Abstract
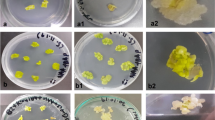
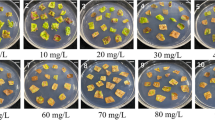
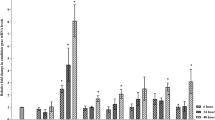
The genes encoding for a cucumber class III chitinase and Nicotiana plumbaginifolia class I glucanase were co-introduced into Slovak potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) breeding line 116/86 using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. For both transgenes the number of integrated copies and level of RNA expression were determined. These analyses demonstrated low variation and significant correlation in expression of the introduced transgenes. The effect of transgene expression on fungal susceptibility of transformants was evaluated in vitro. Hyphal extension assays revealed no obvious differences in the ability of extracts from transformants to inhibit growth of Rhizoctonia solani comparing to non-transformed potato.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen G, Spiker S & Thompson W (2000) Use of matrix attachment regions (MARs) to minimize transgene silencing. Plant Mol. Biol. 43: 241–256
Alonso E, De Carvalho NF, Obregon P, Cheysen G, Inze D, Van Montago M & Castresana C (1995) Differential DNA binding activity to a promoter elements of the gn1 beta-1,3-glucanase gene in hypersensitivity reacting tobacco plants. Plant J. 7: 309–320
Ashfield T, Hammond-Kosack KE, Harrison K & Jones JDG (1994) Cf gene-dependent induction of a ß-1,3-glucanase promoter in tomato plants infected with Cladosporium fulvum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 7: 645–657
Bauer M, Libantová J, Moravčíková J & Békésiová I (1998) Transgenic tobacco plants constitutively expressing acidic chitinase from cucumber. Biologia 53: 749–758
Békésiová I, Nap JP & Mlynárová L (1999) Isolation of high quality DNA and RNA from leaves of the carnivorous plant Drosera rotundifolia. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 17: 267–277
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quanties of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254
Covey SN & Al-Kaff NS (2000) Plant DNA viruses and gene silencing. Plant Mol. Biol. 43: 307–322
De Carvalho F, Gheysen G, Kushnir S, Van Montagu, Inzé D & Castresana C (1992) Suppression of beta-1,3-glucanase transgene expression in homozygous plants. EMBO J. 11: 2595–2602
De Loose M, Alliote T, Gheysen G, Genetello C, Gielen J, Soetaert P, Van Montagu M & Inze D (1988) Primary structure of a hormonally regulated ß-1,3-glucanase of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Gene 70: 13–23
Dean C, Favreau M, Tanmaki S, Bond-Nutter D, Dunsmuir P & Bedbrook J (1988a) Expression of tandem gene fusions in transgenic tobacco plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 16: 7601–7617
Dean C, Jones J, Favreau M, Dunsmuir P & Bedbrook J (1988b) Influences of flaking sequences on variability in expression levels of an introduced gene in transgenic tobacco plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 16: 9267–9283
Fagard M & Vaucheret H (2000) Systemic silencing signal(s). Plant Mol. Biol. 43: 285–293
Hoekema A, Hirch PR, Hooykaas PJJ & Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Tiplasmid. Nature 30: 179–184
Honeé G (1999) Engineered resistance against plant pathogens. Europ. J. Plant Pathol. 105: 319–336
Jach G, Görnhardt B, Mundy J, Logemann J, Pinsdorf E, Leah R, Schell J & Maas C (1995) Enhanced quantitative resistance against fungal disease by combinatorial expression of different barley antifungal proteins in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 8: 97–109
Ji C & Kuc J (1996) Antifungal activity of cucumber ß-1,3-glucanase and chitinase. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 49: 257–265
Jongedijk E, Tigelaar H, Van Roekel JSC, Bres-Vloemans SA, Dekker I, Van Den Elzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC & Melchers L (1995) Synergistic activity of chitinases and ß-1,3-glucanases enhances fungal resistance in transgenic tomato plants. Euphytica 85: 173–180
Kim MG, Lee KO, Cheong NE, Choi YO, Jeong JH, Cho MJ, Kim SCH & Lee SY (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of class III chitinase in pumpkin leaves, which strongly binds to regenerated chitin affinity gel. Plant Sci. 147: 157–163
Kombrink E & Somssich IE (1995) Defence responses of plants to pathogens. Adv. Bot. Res. 21: 2–26
Kubota M & Abiko K (2000) Induced resistance in cucumbers against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum and Rhizoctonia solani AG/2 by infection of the cotyledons. J. Phytopat. 149: 297–300
Leech MJ, May K, Hallard D, Verpoorte R, De Luca V & Christou P (1998) Expression of two constitutive genes of a secondary metabolic pathway in transgenic tobacco: molecular diversity influences levels of expression and product accumulation. Plant Mol. Biol. 38: 765–774
Libantová J, Bauer M, Mlynárová L, Moravčíková J & Békésiová I (1998) Transgenic tobacco and potato plants expressing basic vacuolar ß-1,3-glucanase from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Biologia 53: 739–748
Meins FJR, Neuhas JM, Sperisen C & Ryals J (1993) The primary structure of plant pathogenesis-related glucanohydrolases and their genes. In: Fritig B & Legrand M (eds) Mechanisms of Plant Defense Responses (pp. 245–273). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Melchers LS, Ponstein AS, Sela-Buurlage MB, Vloemans SA & Cornelissen BJC (1993) In vitro antimicrobial activities of defense proteins and biotechnology. In: Fritig B & Legrand M (eds) Mechanisms of Plant Defense Responses (pp. 401– 410). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Métraux JP, Burkhart W, Moyer M, Dichner S, Middlesteadt W, Williams S, Payne G, Carnes M & Ryals J (1989) Isolation of a complementary DNA encoding a chitinase with structural homology to a bifunctional lysozyme/chitinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 896–900
Mlynárová L, Jansen RC, Conner AJ, Stiekema WJ & Nap JP (1995) The MAR-mediated reduction in position effect can be uncoupled from copy number-dependent expression in transgenic plants. Plant Cell 7: 599–609
Mlynárová L, Loonen A, Mietkiewska E, Jansen RC & Nap JP (2002) Assembly of two transgenes in an artificial chromatin domain gives highly coordinated expression in tobacco. Genetics 160: 727–740
Moravčiková J, Libantová J, Matušíková, Libiaková G, Nap JP & Mlynárová L (2003) Genetic transformation of Slovak cultivar of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): efficiency and the behaviour of the transgene. Biologia 6, in press
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plantarum 15: 473–497
Neuhaus JM, Friting B, Linthorst HJM, Meins F, Mikkelsen JD & Ryals J (1996) A revised nomenclature for chitinase genes. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 14: 102–104
Paxton DJ (1991) Assays for antifungal activity. Meth. Plant Biochem. 6: 33–46
Rojas-Herrera R & Loyola-Vargas VM (2002) Induction of class III chitinase in foliar explants of Coffea arabica L. during somatic embryogenesis and wounding. Plant Sci. 4: 705–711
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF & Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sela-Buurlage MB, Ponstein AS, Bres-Vloemans SA, Melchers LS, Van Den Elzen PJM & Cornelissen BJC (1993) Only specific tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) chitinase and b-1,3-glucanase exhibit antifungal activity. Plant Physiol. 101: 857–863
Simon R, Priefer U & Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Bio/Tech. 1: 784–791
Van Engelen A, Molthoff JW, Conner AJ, Nap JP, Pereira A & Stiekema WJ (1995) pBINPLUS: an improved plant transformation vector based on pBIN19. Transg. Res. 4: 288–290
Vaucheret H, Elmayan T, Thierry D, Van der Geest A, Hall T, Conner AJ, Mlynarova L & Nap JP (1998) Flank matrix regions (MARs) from chicken, bean, yeast or tobacco do not prevent homology dependent trans-silencing in transgenic tobacco plants. Mol. Gen. Genet. 259: 388–392
Vierheilig H, Alt M, Lange J, Gut-Rella M, Wiemken A & Boller T (1995) Colonization of transgenic tobacco constitutively expressing pathogenesis-related proteins by the vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae. Envir. Microbiol. 8: 3031–3034
Zhang YY & Punja ZK (1994) Induction and characterization of chitinase isoforms in cucumber (Cucumis sativum L.) effect of elicitors, wounding and pathogen inoculation. Plant Sci. 2: 141–150
Zupan J, Muth TR, Draper O & Zambryski P (2000) The transfer of DNA from Agrobacterium tumefaciens into plants: a feast of fundamental insights. Plant J. 23: 11–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moravčíková, J., Matušíková, I., Libantová, J. et al. Expression of a cucumber class III chitinase and Nicotiana plumbaginifoliaclass I glucanase genes in transgenic potato plants. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 79, 161–168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-0656-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-0656-x