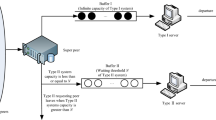
Abstract
In this paper, we consider the problem of admission control in a distributed service system. For the distributed structure of the system, service requests are assigned for service according to the node selection strategy. However, the admitted requests may be dropped since the service capacity of each service node in the system is limited. The desired admission control (AC) policy is to maximize the system performance while keep the dropping probability of the admitted requests below a certain threshold. The event-based optimization framework is applied to formulate the AC process. With the event-based policy, controllers at each service node make decisions only at the epoch when an event of request arrival occurs. The optimization of AC is thus modeled as a probabilistic constrained problem. We present the concept of risk-event to describe the event which happens may lead to dropping of the admitted request, and define the risk of system to denote the probability of a request been dropped. Using the Lagrangian approach, the original problem is converted to an unconstrained problem. Then, by applying the sensitivity analysis method, we derive the performance gradient formula with respect to the policy parameter based on event. Finally, numerical experiments are designed to verify the efficiency of the proposed method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia, Z., Hao, W., Yen, I., & Li, P. (2005). Architecture of portable electronic medical records system integrated with streaming media. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 16(12), 1143–1153.
Huang, Y., Fu, T. Z. J., Chiu, D. M., Lui, J. C. S., & Huang, C. (2008). Challenges, design and analysis of a large-scale P2P-VoD system. In Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM on data communication (pp. 375–388). New York: ACM.
Zhou, Y. P., Chiu, D. M., & Lui, J. C. S. (2011). A simple model for chunk scheduling strategies in P2P streaming. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 19(1), 42–54.
Chen, W., & Shih, C. (2012). Architecture of portable electronic medical records system integrated with streaming media. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(1), 25–31.
Zhang, F., Sun, W., & Huo, Y. (2012). P2P streaming media technology in the remote education system. Advanced Materials Research, 433, 4893–4897.
Wu, S., Wong, K. Y., & Li, B. (2002). A dynamic call admission policy with precision QoS guarantee using stochastic control for mobile wireless networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Network, 10, 257–271.
Li, T., Iraqi, Y., & Boutaba, R. (2004). Pricing and admission control for QoS-enabled Internet. Computer Network, 46, 87–110.
Abundo, M., Cardellini, V., & Presti, F. L. (2012). Admission control policies for a multi-class QoS-aware service oriented architecture. ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, 39(4), 89–98.
Zimmerman, R., & Fu, K. (2003). Comprehensive statistical admission control for streaming media servers. In Proceedings of ACM international conference on multimedia (pp. 75–85). New York: ACM.
Altman, E., Jimenez, T., & Koole, G. (2001). On optimal call admission control in a resource-sharing system. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 49(9), 1659–1668.
Xia, L., Jia, Q., & Cao, X. (2014). A tutorial on event-based optimization-a new optimization framework. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems: Theory and Applications, 24(2), 103–132.
Thng, I. L., & Luo, X. (2004). A robust M/M/1/k scheme for providing hand off dropping QoS in multi-service mobile networks. Wireless Networks, 10(3), 301–309.
Zhi, Y., Zhu, Z., Ma, X., & Wang, B. (2006). Client-class based admission control for distributed video-on-demand system. In Proceedings of IET international conference on wireless, mobile and multimedia networks, IEEE, Hangzhou (pp. 1–4).
Ni, J., Tstang, D. H. K., Tatikonda, S., & Bensaou, B. (2007). Optimal and structured call admission control policies for resource-sharing systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 55(1), 158–170.
Lin, F., Yin, B., Huang, J., & Wu, X. (2012). Admission control with elastic QoS for video on demand systems. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 9(5), 467–473.
Mundur, P., Sood, A. K., & Simon, R. (2005). Class-based access control for distributed video-on-demand systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 15(7), 844–853.
Yin, B., Lu, S., & Guo, D. (2011). Analysis of admission control in P2p-based media delivery network based on POMDP. International Journal of Innovative Computing Information and Control, 7(7B), 4411–4422.
Lu, X., Yin, B., Zhang, H., & Ling, Q. (2012). Admission control scheme for distributed service systems based on model and prediction. In Proceedings of Chinese control conference, IEEE, Hefei (pp. 5518–5523).
Lu, X., Yin, B., & Zhang, H. (2014). Switching-POMDP based admission control policies for service systems with distributed architecture. In Proceedings of international conference on networking, sensing and control, IEEE, Miami (pp. 209–214).
Lu, X., Yin, B., & Zhang, H. (2014). A reinforcement-learning approach for admission control in distributed network service systems. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization. doi:10.1007/s10878-014-9820-3.
Cao, X. (2005). Basic ideas for event-based optimization of Markov systems. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems: Theory and Applications, 15, 169–197.
Cao, X. (2007). Stochastic learning and optimization a sensitivity-based approach. New York: Springer.
Jia, Q. (2011). On solving event-based optimization with average reward over infinite stages. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56, 2912–2917.
Jia, Q. (2012). Event-based optimization with lagged state information. In Proceedings of Chinese control conference, IEEE, Hefei (pp. 2055–2060).
Xia, L. (2014). Event-based optimization of admission control in open queueing networks. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems: Theory and Applications, 24(2), 133–151.
Puterman, M. L. (1994). Markov decision processes: Discrete stochastic dynamic programming. New York: Wiley.
Geibel, P., & Wysotzki, F. (2005). Risk-sensitive reinforcement learning applied to control under constraints. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 24, 81–108.
Cao, X., & Zhang, J. (2008). Event-based optimization of Markov systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 53, 1076–1082.
Baxter, J., & Bartlett, P. L. (2001). Infinite-horizon policy-gradient estimation. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 15, 319–350.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61174124, 61233003, in part by Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant No. 20123402110029 and in part by Natural Science Research Program of the Anhui High Education Bureau of China under Grant No. KJ2012A286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Yin, B., Zhang, X. et al. Event-based optimization for admission control in distributed service system. Telecommun Syst 62, 553–567 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0094-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0094-6