Abstract
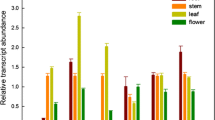
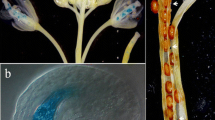
Two transgenic Arabidopsis lines were derived that expressed promoter regions for either AtTPS1 (At1g78580) or AtTPPB (At1g78090) using constructs containing the β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene. These two genes function in tandem to produce the disaccharide, trehalose, and they likely have important regulatory and signaling functions in higher plants. Both genes were expressed nearly constitutively in Arabidopsis and expression was high in younger tissue and typically diminished with age. Similar expression patterns for both promoters were observed in etiolated and in light grown seedlings. Dense expression of both genes was observed during germination on day 1 but expression was absent from hypocotyls 3 days later. In contrast to AtTPS1, the expression of AtTPPB was concentrated in the root meristem of 7-day old light grown seedlings. The expression of both AtTPS1 and AtTPPB was mainly observed in young, actively dividing tissues, such as the shoot apex, and in flower parts including anthers, pistils, siliques and developing seeds. Expression of both genes also was clearly associated with vascular bundles, the root-hypocotyl junction, the pedicel-silique junction and related structures involved in bulk solute transport. Transcript levels of AtTPS1 and AtTPPB were either repressed or were little affected by exogenous sucrose, glucose, fructose or trehalose when measured by quantitative real-time PCR. However, both trehalose biosynthesis genes were induced two to tenfold by sorbitol, mannitol and NaCl. Responses of AtTPS1 and AtTPPB to the same chemical and stress treatments were not detected by changes in GUS activity. This may be due to the stability of the GUS protein relative to transcript levels. Because AtTPS1 and AtTPPB function in tandem to produce trehalose it was not surprising that the expression of both genes was distributed similarly in Arabidopsis tissues.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase
- QPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- TPPB:
-
Trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase B
- TPS1:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1
References
Almeida AM, Santos M, Villalobos E, Araújo SS, van Dijck P, Leyman B, Cardoso LA, Santos D, Fevereiro PS, Torné JM (2007) Immunogold localizatation of trehalose 6-phosphate synthase in leaf segments of wild-type and transgenic tobacco plants expressing the AtTPS1 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Protoplasma 230:41–49
Avonce N, Leyman B, Mascorro-Gallardo J, van Dijck P, Thevelein J, Iturriaga G (2004) The Arabidopsis trehalose-6-P synthase AtTPS1 gene is a regulator of glucose, abscisic acid, and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 136:649–3659
Bae H, Sicher RC (2004) Changes of soluble protein expression and leaf metabolite levels in Arabidopsis thaliana grown in elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide. Field Crops Res 90:61–73
Blázquez MA, Lagunas R, Gancedo R, Gancedo JM (1993) Trehalose 6-phosphate, a new regulator of yeast glycolysis that inhibits hexokinases. FEBS Lett 329:51–54
Blázquez MA, Santos E, Flores C-L, Martínez-Zapater JM, Salinas J, Gancedo C (1998) Isolation and molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis TPS1 gene, encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase. Plant J 13:685–689
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Drennan PM, Smith MT, Goldsworthy D, van Staden J (1993) The occurrence of trehalose in the leaves of the desiccation-tolerant angiosperm Myrothamnus flabellifolius (Welw). J Plant Physiol 142:493–496
Eastmond PJ, Graham IA (2003) Trehalose metabolism: a regulatory role for trehalose-6 phosphate? Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:231–235
Eastmond PJ, van Dijken AJH, Spielma M, Kerr A, Tissier AF, Dickinson HG, Jones JDG, Smeekens SC, Graham IA (2002) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1, which catalyses the first step in trehalose synthesis, is essential for Arabidopsis embryo maturation. Plant J 29:225–235
Goddijn OJM, van Dun K (1999) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4:315–319
Goddijn OJM, Verwoerd TC, Voogd E, Krutwagen RWHH, de Graaf PTHM, Poels J, van Dun K, Ponstein AS, Damm B, Pen J (1997) Inhibition of trehalase activity enhances trehalose accumulation in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 113:181–190
Hofgen R, Willmitzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation. Nucleic Acid Res 16:9877
Leyman B, van Dijck P, Hevelein JM (2001) An unexpected plethora of trehalose biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 6:510–513
Lunn JE (2007) Gene families and evolution of trehalose metabolism in plants. Funct Plant Biol 34:550–563
Müller J, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A, Boller T, Wiemken A (2001) Trehalose and trehalase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 125:1086–1093
Paul MJ, Pellny TK (2003) Carbon metabolite feedback regulation of leaf photosynthesis and development. J Exp Bot 54:539–1047
Paul MJ, Primavesi LF, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y (2008) Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:417–441
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acid Res 29:2003–2007
Ramon M, de Smet I, Vandensteene L, Naudts M, Leyman B, van Dijck P, Rolland P, Beeckman T, Thevelein JM (2009) Extensive expression regulation and lack of heterologous enzymatic activity of the class II trehalsoe metabolism proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 32:1015–1032
Rodrigues-Pousada RA, De Rycke R, Dedonder A, van Caeneghem W, Engler G, van Montagu M, van Der Straeten D (1993) The Arabidopsis 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene 1 is expressed during early development. Plant Cell 5:897–911
Schluepmann H, Pellny T, van Dijken A, Smeekens S, Paul M (2003) Trehalose 6-phosphate is indispensable for carbohydrate utilization and growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 100:6849–6854
Schluepmann H, van Dijken A, Aghdasi M, Paul M, Smeekens S (2004) Trehalose mediated growth inhibition of Arabidopsis seedlings is due to trehalose-6-phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 135:879–890
Suleiman AAA, Bacon J, Christie A, Lewis A, Lewis DH (1979) The carbohydrates of the leafy liverwort Plagiochila asplenoides (L.) Dum. New Phytol 82:439–448
van Dijken AJH, Schluepmann H, Smeekens S (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135:969–977
Vogel G, Aeschbacher RA, Müller J, Boller T, Wiemken A (1998) Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatases from Arabidopsis thaliana: identification by functional complementation of yeast tps2 mutant. Plant J 13:673–683
Vogel G, Fiehn O, Jean-Richard-dit-Bressel L, Boller T, Wiemken A, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A (2001) Trehalose metabolism in Arabidopsis: occurrence of trehalose and molecular cloning and characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homologues. J Exp Bot 52:1817–1826
Watkinson JI (2002) Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with a mycorrhizal fungus Thanatephorus pennatus. Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Wingler A (2002) The function of trehalose biosynthesis in plants. Phytochemistry 60:437–440
Acknowledgments
The authors thank F. Caulfield and R. Erdman for assistance with growing the mature plants and K. Moon for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, H., Sicher, R., Natarajan, S. et al. In situ expression of trehalose synthesizing genes, TPS1 and TPPB, in Arabidopsis thaliana using the GUS reporter gene. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 98, 311–319 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9565-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9565-3