Abstract
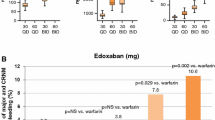
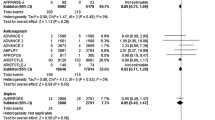
Anticoagulant therapy is a mainstay in the management of patients with cardiovascular disease. The use of conventional anticoagulants carries potential side effects, mainly bleeding. Drugs targeting Factor XI (FXI) have been investigated in randomized controlled trials as a new option with more favorable outcomes. A comprehensive literature search was conducted to identify relevant studies comparing FXI inhibitors to placebo or standard therapy. The primary outcomes were incidence of all bleeding events, major bleeding, and thromboembolism. Secondary outcomes included incidence of all adverse events (AE), serious AE, and all-cause mortality. A total of 11 studies involving 10,536 patients were included. FXI inhibitors were associated with a trend toward reduction of bleeding events and incidence of thromboembolism compared to the control group (placebo/standard therapy). There was no statistically significant difference between both groups in terms of adverse events and all-cause mortality. When compared to enoxaparin, FXI inhibitors significantly reduced the risk of bleeding events (RR = 0.42, 95% CI: 0.23–0.76, P = 0.004) and thromboembolism (RR = 0.59, 95% CI: 0.44–0.77, P = 0.001). On the other hand, when compared to DOACs, FXI inhibitors were associated with a significant reduction in bleeding events but not thromboembolism. Whereas, compared to placebo, FXI inhibitors did not increase the risk of bleeding events, adverse events, or all-cause mortality (P > 0.05). FXI inhibitors could be a safer and more potent option for prevention of thromboembolism than conventional therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FXI:
-
Factor XI
- AE:
-
Adverse events
- SAE:
-
Serious adverse events
- RR:
-
Risk ratio
- TKA:
-
Total Knee arthroplasty
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- VTE:
-
Venous thromboembolism
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- DOACs:
-
Direct oral anticoagulants
- VKAs:
-
Vitamin K antagonists
- MR:
-
Mendelian randomization
- RCTs:
-
Randomized clinical trials
- LMWH:
-
Low molecular weight heparin
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- APTT:
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time
- DVT:
-
Deep vein thrombosis
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- TIA:
-
Transient ischemic attack
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- ISTH:
-
International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis
- BARC:
-
Bleeding Academic Research Consortium
References
Piccini JP, Caso V, Connolly SJ, Fox KAA, Oldgren J, Jones WS, Gorog DA, Durdil V, Viethen T, Neumann C, Mundl H, Patel MR (2022) Safety of the oral factor XIa inhibitor asundexian compared with apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation (PACIFIC-AF): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, dose-finding phase 2 study. Lancet 399(10333):1383–1390. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(22)00456-1
Walsh M, Bethune C, Smyth A, Tyrwhitt J, Jung SW, Yu RZ, Wang Y, Geary RS, Weitz J, Bhanot S (2022) Phase 2 study of the factor XI antisense inhibitor IONIS-FXI(rx) in patients with ESRD. Kidney Int Rep 7(2):200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2021.11.011
Lorentz CU, Tucker EI, Verbout NG, Shatzel JJ, Olson SR, Markway BD, Wallisch M, Ralle M, Hinds MT, McCarty OJT, Gailani D, Weitz JI, Gruber A (2021) The contact activation inhibitor AB023 in heparin-free hemodialysis: results of a randomized phase 2 clinical trial. Blood 138(22):2173–2184. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021011725
Verhamme P, Yi BA, Segers A, Salter J, Bloomfield D, Büller HR, Raskob GE, Weitz JI (2021) Abelacimab for Prevention of venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 385(7):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2105872
Büller HR, Bethune C, Bhanot S, Gailani D, Monia BP, Raskob GE, Segers A, Verhamme P, Weitz JI (2015) Factor XI antisense oligonucleotide for prevention of venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med 372(3):232–240. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1405760
Weitz JI, Bauersachs R, Becker B, Berkowitz SD, Freitas MCS, Lassen MR, Metzig C, Raskob GE (2020) Effect of Osocimab in preventing venous thromboembolism among patients undergoing knee arthroplasty: the FOXTROT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 323(2):130–139. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.20687
Weitz JI, Strony J, Ageno W, Gailani D, Hylek EM, Lassen MR, Mahaffey KW, Notani RS, Roberts R, Segers A, Raskob GE (2021) Milvexian for the Prevention of venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 385(23):2161–2172. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2113194
Shoamanesh A, Mundl H, Smith EE, Masjuan J, Milanov I, Hirano T, Agafina A, Campbell B, Caso V, Mas JL, Dong Q, Turcani P, Christensen H, Ferro JM, Veltkamp R, Mikulik R, De Marchis GM, Robinson T, Lemmens R, Hart RG (2022) Factor XIa inhibition with asundexian after acute non-cardioembolic ischaemic stroke (PACIFIC-Stroke): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet 400(10357):997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(22)01588-4
Sharma M, Molina CA, Toyoda K, Bereczki D, Bangdiwala SI, Kasner SE, Lutsep HL, Tsivgoulis G, Ntaios G, Czlonkowska A, Shuaib A, Amarenco P, Endres M, Yoon BW, Tanne D, Toni D, Yperzeele L, von Weitzel-Mudersbach P, Silva S, Hankey G, G. J (2024) Safety and efficacy of factor XIa inhibition with milvexian for secondary stroke prevention (AXIOMATIC-SSP): a phase 2, international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding trial. Lancet Neurol 23(1):46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00403-9
Rao SV, Kirsch B, Bhatt DL, Budaj A, Coppolecchia R, Eikelboom J, James SK, Jones WS, Merkely B, Keller L, Hermanides RS, Campo G, Ferreiro JL, Shibasaki T, Mundl H, Alexander JH (2022) A Multicenter, phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, dose-finding trial of the oral factor XIa inhibitor asundexian to prevent adverse Cardiovascular outcomes after Acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 146(16):1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.122.061612
Chen A, Stecker E, B AW (2020) Direct oral anticoagulant use: a practical guide to Common Clinical challenges. J Am Heart Assoc 9(13):e017559. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.120.017559
Greco A, Laudani C, Spagnolo M, Agnello F, Faro DC, Finocchiaro S, Legnazzi M, Mauro MS, Mazzone PM, Occhipinti G, Rochira C, Scalia L, Capodanno D (2023) Pharmacology and Clinical Development of factor XI inhibitors. Circulation 147(11):897–913. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.122.062353
Ali AE, Becker RC (2024) Factor XI: structure, function and therapeutic inhibition. Journal of thrombosis and thrombolysis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02972-5
Hsu C, Hutt E, Bloomfield DM, Gailani D, Weitz JI (2021) Factor XI inhibition to uncouple thrombosis from hemostasis: JACC Review topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol 78(6):625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2021.06.010
Salomon O, Steinberg DM, Koren-Morag N, Tanne D, Seligsohn U (2008) Reduced incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with severe factor XI deficiency. Blood 111(8):4113–4117. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-10-120139
Preis M, Hirsch J, Kotler A, Zoabi A, Stein N, Rennert G, Saliba W (2017) Factor XI deficiency is associated with lower risk for cardiovascular and venous thromboembolism events. Blood 129(9):1210–1215. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-09-742262
Salomon O, Steinberg DM, Zucker M, Varon D, Zivelin A, Seligsohn U (2011) Patients with severe factor XI deficiency have a reduced incidence of deep-vein thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 105(2):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1160/th10-05-0307
Daghlas I, Gill D (2023) Leveraging genetic predictors of factor XI levels to anticipate results from clinical trials. Eur J Neurol 30(7):2112–2116. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.15820
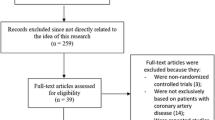
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Mourad, Ouzzani Hossam, Hammady Zbys, Fedorowicz Ahmed, Elmagarmid (2016) Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews Systematic Reviews 5(1) https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
Chapter 8 Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial | Cochrane Training. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-08
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G (2012) Oral anticoagulant therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis. Pract Guidelines Chest 141(2 Suppl). 9th edn.https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-2292. American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinicale44S-e88S
Zirlik A, Bode C (2017) Vitamin K antagonists: relative strengths and weaknesses vs. direct oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43(3):365–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1446-0
Hinojar R, Jiménez-Natcher JJ, Fernández-Golfín C, Zamorano JL (2015) New oral anticoagulants: a practical guide for physicians. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 1(2):134–145. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjcvp/pvv002
Woodruff RS, Sullenger B, Becker RC (2011) The many faces of the contact pathway and their role in thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis 32(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-011-0578-5
Meijers JC, Tekelenburg WL, Bouma BN, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR (2000) High levels of coagulation factor XI as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med 342(10):696–701. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200003093421004
Kyrle PA, Eischer L, Šinkovec H, Eichinger S (2019) Factor XI and recurrent venous thrombosis: an observational cohort study. J Thromb Haemost 17(5):782–786. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14415
Presume J, Ferreira J, Ribeiras R, Mendes M (2022) Achieving higher efficacy without compromising safety with factor XI inhibitors versus low molecular weight heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in major orthopedic surgery-systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost 20(12):2930–2938. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.15890
Galli M, Laborante R, Ortega-Paz L, Franchi F, Rollini F, D’Amario D, Capodanno D, Tremoli E, Gibson CM, Mehran R, Angiolillo DJ (2023) Factor XI inhibitors in early clinical trials: a Meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost 123(6):576–584. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-2043-0346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A.E., Awad, M.K., Ali, K. et al. Factor XI as a new target for prevention of thromboembolism in cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Thromb Thrombolysis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02986-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02986-z