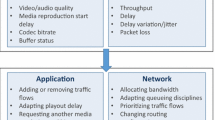
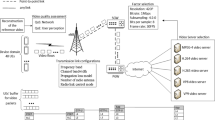
Abstract
User satisfaction is a key factor in the success of novel multimedia services. Yet, to enable service providers and network operators to control and maximize the quality (QoS, QoE) of delivered video streams, quite some challenges remain. In this paper, we particularly focus on three of them. First of all, objectively measuring video quality requires appropriate quality metrics and methods of assessing them in a real-time fashion. Secondly, the recent Scalable Video Coding (SVC) format opens opportunities for adapting video to the available (network) resources, yet the appropriate configuration of video encoding as well as real-time streaming adaptation are largely unaddressed research areas. Thirdly, while bandwidth reservation mechanisms in access/core networks do exist, service providers lack a means for guaranteeing QoS in the increasingly complex home networks (which they are not in full control of). In this paper we offer a broad view on these interrelated issues, by presenting the developments originating in a Flemish research project (including proof-of-concept demonstrations). From a developmental perspective, we propose an architecture combining a real-time video quality monitoring platform, on-the-fly adaptation (optimizing the video quality) and QoS reservation in a heterogeneous home network based on UPnP QoS v3. From a research perspective, we propose a new subjective test procedure that revealed user preference for temporal scalability over quality scalability. In addition, an extensive study on optimizing HD SVC encoding in IPTV scenarios with fluctuating bandwidth showed that under certain bandwidth constraints (prohibiting sufficient fidelity) spatial scalability is a better option than quality scalability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjali, T., Bruni, C., Iacoviello, D., & Scoglio, C. (2006). Dynamic bandwidth reservation for label switched paths: an on-line predictive approach. Computer Communications, 29(16), 3265–3276. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2006.05.004.
Blin, J. L. (2003). SAMVIQ—subjective assessment methodology for video quality (Tech. Rep. EBU BPN 056). EBU Project Group B/VIM (Video In Multimedia).
Chen, J. L., Chen, M. C., & Chian, Y. R. (2007). QoS management in heterogeneous home networks. Computer Networks and ISDN Systems, 51(12), 3368–3379. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2007.01.032.
Cooke, A., Gray, A., Ma, L., Nutt, W., Magowan, J., Oevers, M., Taylor, P., Byrom, R., Field, L., Hicks, S., Leake, J., Soni, M., Wilson, A., Cordenonsi, R., Cornwall, L., Djaoui, A., Fisher, S., Podhorszki, N., Coghlan, B., Kenny, S., & O’callaghan, D. (2003). R-GMA: an information integration system for grid monitoring. In LCNS : Vol. 2888/2003. On the move to meaningful internet systems 2003: CoopIS, DOA, and ODBASE (pp. 462–481). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/b94348.
Coppens, J., Van den Berghe, S., Bos, H., Markatos, E., De Turck, F., Oslebo, A., & Ubik, S. (2003). Scampi: a scalable and programmable architecture for monitoring gigabit networks. In LCNS : Vol. 2839/2003. Management of multimedia networks and services (pp. 475–487). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/b13721.
Domoware (2010). UPnP basedriver. http://sourceforge.net/projects/domoware.
Fang, L., Zhang, R., & Taylor, M. (2008). The evolution of carrier Ethernet services—requirements and deployment case studies. IEEE Communications Magazine, 46(3), 69–76. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2008.4463774.
Hachimi, M. E., Tremblay, B., Kadoch, M., & Bennani, M. (2007). Dynamic bandwidth allocation in SIP based MPLS. In 21st IEEE int. conf. on advanced information networking and applications (AINA’07), Los Alamitos, CA, USA (pp. 917–923). doi:10.1109/AINA.2007.61.
Hall, R. S., & Cervantes, H. (2004). An OSGi implementation and experience report. In Proc. 1st IEEE consumer commun. and networking conf. (CCNC 2004) (pp. 394–399).
Hanemann, A., Boote, J., Boyd, E., Durand, J., Kudarimoti, L., Łapacz, R., Swany, D., Trocha, S., & Zurawski, J. (2005). PerfSONAR: a service oriented architecture for multi-domain network monitoring. In Proc. 3rd int. conf. service-oriented computing (ICSOC 2005), Amsterdam, The Netherlands. doi:10.1007/11596141_19.
Hibler, M., Ricci, R., Stoller, L., Duerig, J., Guruprasad, S., Stack, T., Webb, K., & Lepreau, J. (2008). Large-scale virtualization in the Emulab network testbed. In Proc. USENIX annual technical conference, Boston, MA.
Int. Telecommun. Union (1992). Methodology for subjective assessment of the quality of television pictures. ITU-R Recommendation BT.500-11, Geneva, Switzerland.
Int. Telecommun. Union (1998). Subjective audiovisual quality assessment methods for multimedia applications. ITU-R Recommendation P.911, Geneva, Switzerland.
Int. Telecommun. Union (1999). Subjective video quality assessment methods for multimedia applications. ITU-R Recommendation P.910, Geneva, Switzerland.
Int. Telecommun. Union (2008). Objective perceptual multimedia video quality measurement in the presence of a full reference. ITU-R Recommendation J.247, Geneva, Switzerland.
Int. Telecommun. Union (2008). Perceptual audiovisual quality measurement techniques for multimedia services over digital cable television networks in the presence of a reduced bandwidth reference. ITU-R Recommendation J.246, Geneva, Switzerland.
ITU-T and ISO/IEC JTC 1 (2007). Advanced video coding for generic audiovisual services. ISO/IEC 14496-10 AVC, version 8.
Joint draft ITU-T rec. (2007). H.264/ISO/IEC14496-10/amd.3 scalable video coding. In Joint video team (JVT) of ISO/IEC MPEG & ITU-T VCEG, 24th meeting, Geneva, Switzerland.
Kanumuri, S., Cosman, P., & Reibman, A. R. (2004). A generalized linear model for MPEG-2 packet-loss visibility. In Proc. 14th int. packet video workshop (PV2004), Irvine, CA.
Kanumuri, S., Cosman, P. C., Reibman, A. R., & Vaishampayan, V. A. (2006). Modeling packet-loss visibility in MPEG-2 video. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(2), 341–355. doi:10.1109/TMM.2005.864343.
Lee, H., Moon, S., & Kim, J. W. (2007). Enhanced UPnP QoS architecture for network-adaptive streaming service in home networks. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 53(3), 898–904. doi:10.1109/TCE.2007.4341563.
Mahrenholz, D., & Ivanov, S. (2004). Real-time network emulation with ns-2. In Proc. 8th IEEE int. symp. on distributed simulation and real-time applications (DS-RT 2004) Budapest, Hungary (pp. 29–36). doi:10.1109/DS-RT.2004.34.
Morris, R., Kohler, E., Jannotti, J., & Kaashoek, M. F. (1999). The click modular router. SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev., 33(5), 217–231. doi:10.1145/319344.319166.
MPEG-4 (2005). Applications and requirements for scalable video coding. MPEG-document ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 N6880, Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG), Hong Kong, China. Available on http://www.chiariglione.org/mpeg/working_documents/mpeg-04/svc/requirements.zip.
Newman, H. B., Legrand, I. C., Galvez, P., Voicu, R., & Cirstoiu, C. (2003). MonALISA: a distributed monitoring service architecture. In Proc. conf. computing in high energy and nuclear physics (CHEP03), La Jola, CA.
Presser, A., et al. (2008). UPnP device architecture. http://www.upnp.org/resources/documents.asp.
Reibman, A. R., Kanumuri, S., Vaishampayan, V. A., & Cosman, P. C. (2004). Network monitoring for video quality over IP. In Proc. picture coding symposium (PCS2004). San Francisco, CA.
Reibman, A. R., Kanumuri, S., Vaishampayan, V., & Cosman, P. C. (2004). Visibility of individual packet losses in MPEG-2 video. In Proc. int. conf. on image processing (ICIP ’04) (Vol. 1, pp. 171–174). doi:10.1109/ICIP.2004.1418717.
Reibman, A. R., Vaishampayan, V. A., & Sermadevi, Y. (2004). Quality monitoring of video over a packet network. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 6(2), 327–334. doi:10.1109/TMM.2003.822785.
Ries, M., Nemethova, O., & Rupp, M. (2008). Video quality estimation for mobile H.264/AVC video streaming. Journal on Communications, 3(1), 41–50.
Ritchie, J., & Kühnel, T. (2002). UPnP AV Architecture: 1. http://www.upnp.org/specs/av/default.asp.
Schwarz, H., Marpe, D., & Wiegand, T. (2007). Overview of the Scalable Video Coding extension of the H.264/AVC standard. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 17(9), 1103–1120. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2007.905532.
Seepold, R., Madrid, N. M., & Fernández, J. M. (2007). QoS management for distributed multimedia services. In Proc. 10th IFIP/IEEE int. conf. on management of multimedia and mobile networks and services (MMNS 2007), San Jose, CA. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75869-3_17.
Staelens, N., Moens, S., Van den Broeck, W., Marien, I., Vermeulen, B., Lambert, P., Van de Walle, R., & Demeester, P. (2009). Assessing the perceptual influence of h.264/svc signal-to-noise ratio and temporal scalability on full length movies. In Proc. int. workshop on quality of multimedia experience (QoMEx 2009), San Diego, CA, USA (pp. 29–34). doi:10.1109/QOMEX.2009.5246982.
Staelens, N., Vermeulen, B., Moens, S., Macq, J. F., Lambert, P., Van de Walle, R., & Demeester, P. (2009). Assessing the influence of packet loss and frame freezes on the perceptual quality of full length movies. In Proc. 4th int. workshop on video processing and quality metrics for consumer electronics (VPQM 2009), Scottsdale, AZ, USA.
The Géant2 project (2010). http://www.geant2.net.
UPnP Forum (2010). UPnP QoS. http://www.upnp.org/specs/qos.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2004). Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4), 600–612. doi:10.1109/TIP.2003.819861.
Wien, M., Schwarz, H., & Oelbaum, T. (2007). Performance analysis of svc. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 17(9), 1194–1203. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2007.905530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work presented in this paper was supported by the Flemish government through the Interdisciplinary Institute for Broadband Technology (IBBT), via the Video Q-SAC project. C. Develder is supported by the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO–Vl.) as a postdoctoral fellow.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Develder, C., Lambert, P., Van Lancker, W. et al. Delivering scalable video with QoS to the home. Telecommun Syst 49, 129–148 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9358-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9358-3