Abstract
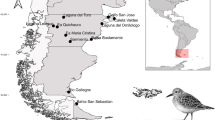
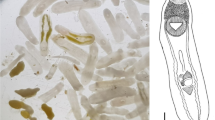
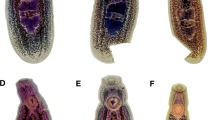
Members of the genus Clinostomum Leidy, 1856, colloquially known as yellow grubs, are cosmopolitan parasites of piscivorous birds, freshwater snails, fish and amphibians. In the southeastern United States, piscivorous birds present a continuous challenge for producers of farm-raised catfish. Ciconiiform birds are common hosts of Clinostomum spp. in North America and are endemic on most commercial catfish operations. The great egret Ardea alba L. is an avian predator often found foraging on commercial catfish operations, but to date the trematode fauna of great egrets preying on catfish ponds remains mostly understudied. Thirteen great egrets were captured from commercial catfish ponds in northeast Mississippi, and examined for trematode infections. Two morphologically distinct Clinostomum spp. were observed in the great egrets sampled, one morphologically consistent with Clinostomum marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819) and one morphologically unique species. These morphological descriptions were supplemented with molecular sequence data (c.4,800 bp of ribosomal DNA and c.600 bp of mitochondrial DNA). Gene sequences confirmed the identification of C. marginatum. However, the second species differed significantly from its congeners in both morphology and DNA sequence. Given these distinct morphological and molecular characters we propose this second species as Clinostomum album n. sp.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403–410.
Barker, S. C., Blair, D., Cribb, T. H., & Tonion, K. (1993). Phylogenetic position of Heronimus mollis (Digenea): Evidence from 18S ribosomal RNA. International Journal for Parasitology, 23, 533–536.
Bonett, R. M., Steffen, M. A., Trujano-Alvarez, A. L., Martin, S. D., Bursey, C. R., & McAllister, C. T. (2011). Distribution, abundance, and genetic diversity of Clinostomum spp. metacercariae (Trematoda: Digenea) in a modified Ozark stream system. Journal of Parasitology, 97, 177–184.
Bravo-Hollis, M. (1947). Dos especies de Clinostomum (Trematoda), de aves procedentes del estado de Nuevo Leon, Mexico. Anales del Instituto de Biología, México, 18, 489–498.
Caffara, M., Bruni, G., Paoletti, C., Gustinelli, A., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2014a). Metacercariae of Clinostomum complanatum (Trematoda: Digenea) in European newts Triturus carnifex and Lissotriton vulgaris (Caudata: Salamandridae). Journal of Helminthology, 88, 278–285.
Caffara, M., Davidovich, N., Falk, R., Smirnov, M., Ofek, T., Cummings, D., Gustinellis, A., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2014b). Redescription of Clinostomum phalacrocoracis metacercariae (Digenea: Clinostomidae) in cichlids from Lake Kinneret, Israel. Parasite, 21, 32.
Caffara, M., Locke, S. A., Gustinelli, A., Marcogliese, D. J., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2011). Morphological and molecular differentiation of Clinostomum complanatum and Clinostomum marginatum (Digenea: Clinostomidae) metacercariae and adults. Journal of Parasitology, 97, 884–891.
Carranza, S., Baguña, J., & Riutort, M. (1997). Are the Platyhelminthes a monophyletic primitive group? An assessment using 18S rDNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 14, 485–497.
Cort, W. W. (1913). Notes on the trematode genus Clinostomum. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 32, 169–182.
Dias, M. L. G. G., Eiras, J. C., Machado, M. H., Souza, G. T. R., & Pavanelli, G. C. (2003). The life cycle of Clinostomum complanatum Rudolphi, 1814 (Digenea, Clinostomidae) on the floodplain of the high Paraná River, Brazil. Parasitology Research, 89, 506–508.
Dzikowski, R., Levy, M. G., Poore, M. F., Flowers, J. R., & Paperna, I. (2004). Clinostomum complanatum and Clinostomum marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819) (Digenea: Clinostomidae) are separate species based on differences in ribosomal DNA. Journal of Parasitology, 90, 413–414.
Glahn, J. F., & King, D. T. (2004). Bird depredation. In: C. S. Tucker, C. S & Hargreaves, J. A. (Eds), Biology and culture of the channel catfish. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier, pp. 503–529.
Glahn, J. F., Reinhold, D. S., & Smith, P. (1999). Wading bird depredations on channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus in northwest Mississippi. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 30, 107–114.
Griffin, M. J., Khoo, L. H., Quiniou, S. M., O’Hear, M. M., Pote, L. M., Greenway, T. E., & Wise, D. J. (2012). Genetic sequence data identifies the cercaria of Drepanocephalus spathans (Digenea: Echinostomatidae), a parasite of the double-crested cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus), with notes on its pathology in juvenile channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Journal of Parasitology, 98, 967–972.
Gustinelli, A., Caffara, M., Florio, D., Otachi, E. O., Wathuta, E. M., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2010). First description of the adult stage of Clinostomum cutaneum Paperna, 1964 (Digenea: Clinostomidae) from grey herons Ardea cinerea L. and a redescription of the metacercaria from the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus niloticus (L.) in Kenya. Systematic Parasitology, 76, 39–51.
Hunter, G. W., & Hunter, W. S. (1934). The life cycle of the yellow grub of fish. Journal of Parasitology, 20, 325.
Hutton, R. F., & Sogandares-Bernal, F. (1960). Studies on the helminth parasites from the coast of Florida. II. Digenetic trematodes from shore birds of the west coast of Florida. I. Bulletin of Marine Science, 10, 40–54.
Kanev, I., Radev, V., & Fried, B. (2002). Family Clinostomidae Lühe, 1901. In: Gibson, D. I., Jones, A. & Bray, R. A. (Eds), Keys to the Trematoda, Vol. 1. Wallingford, UK: CAB International, pp. 113–120.
Kinsella, J. M., Spalding, M. G., & Forrester, D. J. (2004). Parasitic helminths of the American White Pelican, Pelecanus erythrorhynchos, from Florida, U.S.A. Comparative Parasitology, 71, 29–36.
Kudlai, O., Kostadinova, A., Pulis, E. E., & Tkach, V. V. (2015). A new species of Drepanocephalus Dietz, 1909 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) from the double-crested cormorant Phalacrocorax auritus (Lesson) (Aves: Phalacrocoracidae) in North America. Systematic Parasitology, 90, 221–230.
Littlewood, D. T. J., Curini-Galletti, M., & Herniou, E. A. (2000). The interrelationships of Proseriata (Platyhelminthes: Seratia) flatworms tested with molecules and morphology. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 16, 449–466.
Locke, S. A., Caffara, M., Marcogliese, D. J., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2015). A large-scale molecular survey of Clinostomum (Digenea, Clinostomidae). Zoologica Scripta, 44, 203–217.
Lockyer, A. E., Olson, P. D., Ostergaard, P., Rollinson, D., Johnston, D. A., Attwood, S. W., et al. (2003). The phylogeny of the Schistosomatidae based on three genes with emphasis on the interrelationships of Schistosoma Weinland, 1858. Parasitology, 126, 203–224.
Lorio, W. J. (1989). Experimental control of metacercariae of the yellow grub Clinostomum marginatum in channel catfish. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 1, 269–271.
McAllister, C. T. (1990). Metacercaria of Clinostomum complanatum (Rudolphi, 1814) (Trematoda: Digenea) in a Texas Salamander, Eurycea neotenes (Amphibian: Caudata), with comments on C. marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819). Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 57, 69–71.
Morgan, J. A. T., & Blair, D. (1995). Nuclear rDNA ITS sequence variation in the trematode genus Echinostoma: An aid to establishing relationships within the 37-collar-spine group. Parasitology, 111, 609–615.
Moszczynska, A., Locke, S. A., McLaughlin, D., Marcogliese, D. J., & Crease, T. J. (2009). Development of primers for the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I gene in digenetic trematodes (Platyhelminthes) illustrates the challenge of barcoding parasitic helminths. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 75–82.
Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2000). Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. New York: Oxford University Press.
Overstreet, R. M., & Curran, S. S. (2004). Defeating diplostomoid dangers in USA catfish aquaculture. Folia Parasitologica, 51, 153–165.
Paperna, I. (1991). Diseases caused by parasites in the aquaculture of warm water fish. Annual Review of Fish Diseases, 1, 155–194.
Pinto, H. A., Caffara, M., Fioravanti, M. L., & Melo, A. L. (2015). Experimental and molecular study of cercariae of Clinostomum sp. (Trematoda: Clinostomidae) from Biomphalaria spp. (Mollusca: Planorbidae) in Brazil. Journal of Parasitology, 101, 108–113.
Rambaut, A. (2014). FigTree: Tree Figure Drawing Tool v. 1.4.2. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh, http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1571–1574.
Rosser, T. G., Alberson, N. R., Khoo, L. H., Woodyard, E. T., Pote, L. M., & Griffin, M. J. (2016a). Characterization of the life cycle of a fish eye fluke, Austrodiplostomum ostrowskiae (Digenea: Diplostomidae), with notes on two other diplostomids infecting Biomphalaria obstructa (Mollusca: Planorbidae) from catfish aquaculture ponds in Mississippi, USA. Journal of Parasitology, 102, 260–274.
Rosser, T. G., Alberson, N. R., Khoo, L. H., Woodyard, E. T., Wise, D. J., Pote, L. M., & Griffin, M. J. (2016b). Biomphalaria havanensis is a natural first intermediate host for the trematode Bolbophorus damnificus in commercial catfish production in Mississippi. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 78, 189–192.
Sepúlveda, M. S., Spalding, M. G., Kinsella, J. M., Bjork, R. D., & McLaughlin, G. S. (1994). Helminths of the roseate spoonbill, Ajaia ajaja, in southern Florida. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 61, 179–189.
Sepúlveda, M. S., Spalding, M. G., Kinsella, J. M., & Forrester, D. J. (1996). Parasitic helminths of the little blue heron, Egretta caerulea, in southern Florida. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 63, 136–140.
Sepúlveda, M. S., Spalding, M. G., Kinsella, J. M., & Forrester, D. J. (1999). Parasites of the great egret (Ardea albus) in Florida and a review of the helminthes reported for the species. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 66, 7–13.
Sereno-Uribe, A. L., Pinacho-Pinacho, C. D., García-Varela, M., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2013). Using mitochondrial and ribosomal DNA sequences to test the taxonomic validity of Clinostomum complanatum Rudolphi, 1814 in fish-eating birds and freshwater fishes in Mexico, with the description of a new species. Parasitology Research, 112, 2855–2870.
Stuart, J. J., Dismukes, J. F., & Dixon, C. F. (1972). Endoparasites of the cattle egret (Bubulcus ibis) in Alabama. Journal of Parasitology, 58, 518.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Travassos, L., Freitas, J. T., & Kohn, A. (1969). Trematódeos do Brasil. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 67, 1–886.
Van Steenkiste, N., Locke, S. A., Castelin, M., Marcogliese, D. J., & Abbott, C. L. (2015). New primers for DNA barcoding of digeneans and cestodes (Platyhelminthes). Molecular Ecology Resources, 15, 945–952.
Violante-González, J., Monks, S., Gil-Guerrero, S., Rojas-Herrera, A. A., & Flores-Rodriguez, P. (2012). Helminth communities of two species of piscivorous birds, Ardea alba (Linnaeus) and Nyctanassa violacea (Gmelin) (Ciconiiformes: Ardeidae), in two coastal lagoons from Guerrero state, Mexico. Parasitology Research, 111, 309–315.
Werner, S. J., Tobin, M. E., & Fioranelli, P. B. (2001). Great egret preference for catfish size classes. Waterbirds: The International Journal of Waterbird Biology, 24, 381–385.
Wise, D. J., Hanson, T. R., & Tucker, C. S. (2008). Farm-level economic impacts of Bolbophorus infections of channel catfish. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 70, 382–387.
Yost, M. C., Pote, L. M., Wise, D. J., Dorr, B. S., & Richardson, T. D. (2009). Biomphalaria havanensis identified as a potential intermediate host for the digenetic trematode Bolbophorus damnificus. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 71, 10–15.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Katie Hanson-Dorr, Lanna Durst, Alex Crain, Lorelei Ford, and Raleigh Middleton for their assistance in capturing the egrets and during egret necropsies.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Project Number MIS-371530, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service-Catfish Health Initiative, the Mississippi State University College of Veterinary Medicine, and the Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Experiment Station (MAFES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed (IACUC QA 2458).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosser, T.G., Alberson, N.R., Woodyard, E.T. et al. Clinostomum album n. sp. and Clinostomum marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819), parasites of the great egret Ardea alba L. from Mississippi, USA. Syst Parasitol 94, 35–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-016-9686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-016-9686-0