Abstract
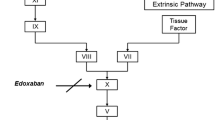
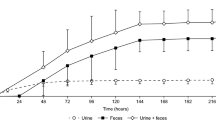
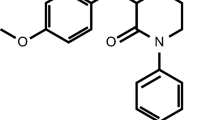
Apixaban has similar affinity for human and rabbit factor Xa (FXa). Rabbits are commonly used in development of thrombosis disease models; however, unlike in other species, apixaban demonstrated poor oral bioavailability (F = 3%) and a high clearance rate (2.55 l/h/kg) in rabbits. Oxidative metabolism of [14C] apixaban by liver microsomes was approximately 20 times faster in rabbits than in rats or humans. Following an intravenous (IV) dose of 5 mg/kg, circulating levels of [14C] apixaban decreased from the earliest sampling time (5 min) to undetectable at 4 h. After an oral dose of 30 mg/kg, levels of [14C] apixaban were only detected at 1 and 4 h. Radioactivity profiling showed that apixaban was a significant component in plasma only after IV administration; O-demethyl apixaban (M2), O-demethyl apixaban glucuronide (M14) and O-demethyl apixaban sulfate (M1) were prominent metabolites after both IV and oral administration. Studies of apixaban in rabbits showed a good correlation between apixaban concentrations and inhibition of FXa activity, prolongation of prothrombin time and modified prothrombin time, with no lag time between these ex vivo pharmacodynamic markers and plasma drug levels. The apixaban concentration required for 50% inhibition (IC50) of FXa activity ex vivo (0.22 ± 0.02 μM) agreed with the IC50 from in vitro experiments in rabbit and human plasma. In summary, apixaban shows similar affinity for human and rabbit FXa. It produces a rapid onset of action, predictable concentration-dependent pharmacodynamic responses, and, unlike rats or humans, a rapid hepatic metabolism in rabbits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weitz JI (2006) Emerging anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 96:274–284
Kimmel SE (2008) Warfarin therapy: in need of improvement after all these years. Expert Opin Pharmacother 9:677–686
Kaiser B (2002) Factor Xa—a promising target for drug development. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:189–192
Samama MM (2002) Synthetic direct and indirect factor Xa inhibitors. Thromb Res 106:V267–V273
Walenga JM, Hoppensteadt DA (2004) Monitoring the new antithrombotic drugs. Semin Thromb Hemost 30:683–695
Mann K, Brummel K, Butenas S (2003) What is all that thrombin for? J Thromb Haemost 1:1504–1514
Pinto DJ, Orwat MJ, Koch S, Rossi KA, Alexander RS, Smallwood A, Wong PC, Rendina AR, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, He K, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PY (2007) Discovery of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J Med Chem 50:5339–5356
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PY, Pinto DJ, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM (2008) Apixaban, an oral, direct and highly selective factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro, antithrombotic and antihemostatic studies. J Thromb Haemost 6:820–829
Frost C, Yu Z, Moore K, Nepal S, Barrett Y, Mosqueda-Garcia R, Shenker A (2007) Apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor: multiple-dose safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in healthy subjects. J Thromb Haemost 5(Suppl 2):P-M-664
Frost C, Yu Z, Nepal S, Mosqueda-Garcia R, Shenker A (2007) Apixaban, an oral direct, factor Xa inhibitor: single-dose safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy subjects. J Thromb Haemost 5(Suppl 2):P-M-665
Wong PC, Watson CA, Crain EJ (2008) Arterial antithrombotic and bleeding time effects of apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, in combination with antiplatelet therapy in rabbits. J Thromb Haemost 6:1736–1741
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Watson CA, Xin B (2009) Favorable therapeutic index of the direct factor Xa inhibitors, apixaban and rivaroxaban, compared to the thrombin inhibitor dabigatran in rabbits. J Thromb Haemost 7:1313–1320
Lassen MR, Davidson BL, Gallus A, Pineo G, Ansell J, Deitchman D (2007) The efficacy and safety of apixaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, as thromboprophylaxis in patients following total knee replacement. J Thromb Haemost 5:2368–2375
Botticelli Investigators, Writing Committee, Büller H, Deitchman D, Prins M, Segers A (2008) Efficacy and safety of the oral direct factor Xa inhibitor apixaban for symptomatic deep vein thrombosis. The Botticelli DVT dose-ranging study. J Thromb Haemost 6:1313–1318
APPRAISE Steering Committee and Investigators, Alexander JH, Becker RC, Bhatt DL, Cools F, Crea F, Dellborg M, Fox KA, Goodman SG, Harrington RA, Huber K, Husted S, Lewis BS, Lopez-Sendon J, Mohan P, Montalescot G, Ruda M, Ruzyllo W, Verheugt F, Wallentin L (2009) Apixaban, an oral, direct, selective factor Xa inhibitor, in combination with antiplatelet therapy after acute coronary syndrome: results of the Apixaban for Prevention of Acute Ischemic and Safety Events (APPRAISE) trial. Circulation 119:2877–2885
Lassen MR, Gallus AS, Pineo GF, Raskob GE (2009) Late breaking clinical trial: the ADVANCE-2 study: a randomized double-blind trial comparing apixaban with enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee replacement. J Thromb Haemost 7(Suppl 2); Abstract LB-MO-005
Lassen MR, Raskob GE, Gallus AS, Pineo GF, Chen D, Portman RJ (2009) Apixaban or enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after knee replacement. N Engl J Med 361:594–604
Lin JH, Cocchetto DM, Duggan DE (1987) Protein binding as a primary determinant of the clinical pharmacokinetic properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 12:402–432
Raghavan N, Frost CE, Yu Z, He K, Zhang H, Humphreys WG, Pinto D, Chen S, Bonacorsi S, Wong PC, Zhang D (2009) Apixaban metabolism and pharmacokinetics after oral administration to humans. Drug Metab Dispos 37:74–81
Zhang D, He K, Raghavan N, Wang L, Mitroka J, Maxwell B, Knabb RM, Frost C, Schuster A, Hao F, Gu Z, Humphreys WG, Grossman SJ (2009) Comparative metabolism of C-14-labeled apixaban in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, and humans. Drug Metab Dispos 37:1738–1748
Davies B, Morris T (1993) Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharma Res 10:1093–1095
He K, He B, Grace JE Jr, Zhang D, Pinto DJ, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, Lam PY, Wexler RR, Humphreys WG, Shyu WC, Grossman SJ (2006) Preclinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of apixaban, a potent and selective factor Xa inhibitor. Blood 108:273a; Abs 910
Walenga JM, Bara L, Petitou M, Samama M, Fareed J, Choay J (1988) The inhibition of the generation of thrombin and the antithrombotic effect of a pentasaccharide with sole anti-factor Xa activity. Thromb Res 51:23–33
Paccaly A, Frick A, Ozoux ML, Chu V, Rosenburg R, Hinder M, Shukla U, Jensen BK (2006) Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationships for otamixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 46:45–51
Turpie AG (2004) Fondaparinux: a Factor Xa inhibitor for antithrombotic therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5:1373–1384
Wang Z, Robinson D, Shenker A, Barrett Y (2008) Anti-Xa is better suited than PT ratio or INR for monitoring of factor Xa inhibitors. Can J Clin Pharmacol 15:e450
Wang L, Raghavan N, He K, Luettgen J, Humphreys WG, Knabb RM, Pinto DJ, Zhang D (2009) Sulfation of O-demethyl apixaban: enzyme identification and species comparison. Drug Metab Dispos 37:802–808
Wong PC, Pinto DJ, Knabb RM (2002) Nonpeptide factor Xa inhibitors: DPC423, a highly potent and orally bioavailable pyrazole antithrombotic agent. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 20:137–152
Hara T, Yokoyama A, Morishima Y, Kunitada S (1995) Species differences in anticoagulant and anti-Xa activity of DX-9065a, a highly selective factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Res 80:99–104
Acknowledgments
Editorial support was provided by Leigh Prevost, BSc, of PAREXEL. This work was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer Inc.
Conflict of interest
The authors are employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., He, K., Raghavan, N. et al. Metabolism, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the factor Xa inhibitor apixaban in rabbits. J Thromb Thrombolysis 29, 70–80 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0401-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0401-8