Biotechnological approaches for sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) and niger (GuizotiaabyssinicaLf Cass.). Asia-Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol 19:2–9
Tiwari V, Chaturvedi AK, Mishra A, Jha B (2015) An efficient method of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation and regeneration in local Indian cultivar of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) Using Grafting. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:436–453
Tsuruoka N, Kidokoro A, Matsumoto I, Abe K, Kiso Y (2005) Modulating effect of sesamin, a functional lignan in sesame seeds, on the transcription levels of lipid and alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in rat liver: a DNA microarray study. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:179–188
Verma OP (2012) Standardization of auxin concentration for root induction in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Adv Appl Sci Res 3:1449–1453
Vooková A, Kormuťák B (2001) Effect of sucrose concentration, charcoal and indole 3-butyric acid on germination of Abiesnumidica somatic embryos. Biologia Plant 44:181–184
Were BA, Gudu S, Onkware AO, Carlsson AS, Welander M (2006) In vitro regeneration of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) from seedling cotyledon and hypocotyl explants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 85:235–239
Yadav M, Chaudhary D, Sainger M, Jaiwal PK (2010) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:377–386
Younghee K (2001) Effects of BA, NAA, 2, 4-D and AgNO3 treatments on callus induction and shoot regeneration from hypocotyl and cotyledon of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). J Korean Soc Hortic Sci 42:70–74
Yuan JL, Yue JJ, Wu XL, Gu XP (2013) Protocol for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis in Moso Bamboo. PLoS ONE 8:e81954
Ziemienowicz A (2014) Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: factors, applications and recent advances. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:95–102
Zimik M, Arumugam N (2017) Induction of shoot regeneration in cotyledon explants of the oilseed crop Sesamum indicum L. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15:303–308
Zouzou M, Kouadio YJ, Koné M, Kouakou TH, Dénézon DO (2000) Callogenèse chez Gossypium hirsutum L.: effets cultivar, conditions de culture et type de matériel. Biot Rev Int Sci Vie Terre 1:48–56
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance in the form of the grant support to this laboratory from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (NAIP/ICAR), Government of India, is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TG and AB conceived and designed research, conducted experiments, analysed data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by K X Tang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gayatri, T., Basu, A. Development of reproducible regeneration and transformation system for Sesamum indicum. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 143, 441–456 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01931-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01931-1