Abstract
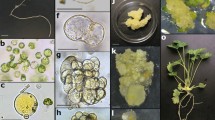
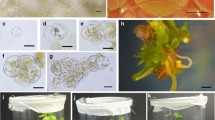
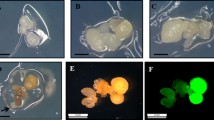
Plants were regenerated from mesophyll protoplasts of Ipomoea cairica L., a wild relative of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.), and somatic hybrids between I. cairica L. and sweetpotato cv. Xushu 18 were obtained by PEG-mediated method. I. cairica L. protoplasts were isolated from the leaves of in vitro grown plants and cultured in a modified MS medium containing 0.05 mg l−1 2,4-D and 0.5 mg l−1 kinetin. Nine weeks after plating, the obtained small calluses up to about 2 mm in diameter were transferred to solid MS medium supplemented with 0.05 mg l−1 2,4-D and 0.5 mg l−1 kinetin for callus proliferation. Three weeks after transfer, the calluses were transferred to MS medium supplemented with 0–1.0 mg l−1 IAA and 1.0–3.0 mg l−1 BAP and further to hormone-free MS medium for plant regeneration. The frequencies of calluses forming plants ranged from 6.0% to 41.3% based on the different concentrations of IAA and BAP, and 2.0 mg l−1 BAP gave the highest regeneration frequency of protoplast-derived calluses in I. cairica L.. The regenerated plants, when transferred to soil, showed 100% survival. No morphological variations were observed. Mesophyll protoplasts of I. cairica L. were fused with protoplasts isolated from embryogenic suspension cultures of Xushu 18 by PEG-mediated method. The fused products were cultured with the best protoplast culture system of I. cairica L.. Finally, 114 plants were produced from 63 of the 182 calluses derived from the fused protoplasts, and 46 plants of them were confirmed to be somatic hybrids through peroxidase isozyme, RAPD, morphological and cytological analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- IAA:
-
3-indoleacetic acid
- MES:
-
2-(N-morpholino)-ethanesulfonic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962)
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
References
Belarmino MM, Abe T, Sasahara T (1993) Shoot formation from protoplast-derived calli of sweetpotato and its wild relatives and the initiation of somatic hybrid. Japan J Breed 43(Suppl. 2):15–19
Bohman S, Wang M, Dixelius C (2002) Arabidopsis thaliana-derived resistance against Leptosphaeria maculans in a Brassica napus genomic background. Theor Appl Genet 105:498–504
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1–42
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1997) Somatic hybrids between Brassica oleracea L. and Sinapis alba L. with resistance to Alternaria brassicae (Berk.). Sacc Theor Appl Genet 94:1078–1085
Hu Q, Hansen LN, Laursen J, Dixelius C, Andersen SB (2002) Intergeneric hybrids between Brassica napus and Orychophragmus violaceus containing traits of agronomic importance for oilseed rape breeding. Theor Appl Genet 105:834–840
Lelivelt CLC, Leunissen EHM, Frederiks HJ, Helsper JPFG, Krens FA (1993) Transfer of resistance to the beet cyst nematode (Heterodera schachtii Schm.) from Sinapis alba L. (white mustard) to the Brassica napus L. gene pool by means of sexual and somatic hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 85:688–696
Li HM, Xing JY, Ma DF, Xie YP, Li Q (2003) Identification of virus-resistance characteristics in sweetpotato and its wild relatives. Crops 3:11–14 (in Chinese)
Liu QC, Kokubu T, Sato M (1990) Plant regeneration in stem, petiole and leaf explant cultures of Ipomoea triloba L. Japan J Breed 40:321–327
Liu QC, Kokubu T, Sato M (1991) Plant regeneration from Ipomoea triloba L. protoplasts. Japan J Breed 41:103–108
Liu QC, Kokubu T, Sato M (1992) Shoot regeneration from protoplast fusions of sweetpoato and its related species. Japan J Breed 42(Suppl. 1):88–89
Liu QC, Mi KX, Zhou HY, Ma B, Zhai H (1998) Regeneration and identification of interspecific somatic hybrid plants between sweetpotato and Ipomoea lacunosa. Acta Agr Sin 24:529–535 (in Chinese)
Liu QC, Zhai H, Wang Y, Zhang DP (2001) Efficient plant regeneration from embryogenic suspension cultures of sweetpotato. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol–Plant 37:564–567
Negrutiu I, Brouwer DD, Watts JW, Sidorov VI, Dirks R, Jacobs M (1986) Fusion of plant protoplasts: a study using auxotrophic mutants of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia, Viviani. Theor Appl Genet 72:279–286
Ukoskit K, Thompson PG, Watson CE Jr, Lawrence GW (1997) Identifying a randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marker linked to a gene for root-knot nematode in sweetpotato. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 122:818–821
Yan CQ, Qian KX, Yan QS, Zhang XQ, Xue GP, Huangfu WG, Wu YF, Zhao YZ, Xue ZY, Huang J, Xu GZ, Wu P (2004) Use of asymmetric somatic hybridization for transfer of the bacterial blight resistance trait from Oryza meyeriana L. to O. sativa L. ssp. Japonica. Plant Cell Rep 22:569–575
Yemets AI, Kundel’chuk OP, Smertenko AP, Solodushko VG, Rudas VA, Gleba YY, Blume YB (2000) Transfer of amiprophosmethyl resistance from a Nicotiana plumbaginifolia mutant by somatic hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 100:847–857
Zhang BY, Liu QC, Zhai H, Zhou HY, Zhang DP, Wang Y (2002) Production of fertile interspecific somatic hybrid plants between sweetpotato and its wild relative, Ipomoea lacunosa. Acta Hort 583:81–85
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Outstanding Younger Science Foundation of China (No.30225028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J.M., Liu, Q.C., Zhai, H. et al. Regeneration of plants from Ipomoea cairica L. protoplasts and production of somatic hybrids between I. cairica L. and sweetpotato, I. batatas (L.) Lam.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 87, 321–327 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9135-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9135-x