Abstract
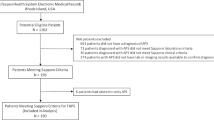
Direct oral anticoagulants have been shown safe and effective in the treatment of pulmonary emboli and deep vein thrombi. Their role in the treatment of patients with hypercoagulability is uncertain. We designed a retrospective exploratory analysis of all patients with definite heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) that were treated with either apixaban or rivaroxaban from September 2011 through November 2015. Patients were reviewed for several clinico-pathologic features, including efficacy and safety. 23 patients were identified (12 patients with HIT and 11 patients with APS). Sixteen patients (70 %) were treated with apixaban and seven patients (30 %) were treated with rivaroxaban over a median follow up of 7 months (range 2–39). Zero patients developed recurrent thrombi. Two patients being treated for HIT developed major bleeding leading to discontinuation of all anticoagulation. Therefore, apixaban and rivaroxaban appear safe and effective for treatment of patients with HIT and APS in this small retrospective cohort and should be considered on an individual basis for patients who refuse, fail or are intolerant of warfarin. There were no sources of funding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauersachs R, Berkowitz SD, Brenner B, Buller HR, Decousus H, Gallus AS, Lensing AW, Misselwitz F, Prins MH, Raskob GE et al (2010) Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 363:2499–2510
Agnelli G, Buller HR, Cohen A, Curto M, Gallus AS, Johnson M, Masiukiewicz U, Pak R, Thompson J, Raskob GE et al (2013) Oral apixaban for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 369:799–808
Greinacher A (2015) Heparin-Induced thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 373:1883–1884
Kelton JG, Arnold DM, Bates SM (2013) Nonheparin anticoagulants for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 368:737–744
Linkins LA, Dans AL, Moores LK, Bona R, Davidson BL, Schulman S, Crowther M (2012) Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 141:e495S–e530S
Pengo V, Ruffatti A, Legnani C, Gresele P, Barcellona D, Erba N, Testa S, Marongiu F, Bison E, Denas G et al (2010) Clinical course of high-risk patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Thromb Haemost 8:237–242
Krauel K, Hackbarth C, Furll B, Greinacher A (2012) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: in vitro studies on the interaction of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and low-sulfated heparin, with platelet factor 4 and anti-PF4/heparin antibodies. Blood 119:1248–1255
Walenga JM, Prechel M, Jeske WP, Hoppensteadt D, Maddineni J, Iqbal O, Messmore HL, Bakhos M (2008) Rivaroxaban–an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor–has potential for the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 143:92–99
Walenga JM, Prechel M, Hoppensteadt D, Escalante V, Chaudhry T, Jeske WP, Bakhos M (2013) Apixaban as an alternate oral anticoagulant for the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 19:482–487
Erkan D, Aguiar CL, Andrade D, Cohen H, Cuadrado MJ, Danowski A, Levy RA, Ortel TL, Rahman A, Salmon JE et al (2014) 14th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies: task force report on antiphospholipid syndrome treatment trends. Autoimmun Rev 13:685–696
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, Derksen RH, PG, D.E.G., Koike T, Meroni PL et al (2006) International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost 4:295–306
Castellucci LA, Le Gal G, Rodger MA, Carrier M (2014) Major bleeding during secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients who have completed anticoagulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost 12:344–348
Schaefer JK, McBane RD, Black DF, Williams LN, Moder KG, Wysokinski WE (2014) Failure of dabigatran and rivaroxaban to prevent thromboembolism in antiphospholipid syndrome: a case series of three patients. Thromb Haemost 112:947–950
Son M, Wypasek E, Celinska-Lowenhoff M, Undas A (2015) The use of rivaroxaban in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: a series of 12 cases. Thromb Res 135:1035–1036
Win K, Rodgers GM (2014) New oral anticoagulants may not be effective to prevent venous thromboembolism in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Hematol 89:1017
Noel N, Dutasta F, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Bienvenu B, Mariette X, Geffray L, Sene D, Chaidi RB, Michot JM, Fain O et al (2015) Safety and efficacy of oral direct inhibitors of thrombin and factor Xa in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun Rev 14:680–685
Bachmeyer C, Elalamy I (2014) Rivaroxaban as an effective treatment for recurrent superficial thrombophlebitis related to primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol 39:840–841
Delgado MG, Rodriguez S, Garcia R, Sanchez P, Saiz A, Calleja S (2015) Antiphospholipid syndrome of late onset: a difficult diagnosis of a recurrent embolic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24:e209–e211
Joalland F, de Boysson H, Darnige L, Johnson A, Jeanjean C, Cheze S, Augustin A, Auzary C, Geffray L (2014) Seronegative antiphospholipid syndrome, catastrophic syndrome, new anticoagulants: learning from a difficult case report. Rev Med Interne 35:752–756
Sciascia S, Breen K, Hunt BJ (2015). Rivaroxaban use in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome and previous venous thromboembolism. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 26:476–477
Signorelli F, Nogueira F, Domingues V, Mariz HA, Levy RA (2016). Thrombotic events in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome treated with rivaroxaban: a series of eight cases. Clin Rheumatol 35:801–805
Betancur JF, Bonilla-Abadia F, Hormaza AA, Jaramillo FJ, Canas CA, Tobon GJ (2016) Direct oral anticoagulants in antiphospholipid syndrome: a real life case series. Lupus 25:658–662
Crowther MA, Ginsberg JS, Julian J, Denburg J, Hirsh J, Douketis J, Laskin C, Fortin P, Anderson D, Kearon C et al (2003) A comparison of two intensities of warfarin for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. N Engl J Med 349:1133–1138
Finazzi G, Marchioli R, Brancaccio V, Schinco P, Wisloff F, Musial J, Baudo F, Berrettini M, Testa S, D’Angelo A et al (2005) A randomized clinical trial of high-intensity warfarin vs. conventional antithrombotic therapy for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome (WAPS). J Thromb Haemost 3:848–853
Agnelli G, Buller HR, Cohen A, Gallus AS, Lee TC, Pak R, Raskob GE, Weitz JI, Yamabe T (2015) Oral apixaban for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: results from the AMPLIFY trial. J Thromb Haemost 13:2187–2191
Vigano D’Angelo S, Comp PC, Esmon CT, D’Angelo A (1986) Relationship between protein C antigen and anticoagulant activity during oral anticoagulation and in selected disease states. J Clin Invest 77:416–425
Woller SC, Stevens SM, Kaplan DA, Branch DW, Aston VT, Wilson EL, Gallo HM, Johnson EG, Rondina MT, Lloyd JF et al (2016) Apixaban for the secondary prevention of thrombosis among patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: study rationale and design (ASTRO-APS). Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 22:239–247
Linkins LA, Warkentin TE, Pai M, Shivakumar S, Manji R, Wells PS, Wu CM, Nazi I, Crowther MA (2015) Rivaroxaban for treatment of suspected or confirmed heparin-induced thrombocytopenia study. In: ASH annual conference, volume abstract 3468. Orlando, FL
Hantson P, Lambert C, Hermans C (2015) Rivaroxaban for arterial thrombosis related to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 26:205–206
Sartori M, Favaretto E, Cini M, Legnani C, Cosmi B (2015) Rivaroxaban in the treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Thrombolysis 40:392–394
Mirdamadi A (2013) Dabigatran, a direct thrombin inhibitor, can be a life-saving treatment in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. ARYA Atheroscler 9:112–114
Ng HJ, Than H, Teo EC (2015) First experiences with the use of rivaroxaban in the treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res 135:205–207
Pollack CV Jr, Reilly PA, Eikelboom J, Glund S, Verhamme P, Bernstein RA, Dubiel R, Huisman MV, Hylek EM, Kamphuisen PW et al (2015) Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal. N Engl J Med 373:511–520
Siegal DM, Curnutte JT, Connolly SJ, Lu G, Conley PB, Wiens BL, Mathur VS, Castillo J, Bronson MD, Leeds JM et al (2015) Andexanet alfa for the reversal of factor Xa inhibitor activity. N Engl J Med 373:2413–2424
Funding
No funding was provided for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunk, P.R., Brown, J., McShane, M. et al. Direct oral anticoagulants in hypercoagulable states. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43, 79–85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1420-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1420-x