Abstract
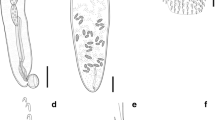
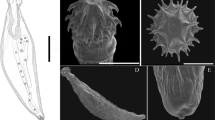
The acanthocephalan Moniliformis saudi Amin, Heckmann, Mohammed, Evans, 2016 was originally described from the desert hedgehog, Paraechinus aethiopicus (Ehrenberg) in central Saudi Arabia. The distribution of P. aethiopicus extends to North Africa and west to Mauritania. Moniliformis saudi was recently found in the Algerian hedgehog Atelerix algirus (Lereboullet) in Malta. The distribution of A. algirus is restricted to the North African and east Iberian Mediterranean coast and associated islands. Both host species cohabit and share the same feeding grounds in northern Algeria where common infections appear to take place. The morphology of specimens from both acanthocephalan populations was similar, with minor variations mostly related to the relatively larger Maltese specimens especially the trunk and the male reproductive system. Taxonomic features like the cone-shaped anterior trunk, size and formula of proboscis and hooks, the receptacle, size and shape of eggs, anatomy of the apical proboscis sensory pores, and the stellate body wall giant nuclei were, however, practically identical. SEM and microscope images of specimens of the Maltese population emphasize their qualitative characteristics such as the degree of the extreme spiral muscle development and the development of the posterior nucleated pouches of the proboscis receptacle. Proboscis hooks of specimens from both the Maltese and the Saudi populations had similarly high levels (percent weights) of calcium, moderate levels of phosphorus, and minimal levels of sulfur, magnesium and sodium marking the diagnostic value of the Energy Dispersive x-ray analysis in species recognition. Newly generated partial sequences of the 18S ribosomal RNA and cytochrome C oxidase subunit 1 (Cox1) of the mitochondrial gene were generated from M. saudi from Malta. Moniliformis saudi from Malta, when compared with other available sequences of the same species isolates available in the GenBank database, formed a strongly supported clade with other congeners. The comparison of the molecular profiles of specimens from populations in Malta, Spain, and Saudi Arabia shows no or low genetic variation between them. Ultimately, we provide a morphological and molecular description of a new population of M. saudi from a new host species in a new geographical location, vastly exceeding the originally described ones from Saudi Arabia. A Cox 1 haplotype network inferred with 10 sequences revealed the presence of eight haplotypes, one of which was shared between the populations of Malta and Spain of M. saudi.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, O.M. (2013). Classification of the Acanthocephala. Folia Parasitologica, 60, 273–305. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.031.
Amin, O.M., Ahmed, M., Chaudhary, A., Heckmann, R.A., Singh, H.S. (2022). The morphological and molecular description of Neoechinorhynchus (Neoechinorhynchus) poonchensis sp. n. from Schizothorax richardsonii (Gray) in Poonch, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Folia Parasitologica, 69, 001. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2022.001.
Amin, O.M., Chaudhary, A., Singh, H.S. (2023). Redescription of Illiosentis cetratus Van Cleave, 1945 (Acanthocephala: Illiosentidae) from Menticirrhus undulatus (Girard) in California, with notes on Illiosentis furcatus from Peru. Folia Parasitologica In press.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A. (2016). Nematodes and cestodes from the desert hedgehog, Paraechinus aethiopicus (Ehrenberg) in central Saudi Arabia, revealed by SEM and microscopy, with notes on histopathology. Scientia Parasitologica, 17, 26-35.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Radwan, N.A., Mantuano, J.S., Alcivar, M.A.Z. (2009). Redescription of Rhadinorhynchus ornatus (Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from skipjack tuna, Katsuwonus pelamis, collected in the Pacific Ocean off South America, with special reference to new morphological features. Journal of Parasitology, 95, 656–664. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1804.1.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Halajian, A., El-Naggar, A.M. (2011). The morphology of an unique population of Corynosoma strumosum (Acanthocephala, Polymorphidae) from the Caspian seal, Pusa caspica, in the land-locked Caspian Sea using SEM, with special notes on histopathology. Acta Parasitologica, 56, 438–445. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-011-0070-6.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Mohamed, O., Evans, R.P. (2016). Morphological and molecular descriptions of Moniliformis saudi sp. n. (Acanthocephala: Moniliformidae) from the desert hedgehog Paraechinus aethiopicus (Ehrenberg) in Saudi Arabia, with a key to species and notes on histopathology. Folia Parasitologica, 63, 014. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2016.014.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Bannai, M. (2018). Cavisoma magnum (Cavisomidae), a unique Pacific acanthocephalan redescribed from an unusual host, Mugil cephalus (Mugilidae), in the Arabian Gulf, with notes on histopathology and metal analysis. Parasite, 25, 5. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2018006.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Sharifdini, M., Albayati, N.Y. (2019). Moniliformis cryptosaudi n. sp. (Acanthocephala: moniliformidae) from the long-eared hedgehog Hemiechinus auritus (Gmelin) (Erinaceidae) in Iraq; a case of incipient cryptic speciation related to M. saudi in Saudi Arabia. Acta Parasitologica, 64, 195-204. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-018-00021-9.
Amin, O.M., Heckmann, R.A., Sharifdini, M., Rubtsova, N., Chine, H.J. (2020). On the Neoechinorhynchus agilis (Acanthocephala: Neoechinorhynchidae) complex, with the description of Neoechinorhynchus ponticus n. sp. from Chelon auratus Risso in the Black Sea. Parasite, 27, 48. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2020044.
Amori, G., Hutterer, R., Kryštufek, B., Yigit, N., Mitsainas, G., Palomo, L. (2021). [amended version of 2008 assessment]. "Atelerix algirus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, e.T27926A197498795. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T27926A197498795.en.
Bandelt, H.J., Forster, P., Röhl, A. (1999). Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036.
Best, T.L. (2018). Family Erinaceidae (Hedgehogs and Gymnures). In D. E. Wilson, R. A. Mittermeier (Eds.), Handbook of the Mammals of the World (pp. 288–331). Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
Byram, J.E., Fisher, F.M., Jr. (1973). The absorptive surface of Moniliformis dubius (Acanthocephala). 1. Fine structure. Tissue & cell, 5, 553–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-8166(73)80045-x.
Chandler, A.C. (1921). Notes on the occurrence of Moniliformis sp. in rats of Texas. Journal of Parasitology, 7, 179-183.
Dai, G. D., Yan, H. B., Li, L., Zhang, L. S., Liu, Z. L., Gao, S. Z., Ohiolei, J. A., Wu, Y. D., Guo, A. M., Fu, B. Q., Jia, W. Z. (2022). Molecular Characterization of a New Moniliformis sp. From a Plateau Zokor (Eospalax fontanierii baileyi) in China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 806882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.806882.
El-Farhati, H., Khaldi, M., Ribas, A., Hizem, M.W., Nouira, S., Nicolas, V. (2021). Evolutionary history of the two North African hedgehogs (Mammalia: Erinaceidae) Atelerix algirus and Paraechinus aethiopicus based on phylogeography and species distribution modeling. Vertebrate Zoology, 71, 799-811. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3897/vz.71.e70989.
Esteban, J.G., Galan-Puchades, M.T., Bargues, M.D., Valero, M.A., Mas-Coma, S. (1987). Sobre la helmintofauna del erizo moruno, Erinaceus (Aethechinus) algirus (Lereboullet, 1842) (Insectivora: Erinaceidae), en el Archipiélago Balear (Islas Gimnésicas y Pitiusas). In V. Sans-Coma, S. Mas-Coma, & J. Gosábez (Eds.), Mammíferos y Helmintos (pp. 163–166). Ketres, Barcelona.
Feliu, C., López, M., Gómez, M. S., Torres, J., Sánchez, S., Miquel, J., Abreu-Acosta, N., Segovia, J. M., Martín-Alonso, A., Montoliu, I., Villa, M., Fernández-Álvarez, A., Bakhoum, A. J., Valladares, B., Orós, J., & Foronda, P. (2012). Parasite fauna of rodents (Murinae) from El Hierro (Canary Islands, Spain): a multidisciplinary approach. Acta Parasitologica, 57(2), 171–178. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-012-0016-7
Folmer, O., Black, M., Hoeh, W., Lutz, R., Vrijenhoek, R. (1994). Primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294 – 299.
García-Varela, M., Pérez-Ponce de León, P. (2015). Advances in the classification of acanthocephalans: evolutionary history and evolution of the parasitism. In S. Morand, B. R. Krasnov, & D. T. J. Littlewood (Eds.), Parasite diversity and diversification: evolutionary ecology meets phylogenetics (pp. 182–201). Cambridge, University Press.
Gomes, A. P. N., Costa, N. A., Gentile, R., Vilela, R. V., Maldonado, A. (2020). Morphological and genetic description of Moniliformis necromysi sp. n. (Archiacanthocephala) from the wild rodent Necromys lasiurus (Cricetidae: Sigmondontinae) in Brazil. Journal of Helminthology, 94, e138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X20000188.
Grassi, B., Calandruccio, S. (1888). Ueber einen Echinorhynchus, welcher auch im Menschen parasitirt und dessen Zwischenwirth ein Blaps ist. Centralbi. Bakt., 3, 521-525
Harrison, D., Bates, P.J. (1991). The Mammals of Arabia, second Edition. Harrison Zoological Museum Publications, Sevenoaks.
Heckmann, R.A. (2006). Energy dispersive x-ray analysis (EDXA) in conjunction with electron optics, a tool for analyzing aquatic animal parasite diseases and deaths, an update. Proceedings of Parasitology, 41, 1–18.
Heckmann, R.A., Amin, O.M., Radwan, N.A.E., Standing, M.D., Eggett, D.L. (2012a). Comparative chemical element analysis using energy dispersive x-ray microanalysis (EDXA) for four species of Acanthocephala. Scientia Parasitologica, 13, 37–27-35.
Heckmann, R.A., Amin, O.M., Radwan, N.A.E., Standing, M.D., Eggett, D.L., El Naggar, A.M. (2012b). Fine structure and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDXA) of the proboscis hooks of Radinorynchus ornatus, Van Cleave 1918 (Rhadinorynchidae: Acanthocephala). Scientia Parasitologica, 13, 37–43.
Heckmann, R.A., Amin, O.M., Standing, M.D. (2007). Chemical analysis of metals in Acanthocephalans using energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDXA, XEDS) in conjunction with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Comparative Parasitology, 74, 388–391.
Heckmann, R.A., Amin, O.M., El Naggar, A.M. (2013). Micropores of Acanthocephala, a scanning electron microscopy study. Scientia Parasitologica, 14, 105–113.
Kaiser, J. E. (1893). Die Acanthocephalen und ihre Entwicklung. Bibloth. Zoology, 7, 1-136.
Khaldi, M., Torres, J., Samso, B., Miquel, J., Biche, M., Benyettou, M., Barech, G., Benelkadi, H.A., Ribas, A. (2012). Endoparasites (helminths and coccidians) in the hedgehogs Atelerix algirus and Paraechinus aethiopicus from Algeria. African Zoology, 47, 48 - 54. https://doi.org/10.1080/15627020.2012.11407522.
Kowalski, K., Rzebik-Kowalska, B. (1991). Mammals of Algeria. Polish Academy of Sciences, Ossolineum Publishing House, Wroclaw, Poland.
Lee R.E. (1992). Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis. Englewood Cliffs, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Lühe, M. (1904-5). Geschichte und Ergebnisse der Echinorhynchen-Forschung bis auf Westrumb (1821). Annals of Zoology, 1, 139-353.
Lühe, M. (1911). Acanthocephalen. Die Slsswasserfauna Deutschlands, Heft l6, Jena.
Lynggaard, C., García-Prieto, L., Guzmán-Cornejo, C., García-Varela, M. (2021). Description of a new species of Moniliformis (Acanthocephala: Moniliformidae) from Peromyscus hylocetes (Rodentia: Cricetidae) in Mexico. Parasitology International, 83, 102315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2021.102315
Meyer A. (1932). Acanthocephala. In Dr. H. G. Bronn’s Klassen und Ordnungen des Tierreichs, vol. 4. pp. 1-332. Leipzig, Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft MBH. DOI https://doi.org/10.2307/3283750.
Milne, I., Lindner, D., Bayer, M., Husmeier, D., Mcguire, G., Marshall, D.F., Wright, F. (2009). TOPALiv2: A rich graphical interface for evolutionary analyses of multiple alignments on HPC clusters and multi-core desktops. Bioinformatics, 25, 126–127. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn575
Mas-Coma, S., Esteban, J.G., Fuentes, M.V., Bargues, M.D., Valero, M.A., Galan-Puchades, M.T. (2000). Helminth parasites of small mammals (insectivores and rodents) on the Pityusic island of Eivissa (Balearic Archipelago). Research and Reviews in Parasitology, 60, 41-49.
Miquel, J., Ribas, A., Pino-Vera, R., Izquierdo-Rodríguez, E., Martín-Carrillo, N., Feliu, C., Foronda, P. (2022). New data on Pterygodermatites (Pterygodermatites) plagiostoma Wedl, 1861 (Nematoda, Rictulariidae) parasite of the Algerian Hedgehog Atelerix algirus Linnaeus, 1758 (Eulipotyphla: Erinaceidae) from the Canary Islands. Animals, 12, https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151991.
Nelson, D.R., Ward, H.L. (1966). Acanthocephala from hedgehogs in Egypt. Journal of Tennessee Academy of Science, 37, 101-105.
Ortega-Olivares, M.P., Velázquez-Urrieta, Y., Sereno-Uribe, A.L., Harvey, M.B., García-Varela, M. (2023). A molecular and ecological study of Macracanthorehynchus ingens (von Linstow, 1879) (Acanthocephala: Archiacanthocephala), in its paratenic and definitive hosts in southeastern Mexico and Eastern USA. Systematic Parasitology, 100, 543-556.
Porta A. 1909. Gli Acantocefali dei Mammiferi. Archivio Zoologico (Naples), 4, 239-285.
Posada, D. (2008). jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 25, 1253–1256. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn083.
Rozas, J., Ferrer-Mata, A., Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C., Guirao-Rico, S., Librado, P., Ramos-Onsins, S.E., Sánchez-Gracia, A. (2017). DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3299–3302. Emphasis>https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx248.
Schmidt, G.D. (1985). Development and life cycles. In D.W.T. Crompton, & B.B. Nickol (Eds.), Biology of the Acanthocephala (pp. 273–305). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Standing, M.D., Heckmann, R.A. (2014). Features of Acanthocephalan hooks using dual beam preparation and XEDS phase maps. Microscopy and Microanalysis Meeting: Hartford, CT. Poster. No. 0383–00501.
Stone, R. D. (1995). "Algerian hedgehog (Atelerix algirus)". In IUCN Insectivore, Tree Shrew and Elephant Shrew Specialist Group (ed.). Eurasian insectivores and tree shrews: status survey and conservation action plan. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. pp. 8–10. ISBN 2-8317-0062-0.
Suzuki, N., Hoshino, K., Murakami, K., Takeyama, H., Chow, S. (2008). Molecular diet analysis of phyllosoma larvae of the Japanese spiny lobster Palinurus japonicus (Decapoda: Crustacea). Marine Biotechnology, 10, 49–55. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-007-9038-9.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38, 3022–3027. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120.
Telford, M. J., Holland, P. W. (1993). The phylogenetic affinities of the chaetognaths: a molecular analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 10, 660–676. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040030.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., Higgins, D.G. (1997). The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876.
Travassos, I. (1917). Contribuições para o conhecimento da fauna helmintolojica brazileira. VI. Revisão dos acantocefalos brazileiros. Parte l. Fam. Gigantorhynchidae Hamann, 1892. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 9, 5-62.
Van Cleave, H.J. (1924). A critical study of the Acanthocephala described and identified by Joseph Leidy. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 76, 279-334.
Van Cleave, H.J. (1953). Acanthocephala of North American mammals. Illinois Biological Monographs 23, 1-179.
Whitfield P.J. (1979). The biology of parasitism: an introduction to the study of associating organisms. University Park Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Wright, R. D., Lumsden, R.D. (1969). Ultrastructure of the tegumentary pore canal system of the acanthocephalan Moniliformis dubius. Journal of Parasitology, 55, 993–1003.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Department of Biology, Brigham Young University (BYU), Provo, Utah, and by an Institutional Grant from the Parasitology Center, Inc. (PCI), Scottsdale, Arizona. The valuable support provided by Dr. Richard Gill, Chair, Biology Department and Dr. Michael Whiting, Bean Life Science Museum of BYU is gratefully appreciated. The EDXA and SEM methodologies used in this project have been pioneered by Dr. Richard A. Heckmann (deceased) (BYU) to whom we shall always dedicate our highest gratitude. We are grateful to the Electron Optics Laboratory (BYU) for technical help and expertise, especially noting Michael Standing. The authors thank the Department of Zoology, Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut, India for providing laboratory facilities. Last but not least, we would like to extend our grateful appreciation for Dr. Nataliya Rubtsova at the Scottsdale Parasitology Center for her expertise in the production of the map and the final light microscope images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.A.: Did the research and wrote wrote the manuscript except the molecular part A.C.: Did the molecular work S.F. :Did the SEM and EDXA work A.L.: Collected the specimens H.S.: provided the molecular laboratory facilities
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare conflicts of interest none.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that they have observed all applicable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, O.M., Chaudhary, A., Farrer, S. et al. The discovery of Moniliformis saudi (Acanthocephala: Moniliformidae) in the Algerian hedgehog Atelerix algirus in Malta: morphological, molecular, and metal analyses. Syst Parasitol 101, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10128-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10128-x