Abstract
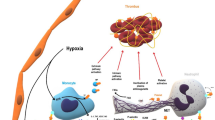
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) includes both deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism. The 2009 JUPITER trial showed a significant decrease in DVT in non-hyperlipidemic patients, with elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, treated with rosuvastatin. The effects of statins on thrombosis are unclear, prompting this literature review. A literature search was performed (1950 to February 2011) with MEDLINE, EMBASE, and PUBMED databases including the following keywords: “statins”, “hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors”, “VTE”, “PE”, “DVT”, and either “anti-coagulation” or “inflammation”. Editorials, reviews, case reports, meta-analysis and duplicates were excluded. Inflammatory biomarkers of DVT, include interleukin (IL)-6, CRP, IL-8, and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1). Statin therapy reduces IL-6 expression of CRP and MCP-1, usually elevated in VTE. Reduction of IL-6 induced MCP-1 has been linked to vein wall fibrosis, promoting post thrombotic syndrome (PTS) and recurrent DVT in patients. Also, our review suggests that the anti-thrombotic effects are likely exhibited through the anti-inflammatory properties of statins. This work supports that statin therapy has the ability to decrease the incidence and recurrence of VTE and the potential to decrease PTS. This is mainly due to the anti-inflammatory effects of statins and may explain why normolipidemic patients, with elevated CRP, appear to have the greatest reduction in VTE. Given their low risk of bleeding, statins have the potential to serve as a safe adjunctive pharmacological therapy to current treatments in select patients with VTE, however further investigations into this concept are needed and essential.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VTE:
-
Venous thromboembolism
- DVT:
-
Deep vein thrombosis
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- PTS:
-
Post-thrombotic syndrome
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- LDL-C:
-
Low density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HMG-CoA reductase:
-
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein 1
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- sP-selectin:
-
Soluble P-selectin
- hs-CRP:
-
High sensitivity C-reactive protein
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
References
Raskob GE, Silverstein R, Bratzler DW, Heit JA, White RH (2010) Surveillance for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: recommendations from a national workshop. Am J Prev Med 38(4 Suppl):S502–S509
Cohen AT, Agnelli G, Anderson FA, Arcelus JI, Bergqvist D, Brecht JG, Greer IA, Heit JA, Hutchinson JL, Kakkar AK et al (2007) Venous thromboembolism (VTE) in Europe. The number of VTE events and associated morbidity and mortality. Thromb Haemost 98(4):756–764
Hopkins NF, Wolfe JH (1992) ABC of vascular diseases. Deep venous insufficiency and occlusion. BMJ 304(6819):107–110
Ackroyd JS, Browse NL (1986) The investigation and surgery of the post-thrombotic syndrome. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 27(1):5–16
Negus D (1970) The post-thrombotic syndrome. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 47(2):92–105
Ashrani AA, Heit JA (2009) Incidence and cost burden of post-thrombotic syndrome. J Thromb Thrombolysis 28(4):465–476
Heit JA, Kobbervig CE, James AH, Petterson TM, Bailey KR, Melton LJ 3rd (2005) Trends in the incidence of venous thromboembolism during pregnancy or postpartum: a 30-year population-based study. Ann Intern Med 143(10):697–706
Linkins LA, Choi PT, Douketis JD (2003) Clinical impact of bleeding in patients taking oral anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 139(11):893–900
Glynn RJ, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG et al (2009) A randomized trial of rosuvastatin in the prevention of venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 360(18):1851–1861
Undas A, Brozek J, Musial J (2002) Anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects of statins in the management of coronary artery disease. Clin Lab 48(5–6):287–296
Arslan F, Pasterkamp G, de Kleijn DP (2008) Unraveling pleiotropic effects of statins: bit by bit, a slow case with perspective. Circ Res 103(4):334–336
Nishino M, Hoshida S, Kato H, Egami Y, Shutta R, Yamaguchi H, Tanaka K, Tanouchi J, Hori M, Yamada Y (2008) Preprocedural statin administration can reduce thrombotic reaction after stent implantation. Circ J 72(2):232–237
Perez A, Bartholomew JR (2010) Interpreting the JUPITER trial: statins can prevent VTE, but more study is needed. Cleve Clin J Med 77(3):191–194
Ali T, Humphries J, Burnand K, Sawyer B, Bursill C, Channon K, Greaves D, Rollins B, Charo IF, Smith A (2006) Monocyte recruitment in venous thrombus resolution. J Vasc Surg 43(3):601–608
Ay C, Jungbauer LV, Sailer T, Tengler T, Koder S, Kaider A, Panzer S, Quehenberger P, Pabinger I, Mannhalter C (2007) High concentrations of soluble P-selectin are associated with risk of venous thromboembolism and the P-selectin Thr715 variant. Clin Chem 53(7):1235–1243
Henke PK, Wakefield TW, Kadell AM, Linn MJ, Varma MR, Sarkar M, Hawley A, Fowlkes JB, Strieter RM (2001) Interleukin-8 administration enhances venous thrombosis resolution in a rat model. J Surg Res 99(1):84–91
Meier TR, Myers DD Jr, Wrobleski SK, Zajkowski PJ, Hawley AE, Bedard PW, Ballard NE, Londy FJ, Kaila N, Vlasuk GP et al (2008) Prophylactic P-selectin inhibition with PSI-421 promotes resolution of venous thrombosis without anticoagulation. Thromb Haemost 99(2):343–351
Ramacciotti E, Blackburn S, Hawley AE, Vandy F, Ballard-Lipka N, Stabler C, Baker N, Guire KE, Rectenwald JE, Henke PK et al (2011) Evaluation of soluble p-selectin as a marker for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 17(4):425–431
Roumen-Klappe EM, den Heijer M, van Uum SH, van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, van der Graaf F, Wollersheim H (2002) Inflammatory response in the acute phase of deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg 35(4):701–706
Roumen-Klappe EM, Janssen MC, Van Rossum J, Holewijn S, Van Bokhoven MM, Kaasjager K, Wollersheim H, Den Heijer M (2009) Inflammation in deep vein thrombosis and the development of post-thrombotic syndrome: a prospective study. J Thromb Haemost 7(4):582–587
Tsai AW, Cushman M, Rosamond WD, Heckbert SR, Tracy RP, Aleksic N, Folsom AR (2002) Coagulation factors, inflammation markers, and venous thromboembolism: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology (LITE). Am J Med 113(8):636–642
van Aken BE, den Heijer M, Bos GM, van Deventer SJ, Reitsma PH (2000) Recurrent venous thrombosis and markers of inflammation. Thromb Haemost 83(4):536–539
van Aken BE, Reitsma PH, Rosendaal FR (2002) Interleukin 8 and venous thrombosis: evidence for a role of inflammation in thrombosis. Br J Haematol 116(1):173–177
Vormittag R, Hsieh K, Kaider A, Minar E, Bialonczyk C, Hirschl M, Mannhalter C, Pabinger I (2006) Interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism (-174) G > C in patients with spontaneous venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 95(5):802–806
Vormittag R, Vukovich T, Schonauer V, Lehr S, Minar E, Bialonczyk C, Hirschl M, Pabinger I (2005) Basal high-sensitivity-C-reactive protein levels in patients with spontaneous venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 93(3):488–493
Wakefield TW, Greenfield LJ, Rolfe MW, DeLucia A 3rd, Strieter RM, Abrams GD, Kunkel SL, Esmon CT, Wrobleski SK, Kadell AM et al (1993) Inflammatory and procoagulant mediator interactions in an experimental baboon model of venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 69(2):164–172
Wakefield TW, Strieter RM, Downing LJ, Kadell AM, Wilke CA, Burdick MD, Wrobleski SK, Phillips ML, Paulson JC, Anderson DC et al (1996) P-selectin and TNF inhibition reduce venous thrombosis inflammation. J Surg Res 64(1):26–31
Wojcik BM, Wrobleski SK, Hawley AE, Wakefield TW, Myers DD Jr, Diaz JA (2011) Interleukin-6: a potential target for post-thrombotic syndrome. Ann Vasc Surg 25(2):229–239
Rezaie-Majd A, Maca T, Bucek RA, Valent P, Muller MR, Husslein P, Kashanipour A, Minar E, Baghestanian M (2002) Simvastatin reduces expression of cytokines interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22(7):1194–1199
Albert MA, Danielson E, Rifai N, Ridker PM (2001) Effect of statin therapy on C-reactive protein levels: the pravastatin inflammation/CRP evaluation (PRINCE): a randomized trial and cohort study. JAMA 286(1):64–70
Arnaud C, Burger F, Steffens S, Veillard NR, Nguyen TH, Trono D, Mach F (2005) Statins reduce interleukin-6-induced C-reactive protein in human hepatocytes: new evidence for direct antiinflammatory effects of statins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1231–1236
Di Garbo V, Bono M, Di Raimondo D, De Simone R, Raneli G, Avellone G (2000) Non lipid, dose-dependent effects of pravastatin treatment on hemostatic system and inflammatory response. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56(4):277–284
Jougasaki M, Ichiki T, Takenoshita Y, Setoguchi M (2010) Statins suppress interleukin-6-induced monocyte chemo-attractant protein-1 by inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription pathways in human vascular endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 159(6):1294–1303
Millar JS, Ky B, Wolfe ML, Pruscino L, Baer A, Rader DJ (2010) Short-term treatment with high-dose atorvastatin reduces LDL cholesterol but shows no anti-inflammatory effects in normolipidemic subjects with normal CRP levels. Clin Transl Sci 3(4):140–146
Morikawa S, Takabe W, Mataki C, Kanke T, Itoh T, Wada Y, Izumi A, Saito Y, Hamakubo T, Kodama T (2002) The effect of statins on mRNA levels of genes related to inflammation, coagulation, and vascular constriction in HUVEC. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Atheroscler Thromb 9(4):178–183
Doggen CJ, Lemaitre RN, Smith NL, Heckbert SR, Psaty BM (2004) HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of venous thrombosis among postmenopausal women. J Thromb Haemost 2(5):700–701
Khemasuwan D, Divietro ML, Tangdhanakanond K, Pomerantz SC, Eiger G (2010) Statins decrease the occurrence of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Am J Med 123(1):60–65
Lacut K, Oger E, Le Gal G, Couturaud F, Louis S, Leroyer C, Mottier D (2004) Statins but not fibrates are associated with a reduced risk of venous thromboembolism: a hospital-based case-control study. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 18(4):477–482
Momi S, Impagnatiello F, Guzzetta M, Caracchini R, Guglielmini G, Olivieri R, Monopoli A, Gresele P (2007) NCX 6560, a nitric oxide-releasing derivative of atorvastatin, inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis and shows anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties. Eur J Pharmacol 570(1–3):115–124
Ramcharan AS, Van Stralen KJ, Snoep JD, Mantel-Teeuwisse AK, Rosendaal FR, Doggen CJ (2009) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, other lipid-lowering medication, antiplatelet therapy, and the risk of venous thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 7(4):514–520
Ray JG, Mamdani M, Tsuyuki RT, Anderson DR, Yeo EL, Laupacis A (2001) Use of statins and the subsequent development of deep vein thrombosis. Arch Intern Med 161(11):1405–1410
Acknowledgments
This work supported in part by NIH 1PO1HL089407. The authors also would like to acknowledge and extend their gratitude to the Michigan Institute for Clinical & Health Research (MCRiT) program, all the members of the Jobst Vascular Surgery Laboratory at the University of Michigan for their time, training, encouragement and continued support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, A.L., Wojcik, B.M., Wrobleski, S.K. et al. Statins, inflammation and deep vein thrombosis: a systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis 33, 371–382 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0687-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0687-9