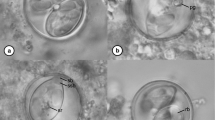
Abstract
While nine nominal species of Eimeria Schneider, 1875 have been described from strigiform birds, molecular sequence data are not available for any of these species. In the present study, oöcysts of a coccidian were isolated by faecal flotation from the lower intestinal contents of an opportunistically collected, recently deceased great horned owl Bubo virginianus (Gmelin), sporulated in potassium dichromate, and subjected to morphological and molecular characterisation. Comparisons of morphological data with previous accounts of Eimeria spp. from owls were consistent with Eimeria megabubonis Upton, Campbell, Weigel & McKown, 1990. Novel molecular data for the 18S ribosomal RNA gene region and the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene are provided. The results of phylogenetic analysis based on concatenated sequence data from these regions are presented and implications for the evolutionary history of Eimeria are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altekar, G., Dwarkadas, S., Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2004). Parallel Metropolis coupled Markov chain Monte Carlo for Bayesian phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics, 20, 407–415.
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403–410.
Averbeck, G. A., Cooney, J. D., Guarnera, T. R., Redig, P., & Stromberg, B. E. (1998). Exogenous stages of Eimeria bemricki n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the great grey owl, Strix nebulosa (Foster). Journal of Parasitology, 84, 976–977.
Baker, D. G., Morishita, T. Y., Bartlett, J. L., & Brooks, D. L. (1996). Corpologic survey of internal parasites of northern California raptors. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, 27, 358–363.
Cawthorn, R. J., & Stockdale, P. H. G. (1981). Description of Eimeria bubonis sp. n. (Protozoa: Eimeriidae) and Caryospora bubonis sp. n. (Protozoa: Eimeriidae) in the great horned owl, Bubo virginianus (Gmelin), of Saskatchewan. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 59, 170–173.
Cawthorn, R. J., Gajadhar, A. A., & Brooks, R. J. (1984). Description of Sarcocystis rauschorum sp. n. (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) with experimental transmission between varying lemmings (Dicrostonyx richardsoni) and snowy owls (Nyctea scandiaca). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 62, 217–225.
Chauhan, M. P. S., & Jain, S. P. (1979). A new coccidium, Eimeria atheni from a spotted owlet, Athene brama (Temmink). Rivista di Parassitologia, 15, 167–169.
Carini, A. (1939). Sobre uma Eimeria da coruja do campo. Arqivos de Biologia (São Paulo), 23, 84–85.
Crespo-Ginés, R., López, D. S., Berriatua, E., Blanco, G., Candela, M. G., & Pérez-García, J. M. (2019). Coccidian prevalence and intensity in free-ranging and rehabilitating wild raptors. Ardeola, 66, 3–14.
da Silva, A. S., Zanette, R. A., Lara, V. M., Gressler, L. T., Carregaro, A. B., Santurio, J. M., & Monteiro, S. G. (2009). Gastrointestinal parasites of owls (Strigiformes) kept in captivity in the Southern region of Brazil. Parasitology Research, 104, 485–487.
Duszynski, D. W. (1971). Increase in size of Eimeria separata oocysts during patency. Journal of Parasitology, 57, 948–952.
Duszynski, D. W. (2011). Eimeria. eLS. New York: Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0001962.pub2.
Duszynski, D. W., Couch, L., & Upton, S. J. (2000). The coccidia of Strigiformes (owls). Accessed 1 January, 2019, from http://biology.unm.edu/coccidia/owls.html.
Eberhard, M. L., da Silva, A. J., Lilley, B. G., & Pieniazek, N. J. (1999). Morphologic and molecular characterization of a new Cyclospora species from Ethiopian monkeys: C. cercopitheci sp. n., and C. papionis sp. n. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 5, 651–658.
Forrester, D. J., & Spalding, M. G. (2003). Owls. In: Forrester, D. J. (Ed.), Parasites and diseases of wild birds in Florida. Florida, USA: University Press of Florida, pp. 835–873.
Globokar, M., Fischer, D., & Pantchev, N. (2017). Occurance of endoparasites in captive birds between 2005 to 2011 as determined by faecal flotation and review of literature. Berliner und Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift. https://doi.org/10.2376/005-9366-16094.
Gottschalk, C. (1972). Beitrag zur Faunistik der Vogelkokzidien Thüringens und Sachsens. Betrage zür Vogelkunde, 18, 61–69.
Huber, E. (1964). Die Endoparasiten von Vogeln des Munchner Tierparks Hellabrunn unter besondere Berucksichtigung der jahreszeitlichen Schwankungen in der Wurmausschedung. PhD Thesis, Universität München, Munich, Germany.
Jankovsky, J. M., Brand, M., & Gerhold, R. W. (2017). Identification of a novel renal coccidian (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the great-horned owl (Bubo virginianus), USA. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 53, 368–371.
Kolářová, I. (1982). First record of Eimeria strigis Kutzer, 1963 from tawny owl Strix aluco L. in Czechoslovakia. Folia Parasitologica, 29, 381.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780.
Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., et al. (2012). Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28, 1647–1649.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870–1874.
Kutzer, E. (1963). Eimeria strigis spec. nov. ein neues Kokzid aus dem Waldkauz. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 106, 378–380.
Kutzer, E., Frey, H., & Nöbauer, H. (1982). Zur Parasitenfauna österreichischer Eulenvögel (Strigiformes). Angewandte Parasitologie, 23, 190–197.
Landan, G., & Graur, D. (2008). Local reliability measures from sets of co-optimal multiple sequence alignments. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 13, 15–24.
Loehry, C. A., & Creamer, B. (1966). Post-mortem study of small-intestinal mucosa. British Medical Journal, 1, 827–829.
McAllister, C. T., Durden, L. A., Richardson, D. M., & Hnida, J. A. (2017). Some parasites (Apicomplexa, Trematoda, Nematoda, Acanthocephala, Phthiraptera) of the great horned owl, Bubo virginianus (Aves: Strigiformes: Strigidae) from southeastern Oklahoma. Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science, 97, 83–90.
Medina, J. P., Medina-Valdez, H., Sánchez-Jasso, J. M., García-Albarrán, M., Salgado-Miranda, C., & Soriano-Vargas, E. (2019). Eimeria aegoliusia n. sp. (Sporozoa: Eimeriidae) from the northern saw-whet owl Aegolius acadicus (Gmelin) (Strigiformes: Strigidae) in Mexico. Systematic Parasitology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09863-x.
Mironenko, V. M., Yatusevich, A. I., & Vorobyeva, I Yu. (2011). Endoparasitic animals of the Minsk Zoo. Scientific Notes of the Vitebsk State Academy of Veterinary Medicine, 47, 53–56.
Ogedengbe, J. D., Hanner, R. H., & Barta, J. R. (2011). DNA barcoding identifies Eimeria species and contributes to the phylogenetics of coccidian parasites (Eimeriorina, Apicomplexa, Alveolata). International Journal for Parasitology, 41, 843–850.
Papini, R., Girivetto, M., Marangi, M., Mancianti, F., & Giangaspero, A. (2012). Endoparasite infections in pet and zoo birds in Italy. The Scientific World Journal. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/253127.
Rambaut, A. (2016). FigTree. Accessed 29 December, 2018, from http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/.
Ratnasingham, S., & Hebert, P. D. N. (2007). The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 355–364.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Santos, T., de Oliveira, J. B., Vaughan, C., & Santiago, H. (2011). Health of an ex situ population of raptors (Falconiformes and Strigiformes) in Mexico: Diagnosis of internal parasites. Revista de Biología, 59, 1265–1274.
Sela, I., Ashkenazy, H., Katoh, K., & Pupko, T. (2015). GUIDANCE2: Accurate detection of unreliable alignment regions accounting for the uncertainty of multiple parameter. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, W7–W14.
Sprenger, L. K., Yoshitani, U. Y., Buzatti, A., & Molento, M. B. (2018). Occurrence of gastrointestinal parasites in wild animals in the state of Panará, Brazil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 90, 231–238.
Todd, K. S., & Hammond, D. M. (1971). Coccidia. In: Davis, J. W., Anderson, R. C., Karstad, L. & Trainer, D. O. (Eds). Infectious and Parasitic Diseases of Wild Birds. Iowa, USA: The Iowa State University Press, pp. 234–281.
Upton, S. J., Campbell, T. W., Weigel, M., & McKown, R. D. (1990). The Eimeriidae (Apicomplexa) of raptors: Review of the literature and description of new species of the genera Caryospora and Eimeria. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 88, 1256–1265.
Volf, J., Koudela, B., & Modrý, D. (1999). Eimeria nycteae sp. n. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae), a new parasite species from the snowy owl. Nyctea scandiaca. Folia Parasitologica, 46, 168–170.
Zhao, X., & Duszynski, D. W. (2001). Molecular phylogenies suggest the oocyst residuum can be used to distinguish two independent lineages of Eimeria spp. in rodents. Parasitology Research, 89, 638–643.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Derek Marshall of Mississippi State University, Donald Duszynski of the University of New Mexico, and Chris McAllister of Eastern Oklahoma State College for assistance with acquiring primary sources. The authors also acknowledge Wes Baumgartner for histological examination of host tissues.
Funding
This work was supported by the College of Veterinary Medicine at Mississippi State University and the College of Forest Resources at Mississippi State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
The present work complied with all applicable institutional requirements for the handling and care of laboratory animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodyard, E.T., Rush, S.A. & Rosser, T.G. Redescription of Eimeria megabubonis Upton, Campbell, Weigel & McKown, 1990 (Apicomplexa: Emeriidae) from the great horned owl Bubo virginianus (Gmelin). Syst Parasitol 96, 585–594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09867-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09867-7