Abstract
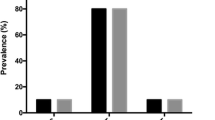
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a life-threatening medical disorder worldwide. A great deal of evidence suggests that prevalence of VTE varies significantly among ethnic populations, with consistently lower incidence found in Asians. While the distribution of genetic risk factors may vary among races, genetic risk factors can play a major role among individuals with different genetic backgrounds. Two clinically evaluated low-frequency genetic mutations that predispose to VTE—the factor V Leiden mutation and prothrombin G20210A mutation—are found predominantly in Caucasians, and virtually never in Asians. The findings of a recent genetic study of VTE in northeast Asians, which greatly advanced our knowledge in this area, indicate that the most frequent genetic risk factors for VTE in northeast Asians can be attributed to a dysfunction of the protein C anticoagulant system. Several low-frequency genetic mutations, PROS1 p.Lys196Glu in Japanese and PROC p.Arg189Trp and p.Lys193del in Chinese, are significantly associated with increased risk for VTE, with odds ratio more than 2 through the reduced protein C anticoagulant activity. Construction of a multifactorial model based on the genetic risk factors in the protein C anticoagulant system could facilitate genetic counseling for VTE risk in these populations. The influence of prevalent genetic mutations on the risk of VTE should be further investigated in Asian countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
White RH, Zhou H, Romano PS (1998) Incidence of idiopathic deep venous thrombosis and secondary thromboembolism among ethnic groups in California. Ann Intern Med 128(9):737–740
Klatsky AL, Armstrong MA, Poggi J (2000) Risk of pulmonary embolism and/or deep venous thrombosis in Asian-Americans. Am J Cardiol 85(11):1334–1337
White RH, Zhou H, Murin S, Harvey D (2005) Effect of ethnicity and gender on the incidence of venous thromboembolism in a diverse population in California in 1996. Thromb Haemost 93(2):298–305
White RH, Keenan CR (2009) Effects of race and ethnicity on the incidence of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Res 123(Suppl 4):S11–S17
Sakuma M, Nakamura M, Yamada N, Ota S, Shirato K, Nakano T, Ito M, Kobayashi T (2009) Venous thromboembolism: deep vein thrombosis with pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis alone, and pulmonary embolism alone. Circ J 73(2):305–309
Lee CH, Cheng CL, Lin LJ, Tsai LM, Yang YH (2011) Epidemiology and predictors of short-term mortality in symptomatic venous thromboembolism. Circ J 75(8):1998–2004
Zakai NA, McClure LA (2011) Racial differences in venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost 9(10):1877–1882
Margaglione M, Grandone E (2011) Population genetics of venous thromboembolism. A narrative review. Thromb Haemost 105(2):221–231
Souto JC, Almasy L, Borrell M, Blanco-Vaca F, Mateo J, Soria JM, Coll I, Felices R, Stone W, Fontcuberta J, Blangero J (2000) Genetic susceptibility to thrombosis and its relationship to physiological risk factors: the GAIT study. Genetic analysis of idiopathic thrombophilia. Am J Hum Genet 67(6):1452–1459
Hamasaki N, Kuma H, Tsuda H (2013) Activated protein C anticoagulant system dysfunction and thrombophilia in Asia. Ann Lab Med 33(1):8–13
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE (2000) Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mut 15(1):7–12
De Stefano V, Finazzi G, Mannucci PM (1996) Inherited thrombophilia: pathogenesis, clinical syndromes, and management. Blood 87(9):3531–3544
Liu HW, Kwong YL, Bourke C, Lam CK, Lie AK, Wei D, Chan LC (1994) High incidence of thrombophilia detected in Chinese patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 71(4):416–419
Shen MC, Lin JS, Tsay W (2000) Protein C and protein S deficiencies are the most important risk factors associated with thrombosis in Chinese venous thrombophilic patients in Taiwan. Thromb Res 99(5):447–452
Ho CH, Chau WK, Hsu HC, Gau JP, Yu TJ (2000) Causes of venous thrombosis in fifty Chinese patients. Am J Hematol 63(2):74–78
Suehisa E, Nomura T, Kawasaki T, Kanakura Y (2001) Frequency of natural coagulation inhibitor (antithrombin III, protein C and protein S) deficiencies in Japanese patients with spontaneous deep vein thrombosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 12(2):95–99
Chen TY, Su WC, Tsao CJ (2003) Incidence of thrombophilia detected in southern Taiwanese patients with venous thrombosis. Ann Hematol 82(2):114–117
Sakata T, Okamoto A, Mannami T, Tomoike H, Miyata T (2004) Prevalence of protein S deficiency in the Japanese general population: the Suita study. J Thromb Haemost 2(6):1012–1013
Sakata T, Okamoto A, Mannami T, Matsuo H, Miyata T (2004) Protein C and antithrombin deficiency are important risk factors for deep vein thrombosis in Japanese. J Thromb Haemost 2(3):528–530
Kinoshita S, Iida H, Inoue S, Watanabe K, Kurihara M, Wada Y, Tsuda H, Kang D, Hamasaki N (2005) Protein S and protein C gene mutations in Japanese deep vein thrombosis patients. Clin Biochem 38(10):908–915
Angchaisuksiri P, Atichartakarn V, Aryurachai K, Archararit N, Rachakom B, Atamasirikul K, Tiraganjana A (2007) Risk factors of venous thromboembolism in Thai patients. Int J Hematol 86(5):397–402
Zhu T, Ding Q, Bai X, Wang X, Kaguelidou F, Alberti C, Wei X, Hua B, Yang R, Wang X, Wang Z, Ruan C, Schlegel N, Zhao Y (2011) Normal ranges and genetic variants of antithrombin, protein C and protein S in the general Chinese population. Results of the chinese hemostasis investigation on natural anticoagulants study I group. Haematologica 96(7):1033–1040
Tang L, Lu X, Yu JM, Wang QY, Yang R, Guo T, Mei H, Hu Y (2012) PROC c.574_576del polymorphism: a common genetic risk factor for venous thrombosis in the Chinese population. J Thromb Haemost 10(10):2019–2026
Shen MC, Lin JS, Tsay W (1997) High prevalence of antithrombin III, protein C and protein S deficiency, but no factor V Leiden mutation in venous thrombophilic Chinese patients in Taiwan. Thromb Res 87(4):377–385
Gandrille S, Borgel D, Sala N, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Simmonds R, Rezende S, Lind B, Mannhalter C, Pabinger I, Reitsma PH, Formstone C, Cooper DN, Saito H, Suzuki K, Bernardi F, Aiach M (2000) Protein S deficiency: a database of mutations—summary of the first update. Thromb Haemost 84(5):918
Yin T, Takeshita S, Sato Y, Sakata T, Shin Y, Honda S, Kawasaki T, Tsuji H, Kojima T, Madoiwa S, Sakata Y, Murata M, Ikeda Y, Miyata T (2007) A large deletion of the PROS1 gene in a deep vein thrombosis patient with protein S deficiency. Thromb Haemost 98(4):783–789
Kimura R, Sakata T, Kokubo Y, Okamoto A, Okayama A, Tomoike H, Miyata T (2006) Plasma protein S activity correlates with protein S genotype but is not sensitive to identify K196E mutant carriers. J Thromb Haemost 4(9):2010–2013
Ikejiri M, Wada H, Sakamoto Y, Ito N, Nishioka J, Nakatani K, Tsuji A, Yamada N, Nakamura M, Ito M, Nobori T (2010) The association of protein S Tokushima-K196E with a risk of deep vein thrombosis. Int J Hematol 92(2):302–305
Miyata T, Hamasaki N, Wada H, Kojima T (2012) More on: racial differences in venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost 10(2):319–320
Yamazaki T, Sugiura I, Matsushita T, Kojima T, Kagami K, Takamatsu J, Saito H (1993) A phenotypically neutral dimorphism of protein S: the substitution of Lys155 by Glu in the second EGF domain predicted by an A to G base exchange in the gene. Thromb Res 70(5):395–403
Shigekiyo T, Uno Y, Kawauchi S, Saito S, Hondo H, Nishioka J, Hayashi T, Suzuki K (1993) Protein S Tokushima: an abnormal protein S found in a Japanese family with thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 70(2):244–246
Kimura R, Honda S, Kawasaki T, Tsuji H, Madoiwa S, Sakata Y, Kojima T, Murata M, Nishigami K, Chiku M, Hayashi T, Kokubo Y, Okayama A, Tomoike H, Ikeda Y, Miyata T (2006) Protein S-K196E mutation as a genetic risk factor for deep vein thrombosis in Japanese patients. Blood 107(4):1737–1738
Miyata T, Kimura R, Kokubo Y, Sakata T (2006) Genetic risk factors for deep vein thrombosis among Japanese: importance of protein S K196E mutation. Int J Hematol 83(3):217–223
Miyata T, Sato Y, Ishikawa J, Okada H, Takeshita S, Sakata T, Kokame K, Kimura R, Honda S, Kawasaki T, Suehisa E, Tsuji H, Madoiwa S, Sakata Y, Kojima T, Murata M, Ikeda Y (2009) Prevalence of genetic mutations in protein S, protein C and antithrombin genes in Japanese patients with deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Res 124(1):14–18
Neki R, Fujita T, Kokame K, Nakanishi I, Waguri M, Imayoshi Y, Suehara N, Ikeda T, Miyata T (2011) Genetic analysis of patients with deep vein thrombosis during pregnancy and postpartum. Int J Hematol 94(2):150–155
Hayashi T, Nishioka J, Suzuki K (1995) Molecular mechanism of the dysfunction of protein S(Tokushima) (Lys155→Glu) for the regulation of the blood coagulation system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1272(3):159–167
Liu W, Yin T, Okuda H, Harada KH, Li Y, Xu B, Yang J, Wang H, Fan X, Koizumi A, Miyata T (2013) Protein S K196E mutation, a genetic risk factor for venous thromboembolism, is limited to Japanese. Thromb Res 132(2):314–315
Tsay W, Shen MC (2004) R147W mutation of PROC gene is common in venous thrombotic patients in Taiwanese Chinese. Am J Hematol 76(1):8–13
Tang L, Guo T, Yang R, Mei H, Wang H, Lu X, Yu J, Wang Q, Hu Y (2012) Genetic background analysis of protein C deficiency demonstrates a recurrent mutation associated with venous thrombosis in Chinese population. PLoS ONE 7(4):e35773
Tsay W, Greengard JS, Montgomery RR, McPherson RA, Fucci JC, Koerper MA, Coughlin J, Griffin JH (1993) Genetic mutations in ten unrelated American patients with symptomatic type 1 protein C deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 4(5):791–796
Tait RC, Walker ID, Reitsma PH, Islam SI, McCall F, Poort SR, Conkie JA, Bertina RM (1995) Prevalence of protein C deficiency in the healthy population. Thromb Haemost 73(1):87–93
Miyata T, Sakata T, Yasumuro Y, Okamura T, Katsumi A, Saito H, Abe T, Shirahata A, Sakai M, Kato H (1998) Genetic analysis of protein C deficiency in nineteen Japanese families: five recurrent defects can explain half of the deficiencies. Thromb Res 92(4):181–187
Matsuda M, Sugo T, Sakata Y, Murayama H, Mimuro J, Tanabe S, Yoshitake S (1988) A thrombotic state due to an abnormal protein C. N Engl J Med 319(19):1265–1268
Miyata T, Zheng YZ, Sakata T, Tsushima N, Kato H (1994) Three missense mutations in the protein C heavy chain causing type I and type II protein C deficiency. Thromb Haemost 71(1):32–37
Sakata T, Kario K, Katayama Y, Matsuyama T, Kato H, Miyata T (2000) Studies on congenital protein C deficiency in Japanese: prevalence, genetic analysis, and relevance to the onset of arterial occlusive diseases. Semin Thromb Haemost 26(1):11–16
Heit JA, Petterson TM, Owen WG, Burke JP, DE Andrade M, Melton LJ 3rd (2005) Thrombomodulin gene polymorphisms or haplotypes as potential risk factors for venous thromboembolism: a population-based case–control study. J Thromb Haemost 3(4):710–717
Sugiyama S, Hirota H, Kimura R, Kokubo Y, Kawasaki T, Suehisa E, Okayama A, Tomoike H, Hayashi T, Nishigami K, Kawase I, Miyata T (2007) Haplotype of thrombomodulin gene associated with plasma thrombomodulin level and deep vein thrombosis in the Japanese population. Thromb Res 119(1):35–43
Tang L, Wang HF, Lu X, Jian XR, Jin B, Zheng H, Li YQ, Wang QY, Wu TC, Guo H, Liu H, Guo T, Yu JM, Yang R, Yang Y, Hu Y (2013) Common genetic risk factors for venous thrombosis in the Chinese population. Am J Hum Genet 92(2):177–187
Delvaeye M, Noris M, De Vriese A, Esmon CT, Esmon NL, Ferrell G, Del-Favero J, Plaisance S, Claes B, Lambrechts D, Zoja C, Remuzzi G, Conway EM (2009) Thrombomodulin mutations in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. New Engl J Med 361(4):345–357
Dennis J, Johnson CY, Adediran AS, de Andrade M, Heit JA, Morange PE, Tregouet DA, Gagnon F (2012) The endothelial protein C receptor (PROCR) Ser219Gly variant and risk of common thrombotic disorders: a HuGE review and meta-analysis of evidence from observational studies. Blood 119(10):2392–2400
Ireland HA, Cooper JA, Drenos F, Acharya J, Mitchell JP, Bauer KA, Morrissey JH, Esnouf MP, Humphries SE (2009) FVII, FVIIa, and downstream markers of extrinsic pathway activation differ by EPCR Ser219Gly variant in healthy men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(11):1968–1974
Chen XD, Tian L, Li M, Jin W, Zhang HK, Zheng CF (2011) Relationship between endothelial cell protein C receptor gene 6936A/G polymorphisms and deep venous thrombosis. Chin Med J (Engl) 124(1):72–75
Yin G, Jin X, Ming H, Zheng X, Zhang D (2012) Endothelial cell protein C receptor gene 6936A/G polymorphism is associated with venous thromboembolism. Exp Ther Med 3(6):989–992
Bezemer ID, Bare LA, Doggen CJ, Arellano AR, Tong C, Rowland CM, Catanese J, Young BA, Reitsma PH, Devlin JJ, Rosendaal FR (2008) Gene variants associated with deep vein thrombosis. JAMA 299(11):1306–1314
Tregouet DA, Heath S, Saut N, Biron-Andreani C, Schved JF, Pernod G, Galan P, Drouet L, Zelenika D, Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Tiret L, Lathrop M, Emmerich J, Morange PE (2009) Common susceptibility alleles are unlikely to contribute as strongly as the FV and ABO loci to VTE risk: results from a GWAS approach. Blood 113(21):5298–5303
de Haan HG, Bezemer ID, Doggen CJ, Le Cessie S, Reitsma PH, Arellano AR, Tong CH, Devlin JJ, Bare LA, Rosendaal FR, Vossen CY (2012) Multiple SNP testing improves risk prediction of first venous thrombosis. Blood 120(3):656–663
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan; the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan; the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and by grants from the Clinical Research Supportive Fund, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army (No. 2012FC-TSYS-3042).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, T., Miyata, T. Dysfunction of protein C anticoagulant system, main genetic risk factor for venous thromboembolism in Northeast Asians. J Thromb Thrombolysis 37, 56–65 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-013-1005-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-013-1005-x