Abstract
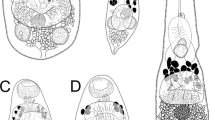
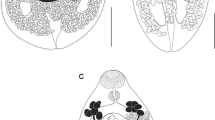
Three new species of the family Bucephalidae Poche, 1907 (Trematoda: Digenea) are described from the yellowtail pike, Sphyraena obtusata Cuvier (Sphyraenidae), from Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. The three species are morphologically consistent with the present broad concept of the genus Bucephalus Baer, 1827, but significant phylogenetic and ecological differences relative to the type-species of Bucephalus require the proposal of a new genus. Aenigmatrema n. g. is proposed for A. undecimtentaculatum n. sp. (type-species), A. inopinatum n. sp. and A. grandiovum n. sp. In addition, based on morphological, ecological and biogeographical similarities, we recombine two existing species of Bucephalus as Aenigmatrema kaku (Yamaguti, 1970) n. comb. and Aenigmatrema sphyraenae (Yamaguti, 1952) n. comb. Although the three species described in this study are extremely morphologically similar, they can be differentiated from each other, and from A. kaku and A. sphyraenae, morphometrically on the basis of egg size, tentacle number and a combination of the caecum and vitelline field lengths. Complete ITS2 rDNA, partial 28S rDNA and partial cox1 mtDNA sequence data were generated for the three new species, which formed a well-supported clade in all 28S phylogenetic analyses. An expanded phylogenetic tree for the subfamily Bucephalinae Poche, 1907 is presented, demonstrating unresolved issues with the morphology-based taxonomy of the subfamily. The three largest genera, Bucephalus, Rhipidocotyle Diesing, 1858 and Prosorhynchoides Dollfus, 1929 remain extensively polyphyletic, indicating the need for significant further systematic revision.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankenbrand, M. J., Keller, A., Wolf, M., Schultz, J., & Förster, F. (2015). ITS2 Database V: Twice as much. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 3030–3032.
Baba, T., Nakamura, D., Hosoi, M., & Urabe, M. (2012). Molecular identification of larval bucephalids, Prosorhynchoides ozakii and Parabucephalopsis parasiluri, infecting the golden mussel, Limnoperna fortune, by PCR-RFLP. Journal of Parasitology, 98, 669–673.
Blasco-Costa, I., Cutmore, S. C., Miller, T. L., & Nolan, M. J. (2016). Molecular approaches to trematode systematics: ‘best practice’ and implications for future study. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 295–306.
Bott, N. J., Miller, T. L., & Cribb, T. H. (2013). Bucephalidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea) of Plectropomus (Serranidae: Epinephelinae) in the tropical Pacific. Parasitology Research, 112, 2561–2584.
Bray, R. A., Cribb, T. H., & Cutmore, S. C. (2018). Lepocreadiidae Odhner, 1905 and Aephnidiogenidae Yamaguti, 1934 (Digenea: Lepocreadioidea) of fishes from Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia, with the erection of a new family and genus. Systematic Parasitology, 95, 479–498.
Bray, R. A., & Justine, J.-L. (2011). Bucephaline digeneans (Bucephalidae) in Sphyraena putnamae Jordan & Seale (Sphyraenidae) from the lagoon off New Caledonia. Systematic Parasitology, 79, 123–138.
Cribb, T. H., Anderson, G. R., Adlard, R. D., & Bray, R. A. (1998). A DNA-based demonstration of a three-host life-cycle for the Bivesiculidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea). International Journal for Parasitology, 28, 1791–1795.
Cribb, T. H., & Bray, R. A. (2010). Gut wash, body soak, blender and heat-fixation: approaches to the effective collection, fixation and preservation of trematodes of fishes. Systematic Parasitology, 76, 1–7.
Cribb, T. H., Bray, R. A., Diaz, P. E., Huston, D. C., Kudlai, O., Martin, S. B., et al. (2016). Trematodes of fishes of the Indo-west Pacific: told and untold richness. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 237–247.
Cutmore, S. C., Diggles, B. K., & Cribb, T. H. (2016). Transversotrema Witenberg, 1944 (Trematoda: Transversotrematidae) from inshore fishes of Australia: description of a new species and significant range extensions for three congeners. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 639–652.
Cutmore, S. C., Nolan, M. J., & Cribb, T. H. (2018). Heterobucephalopsine and prosorhynchine trematodes (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from teleost fishes of Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia, with the description of two new species. Systematic Parasitology, 95, 783–806.
Darriba, D., Taboada, G. L., Doallo, R., & Posada, D. (2012). jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772.
Dyer, W. G., Williams, E. H., & Williams, L. B. (1988). Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes of Okinawa, Japan. Journal of Parasitology, 74, 638–645.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792–1797.
Gupta, P. C., & Gupta, V. C. (1986). Two species of the genus Prosorhynchus Odhner, 1905 (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from marine fishes, of Puri Coast, Orissa. Indian Journal of Helminthology, 38, 112–118.
Hammond, M. D., Cribb, T. H., & Bott, N. J. (2018). Three new species of Prosorhynchoides (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from Tylosurus gavialoides (Belonidae) in Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Parasitology International, 67, 454–464.
Hammond, M. D., Cribb, T. H., Nolan, M. J., & Bott, N. J. (2020). Two new species of Prosorhynchoides (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from Tylosurus crocodilus (Belonidae) from the Great Barrier Reef and French Polynesia. Parasitology International, 75, 102005.
Horton, T., Kroh, A., Ahyong, S., Bailly, N., Boyko, C. B., Brandao, S. N., et al. (2020). World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org at VLIZ. Accessed on 15 May 2019.
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., et al. (2012). Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28, 1647–1649.
Keller, A., Schleicher, T., Schultz, J., Müller, T., Dandekar, T., & Wolf, M. (2009). 5.8S-28S rRNA interaction and HMM-based ITS2 annotation. Gene, 430, 50–57.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., & Tamura, K. (2018). MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 6, 1547–1549.
Littlewood, D. T. J. (1994). Molecular phylogenetics of cupped oysters based on partial 28S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 3, 221–229.
Littlewood, D. T. J., Curini-Galletti, M., & Herniou, E. A. (2000). The interrelationships of Proseriata (Platyhelminthes: Seriata) tested with molecules and morphology. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 16, 449–466.
Littlewood, D. T. J., Rohde, K., & Clough, K. A. (1997). Parasite speciation within or between host species? Phylogenetic evidence from site-specific polystome monogeneans. Parasitology, 27, 1289–1297.
Madhavi, R. (1974). Digenetic trematodes from marine fishes of Waltair Coast, Bay of Bengal. Family Bucephalidae. Rivista di Parassitologia, 35, 189–199.
Manter, H. W. (1940). Digenetic trematodes of fishes from the Galapagos Islands and the neighboring Pacific. Allan Hancock Pacific Expeditions, 2, 325–497.
Martin, S. B., Huston, D. C., Cutmore, S. C., & Cribb, T. H. (2018). A new classification for deep-sea opecoelid trematodes based on the phylogenetic position of some unusual taxa from shallow-water, herbivorous fishes off south-west Australia. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 186, 385–413.
Miller, T. L., Cutmore, S. C., & Cribb, T. H. (2018). Two species of Neometadena Hafeezullah & Siddiqi, 1970 (Digenea: Cryptogonimidae) from Moreton Bay, Australia, including the description of Neometadena paucispina n. sp. from Australian Lutjanidae. Systematic Parasitology, 95, 655–664.
Miller, M. A., Pfeiler, E., & Schwartz, T. (2010). Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), 14 Nov. 2010, New Orleans, LA, pp. 1–8.
Morgan, J. A. T., & Blair, D. (1995). Nuclear rDNA ITS sequence variation in the trematode genus Echinostoma: an aid to establishing relationships within the 37-collar-spine group. Parasitology, 111, 609–615.
Nagaty, H. F. (1937). Trematodes of the Red Sea Part I. Studies on the family Bucephalidae Poche, 1907. Cairo: Egyptian University.
Nahhas, F., Sey, O., & Nakahara, G. (2006). Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes from the Arabian Gulf off the coast of Kuwait. Family Bucephalidae Poche, 1907, and the description of a new species. Helminthologia, 43, 147–157.
Nolan, M. J., & Cribb, T. H. (2005). The use and implications of ribosomal DNA sequencing for the discrimination of digenean species. Advances in Parasitology, 60, 101–163.
Nolan, M. J., Curran, S. S., Miller, T. L., Cutmore, S. C., Cantacessi, C., & Cribb, T. H. (2015). Dollfustrema durum n. sp. and Heterobucephalopsis perardua n. sp. (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from the giant moray eel, Gymnothorax javanicus (Bleeker) (Anguilliformes: Muraenidae), and proposal of the Heterobucephalopsinae n. subfam. Parasitology International, 64, 559–570.
Olson, P. D., Cribb, T. H., Tkach, V. V., Bray, R. A., & Littlewood, D. T. J. (2003). Phylogeny and classification of the Digenea (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda). International Journal for Parasitology, 33, 733–755.
Overstreet, R. M., & Curran, S. S. (2002). Superfamily Bucephaloidea Poche, 1907. In: Bray, R. A., Gibson, D. I. & Jones, A. (Eds) Keys to the Trematoda, Volume 1 (pp. 67–110). Wallingford: CAB International.
Parukhin, A. M. (1970). Study of the trematode fauna of fish in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. Biologiya Morya, 20, 187–213 (In Russian).
Parukhin, A. M. (1976). Parasitic worms of benthic fishes of the southern seas. Kiev: Naukova Dumka (In Russian).
Petkevičiūtė, R., Stunžėnas, V., & Stanevičiūtė, G. (2014). Differentiation of European freshwater bucephalids (Digenea: Bucephalidae) based on karyotypes and DNA sequences. Systematic Parasitology, 87, 199–212.
Pleijel, F., Jondelius, U., Norlinder, E., Nygren, A., Oxelman, B., Schander, C., et al. (2008). Phylogenetics without roots? A plea for the use of vouchers in molecular phylogenetics. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 369–371.
R Core Development Team. (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing,. URL https://www.R-project.org/.
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D. L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., et al. (2012). MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542.
Snyder, S. D., & Tkach, V. V. (2001). Phylogenetic and biogeographical relationships among some Holarctic frog lung flukes (Digenea: Haematoloechidae). Journal of Parasitology, 87, 1433–1440.
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RAxML Version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313.
Stunžėnas, V., Cryan, J. R., & Molloy, D. P. (2004). Comparison of rDNA sequences from colchicine treated and untreated sporocysts of Phyllodistomum folium and Bucephalus polymorphus (Digenea). Parasitology International, 53, 223–228.
Toman, G. (1989). Digenetic trematodes of marine teleost fishes from the Seychelles. Indian Ocean. II. Acta Parasitologica Polonica, 34, 235–246.
Venables, W. N., & Ripley, B. D. (2002). Modern Applied Statistics with S (4th ed.). New York: Springer.
Wee, N. Q.-X., Cribb, T. H., Bray, R. A., & Cutmore, S. C. (2017). Two known and one new species of Proctoeces from Australian teleosts: variable host-specificity for closely related species identified through multi-locus molecular data. Parasitology International, 66, 16–26.
Yamaguti, S. (1934). Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 2, Trematodes of fishes. I. Japanese Journal of Zoology, 5, 249–541.
Yamaguti, S. (1970). Digenetic Trematodes of Hawaiian Fishes. Tokyo: Keigaku Publishing Co.
Zaidi, D. A., & Khan, D. (1997). Digenetic trematodes of fishes from Pakistan. Bulletin of the Department of Zoology of the Panjab (New Series), 9, 1–56.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr John Page, Mr Dave Thompson, Mr Nicholas Wee (The University of Queensland) and Ms Clarisse Louvard (The University of Queensland) for their assistance in the collection of fishes in Moreton Bay, Dr Rodney Bray (The Natural History Museum) for providing a visual key for species of Bucephalus, Dr David Gibson (The Natural History Museum) for providing advice on taxonomic nomenclature, Dr Simone Blomberg (The University of Queensland) for her extremely helpful statistical advice and the staff at the Moreton Bay Research Station for their support of our work.
Funding
THC and SCC acknowledge the Australian Biological Resources Study (ABRS) for their ongoing support. This study was funded by the ABRS National Taxonomy Research Grant RF215-40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E6CAD3E0-0036-40BD-B319-74B3BBF029C1. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corner, R.D., Cribb, T.H. & Cutmore, S.C. A new genus of Bucephalidae Poche, 1907 (Trematoda: Digenea) for three new species infecting the yellowtail pike, Sphyraena obtusata Cuvier (Sphyraenidae), from Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Syst Parasitol 97, 455–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09931-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09931-7