Abstract
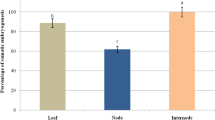
Somatic embryogenesis in mangosteen (Garcinia mangstana L.) was investigated using seed and leaf segments cultured on Murashige and Skoog medium with treatments of 6-benzyladenine (BA) [2.0, 3.0, 4.0 µM] and 2,4-diclorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) [4.5, 9.0, 13.5 µM]. There were four types of structures (globular, nodular compact, friable and spongy) formed. Two treatments resulted in embryogenic characteristics from seed cultures; the highest percentage 46.67 % of globular structure (resembling somatic embryos) grown on 3.0 µM BA and 80 % of nodular compact structures on 4.0 µM BA + 13.5 µM 2,4-D. For the leaf culture, highest percentage, 93.33 % produced nodular compact structures on 2.0 µM BA + 4.5 µM 2,4-D. Histological analysis showed that the globular structure has well-defined protoderm and separated from the original explant. Nodular compact structure also showed the presence of densely cytoplasmic meristematic cells with a high nucleoplasmic ratio. These characteristics observed in globular and nodular compact structure indicates somatic embryo formation. The globular structures which were converted into shoots and roots (60.00 %) showed atypical somatic embryogenesis in mangosteen. Metabolite fingerprinting was carried out using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Amino acids, carbohydrates, organic acids and fatty acids were found in both the embryogenic structures and non-embryogenic structures tested. Multivariate discriminant analyses of the metabolic data revealed significant metabolites (P ≤ 0.05) for both types of structures. Principle component analysis suggested that amino acids and carbohydrates were the major compounds distinguishing embryogenic and non-embryogenic structures. Ornithine and mannose were present at significant level in embryogenic structures as compared to non-embryogenic ones while fructose was significantly higher in non-embryogenic structures.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeyda N, Martin FW (1976) Cultivation of neglected tropical fruits with promise 1. The mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.). US Agric Res Serv South Reg 155:1–18
Arruda SCC, Souza GM, Almeida M, Goncalves AN (2000) Anatomical and biochemical characterization of calcium effect on Eucalyptus urophylla callus morphogenesis in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 63:143–154
Branca C, Torelli A, Fermi P, Altamura MM Basi M (1994) Early phases in in vitro culture of tomato cotyledon: starch accumulation and protein pattern in relation to the hormonal treatment. Proplasma 182:59–64
Businge E, Brackmann K, Moritz T, Egertsdotter U (2012) Metabolite profiling reveals clear metabolic changes during somatic embryo development of Norway spruce (Picea abies). Tree Physiol 32:232–244
Canovas FM, Avila C, Canton FR, Canas RA, Dela TF (2007) Ammonium assimilation and amino acid metabolism in conifers. J Exp Bot 58:2307–2318
Changahuala-Inocente GC, Steiner N, Santos M, Guerra MP (2004) Morphohistological analysis and histochemistry of Feijoa sellowiana somatic embryogenesis. Protoplasma 224:33–40
Cho YH, Yoo SD (2011) Signaling role of fructose mediated by FINS1/FBP in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 7:e1001263. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001263
Choi YH, Tapias EC, Kim HK, Lefeber AWM, Erkelens C, Verhoeven JTJ, Brzin J, Zel J, Verpoorte R (2004) Metabolic discrimination of Catharanthus roseus leaves infected by phytoplasma using 1HNMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Plant Physiol 135:2398–2410
Corredoira E, Ballester A, Vieitez AM (2003) Proliferation, maturation and germination of Castanea sativa Mill. somatic embryos originated from leaf explants. Ann Bot 92:129–136
Corredoira E, Valladarses S, Vieitez AM (2006) Morphohistological analysis of the origin and development of somatic embryos from leaves of mature Quercus robur. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:525–533
Correia S, Cunha AE, Salgueiro L, Canhoto JM (2012) Somatic embryogenesis in tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea): approaches to increase efficiency of embryo formation and plant development. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 109:143–152
Efendi D, Helmi F (2010) Pengaruh umur buah dan jenis media terhadap induksi embrio somatik biji manggis (Garcinia mangostana L.). In: Prosiding Seminar Nasional Hortikultur Indonesia
Elhiti M, Stasolla C, Wang A (2013) Molecular regulation of plant somatic embryogenesis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. doi:10.1007/s11627-013-9547-3
Elviana M, Rohani ER, Ismanizan I, Normah MN (2011) Morphological and histological changes during the somatic embryogenesis of mangosteen. Biol Plant 55:73–736
Fairchild DG (1915) The mangosteen “Queen of fruits”. J Hered 6:338–347
Fernando JA, Vieira MLC, Geraldi IO, Appezzato-da-Gloria B (2002) Anatomical study of somatic embryogenesis in Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Braz Arch Biol Tech 45:277–286
Goh HKL, Rao AN, Loh CS (1988) In vitro plantlet formation in mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) Ann Bot 62:87–93
Goh HKL, Rao AN, Loh CS (1990) Direct shoot bud formation from leaf explant of seedlings and mature mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) trees. Plant Sci 68:11–121
Goh CJ, Lakshmanan P, Loh CS (1994) High frequency direct shoot bud regeneration from excised leaves of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) Plant Sci 101:173–180
Goodpaster AM, Kennedy MA (2011) Quantification and statistical significance analysis of group separation in NMR-based metabonomics studies. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 109:162–170
Gullberg J, Jonsson P, Nordstrom A, Sjostrom M, Moritz T (2004) Design of experiments: an efficient strategy to identify factors influencing extraction and derivatization of Arabidopsis thaliana samples in metabolomic studies with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 331:283–295
Holm IB, Krogstrup P, Hansen J (1997) Embryogenic callus formation, growth and regeneration in callus and suspension cultures of Miscanthus ogiformis Honda Giganteus, as affected by proline. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 50:203–210
Huang L-C, Huang B-L, Wang C, Kuo C-I, Murashige T (2000) Developing an improved in vitro propagation system for slow rowing species using Garcinia mangostana L. (mangosteen). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:501–504
Jeyaseelan M, Rao M (2005) Biochemical studies of embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. Indian J Exp Biol 43(6):555
Jimenez VM, Bangerth F (2001) Endogenous hormone levels in explants and in embryogenic and non embryogenic cultures of carrot. Physiol Plant 111:389–395
Kieffer F, Triouleyre C, Bertsch C, Farine S, Leva Y, Walter B (2004) Mannose and xylose cannot be used as selectable agents for Vitis vinifera L. transformation. Vitis 43:35–39
Lim AL (1984) The embryology of Garcinia mangostana L. (Clusiacea). Gard Bull Singap 37:93–103
Llyod GB, Mc Cown BH (1980) Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot-tip culture. Proc Int Plant Propag Soc 30:421–427
Lu J, Chen R, Zhang M, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ma G (2013) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis from immature cotyledons of Camellia nitidissima Chi. J Plant Physiol 170:1202–1211
Lulsdorf MM, Tautorus TE, Kikcio SI, Dunstan DI (1992) Growth parameters of embryogenic suspension culture of interior spruce (Picea glauca-engelmannii complex) and black spruce (Piceamariana mill.) Plant Sci 82:227–234
Mahmud I, Shrestha B, Boroujerdi A, Chowdhury K (2015) NMR-based metabolomics profile comparisons to distinguish between embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus tissue of sugarcane at the biochemical level. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 51:340–349. doi:10.1007/s11627-015-9687-8
Mala J, Cvikrova M, Machova P, Martincova O (2009) Polyamines during somatic embryo development in Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) J For Sci 55:75–80
Marchant R, Davey MR, Lucas JA, Power JB (1996) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Floribunda rose (Rosa hybrida L.) cvs. Trumpeter and Glad Tidings. Plant Sci 120:95–105
Mari S, Engelmann F, Chabrillange N, Huat C, Michaux-Ferriere N (1995) Histo-cytological study of apices of coffee (Coffea racemosa and C. sessiliflora) in vitro plantlets during their cryopreservation using the encapsulation-dehydration technique. Cryo Lett 16:289–298
Martin AB, Cuadrodo Y, Guerra H, Gallego P, Hita O, Martin L, Dorado A, Villalobos N (2000) Differences in the contents of total sugars, starch and sucrose in embryogenic and non-embryogenic calli from Medicago sativa L. Plant Sci 154:143–151
Minocha SC, Minocha R (1995) Role of polyamines in somatic embryogenesis. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and Forestry, somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed, vol 30. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 55–72
Minocha R, Minocha SC, Long S (2004) Polyamines and their biosynthetic enzymes during somatic embryo development in red spruce (Picea rubens Sarg.) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 40:572–580
Mondal TK, Bhattacharya A, Laxmikumaran M, Ahuja PS (2004) Recent advances of tea (Camellia sinensis) biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 76:195–254
Mubarak AK, Bilal HA, Huma A, Mohammad A, Mohammad A, Ishtiaq H (2015) Temporal variations in metabolite profiles at different growth phases during somatic embryogenesis of Silybum marianum L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:127–139
Mujib A, Banarjee S, Ghosh PD (2005) Origin, development and structure of somatic embryos in selected bulbous ornamentals: BA as inducer. Plant Cell Monogr 15–24
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nagendra PK, Siva PM, Shivamurthy GR, Aradhya SM (2006) Callus induction from Ipomoea aquatica leaf and its antioxidant activity. Indian J Biotechnol 5:107–111
Nakagawa R, Ogita S, Kubo T, Funada R (2006) Effect of polyamines and L-ornithine on the development of proembryogenic masses of Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 85:229–234
Nieves N, Segura-Nieto M, Blanco MA, Sánchez M, González A, González JL, Castillo R (2003) Biochemical characterization of embryogenic and non-embryogenic calluses of sugarcane. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:343–345
Normah MN (1992) Micropropagation of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) through callus and multiple shoot formation. Biotrop Spec Publ 49:81–85
Normah MN, Nor-Azza AB, Aliudin R (1995) Factors affecting in vitro shoot proliferation and ex vitro establishment of mangosteen. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 43:291–294
Normah MN, Aizat WM, Hussin K, Rohani ER (2016) Seed characteristics and germination properties of four Garcinia (Cluasiaceae) fruit species. Fruits 71:199–207
Overy SA, Walker HJ, Malone S, Howard TP, Baxter CJ, Sweetlove LJ, Hill SA, Quick WP (2005) Application of metabolite profiling to the identification of traits in a population of tomato introgression lines. J Exp Bot 56:287–296
Pachego G, Gagliardi RF, Carneiro LA, Callado CH, Valls JFM, Mansur E (2007) The role of BA in somatic embryogenesis induction from seed explants of Arachis species from sections Erectoides and Procumbentes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 88:121–126
Park SY, Lee WY, Kim YW, Moon HK (2011) Characterization of metabolic differences between embryogenic and non-embryogenic cells in forest trees. BMC Proc 5:146
Richard AJ (1990) Studies in Garcinia, dioecious tropical forest trees: the origin of mangosteen (G. mangostana L.). Bot J Linn Soc 103:301–308
Roessner U, Leudemann A, Brust D, Fiehn O, Linke T, Willmitzer L, Fernie AR (2001) Metabolic profiling allows comprehensive phenotyping of genetically or environmentally modified plant systems. Plant Cell 13:11–29
Rohani ER, Ismanizan I, Normah MN (2012) Somatic embryogenesis of mangosteen. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 110:251–259. doi:10.1007/s11240-012-0147-4
Rostika I, Sunarlim N, Mariska I (2008) Micropropagation of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.). Indones J Agric 1: 28–33
Salaj J, von Recklinghausen I, Hecht V, de Vreis S, Schel J, van Lammeren A (2008) AtSERK1 expression precedes and coincides with early somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:709–714
Santiago J, Henzler C, Hothorn M (2013) Molecular mechanism for plant steroid receptor activation by somatic embryogenesis co-receptor kinases. Science 341:889–892
Schmidt EDT, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vreis SC (1997) A leucine rich repeat containing reseptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Shetty K, McKersie BD (1993) Proline and thioproline and potassium mediated stimulation of somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Plant Sci 88:185–193
Silveira V, de Vita AM, Macedo AF, Dias MFR, Floh EIS, Santa-Catarina C (2013) Morphological and polyamine content changes in embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus of sugarcane. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. doi:10.1007/s11240-013-0330-2
Sirchi MHT, Kadir MA, Aziz MA, Rashid AA, Rafat A Javadi MB (2008) Amelioration of mangoteen micro propagation through leaf and seeds segments (Garcinia mangostana L.) Afr J Biotechnol 7:2025–2029
Sundram TCM, Suffian M, Annuar M, Norzulaani K (2012) Optimization of culture condition for callus induction from shoot buds for establishment of rapid growing cell suspension cultures of Mango ginger (Curcuma mangga). Aust J Crop Sci 6:1139–1146
Te-chato S, Lim M (2000) Improvement of mangosteen micropropagation through meristematic nodular callus formation from in vitro-derived leaf explants. Sci Hortic 86:291–298
Te-chato S, Lim M, Suranilpong P (1995) Embryogenic callus induction in mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.). Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 1:115–120
Thengane SR, Deodhar SR, Bhosle SV, Rawal SK (2006) Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Garcinia indica Choiss. Curr Sci 91:1074–1078
Williams EG, Maheswaran G (1986) Somatic embryogenesis: Factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann Bot 57:443–462
Zhang N, Fang W, Shi Y, Liu Q, Yang H, Gui R, Lin X (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis in Dendrocalamus hamiltonii. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:325–332
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5:1411–1423
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Barbara M. Reed for her editorial comments on this paper. This research was supported by the Research University Grant under the Economic Transformation Programme (UKM-ETP-2013-015) from Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2016_1068_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1. Supplementary Fig. 1 Direct shoot formation from mangosteen seed culture. Bar = 0.5 cm (TIF 2717 KB)
11240_2016_1068_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2. Supplementary Fig. 2 Direct shoot formation from mangosteen leaf culture. Bar = 0.5 cm (TIF 1993 KB)
11240_2016_1068_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 3. Supplementary Fig. 3 Histological section showing vascular tissue of shoots connected with seed procambium in mangosteen seed culture. Bar = 500 µm (TIF 1871 KB)
11240_2016_1068_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 4. Supplementary Fig. 4 Histological section showing mangosteen seed germination with plumule and radicle emergence from the procambium strand. Bar = 500 µm (TIF 2318 KB)
11240_2016_1068_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 5. Supplementary Fig. 5 Conversion of nodular compact structure to globular-like structure which later formed shoots. Bar = 0.5 cm (TIF 2030 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maadon, S.N., Rohani, E.R., Ismail, I. et al. Somatic embryogenesis and metabolic differences between embryogenic and non-embryogenic structures in mangosteen. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 127, 443–459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1068-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1068-4