Abstract
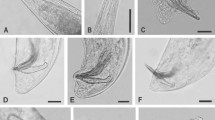
Steinernemar robustispiculum n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) was isolated from woodland in Chumomray National Park, Sason, Sathay, Kontum, Vietnam. Its morphology, morphometrics, cross-hybridisation and the ITS-rDNA sequence analysis revealed that S. robustispiculum clearly differs from other known Steinernema spp. As in the cases of S. intermedium (Poinar, 1985), S. robustispiculum has very robust spicules, but it can be distinguished by the longer tail of the infective juvenile, lower E%, shorter spicules, the shape of the spicules, the number of genital papillae in the caudal region and the presence of a mucron on the male tail. S. robustispiculum has a lateral field resembling that of S. sangi Phan, Nguyen & Moens, 2001, but can be distinguished by a higher E%, higher D%, smaller length to width ratio of the spicules and the morphology of both the spicule head (manubrium) and the dorsal lobe of the spicule. The morphometrics of infective juveniles of S. robustispiculum are similar to those of S. monticolum Stock, Choo & Kaya, 1997; these species can be distingusihed by the position of the excretory pore, the smaller length to width ratio of the spicules, and the length and morphology of the spicule head (manubrium). The phylogenetic relationships within Steinernema Travassos, 1927, including the newly sequenced Vietnamese species S. robustispiculum n. sp., S. loci Phan, Nguyen & Moens, 2001, S. thanhi Phan, Nguyen & Moens, 2001 and S. sangi, are presented based on analyses of the ITS-rDNA. The ITS RFLP profiles obtained from 17 different restriction enzymes are also presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Akhurst (1987) ArticleTitleUse of starch gel electrophoresis in the taxonomy of the genus Heterorhabditis(Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae) Nematologica 33 1–9
R.A. Bedding R.J. Akhurst (1975) ArticleTitleA simple technique for the determination of insect parasitic rhabditid nematodes in soil Nematologica 21 109–110
R.A. Bedding (1990) Logistics and strategies for introducing entomopathogenic nematodes technology into developing countries R. Gaugler H.K. Kaya (Eds) Entomopathogenicnematodesinbiologicalcontrol CRC Press Boca Raton, Florida 233–245
A.T. De Grisse (1969) ArticleTitleRedescription ou modi.cations de quelques techniques utilisées dans l’étude de nématodes phytoparasitaires Mededelingen Rijksfaculteit Landbouwwetenschappen Gent 34 315–359
R. Hickson C. Simon S.W. Perrey (2000) ArticleTitleThe performance of several multiple-sequence alignment programs in relation to secondary-structure features for an rRNA sequence Molecular Biology and Evolution 17 530–539
W.M. Hominick B.R. Briscoe F.G. Del-Pino J. Heng D.J. Hunt E. Kozodoy Z. Mráček K.B. Nguyen A.P. Reid S. Spiridonov P. Stock D. Sturhan C. Waturu M. Yoshida (1997) ArticleTitleBiosystematics of entomopathogenic nematodes: current status, protocols and definitions Journal of Helminthology 71 271–298
Joyce, S.A., Reid, A., Driver, F. & Curran, J. (1994) Application of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods to identification of entomogenic nematodes. In: Burnell, A.M., Ehlers, R.U. & Masson, J.P. (Eds) Proceeding of Symposium & Workshop, St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, Co. Kildare, Ireland. Luxembourg: European Commission, DGXII, pp. 178–187.
J. Liu R.E. Berry (1995) ArticleTitleDetermination of PCR conditions for RAPD analysis in entomopathogenic nematodes (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 65 79–81
J. Liu R.E. Berry A.F. Moldenke (1997) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships of entomopathogenic nematodes (Heterorhabditidae and Steinernematidae) inferred from partial 18S rDNA gene sequences Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 69 246–252
D.A. Morrison J.T. Ellis (1997) ArticleTitleEffects of nucleotide sequence alignment on phylogeny estimation: a case of 18S rDNA of Apicomplexa Molecular Biology and Evolution 14 428–441
K.B. Nguyen G.C. Smart ParticleJr (1995) ArticleTitleMorphometrics of infective juveniles of Steinernema spp. and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nemata: Rhabditida). Journal of Nematology 27 206–212
K.B. Nguyen J. Maruniak B.J. Adams (2001) ArticleTitleDiagnostic and phylogenetic utility of the rDNA internal transcribed spacer sequences of Steinernema Journal of Nematology 33 73–82
K.B. Nguyen L.W. Duncan (2002) ArticleTitleSteinernema diaprepesi n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a parasite of the citrus root weevil Diaprepes abbreviatus(L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Journal of Nematology 34 159–170
V.L. Pham K.B. Nguyen A.P. Reid S.E. Spiridonov D. Sturhan (2000) ArticleTitleSteinernema tami sp. n. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) from Cat Tien forest, Vietnam. Russian Journal of Nematology 8 33–43
K.L. Phan N.C. Nguyen M. Moens (2001a) ArticleTitleSteinernema sangi sp. n. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) from Vietnam. Russian Journal of Nematology 9 1–7
K.L. Phan N.C. Nguyen M. Moens (2001b) ArticleTitleSteinernema loci sp. n. and Steinernema thanhi sp. n. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) from Vietnam. Nematology 3 503–514
K.L. Phan S.A. Subbotin N.C. Nguyen M. Moens (2003) ArticleTitleHeterorhabditis baujardi sp. n. (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae) from Vietnam with morphometric data for H. indica populations. Nematology 5 367–382
G.O. Poinar ParticleJr (1985) ArticleTitleNeoaplectana intermedian. sp. (Steinernematidae: Nematoda) from South Carolina. Revue de Nématologie 8 321–327
G.O. Poinar ParticleJr. (1990) Taxonomy and biology of Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae R. Gaugler H.K. Kaya (Eds) Entomopathogenic nematodes inbiological control CRC Press Boca Raton, Florida 23–61
D. Posada K. Crandall (1998) ArticleTitleMODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution Bioinformatics 14 817–818 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlCltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9918953
J.W. Seinhorst (1959) ArticleTitleA rapid method for the transfer of nematodes from fixative to anhydrous glycerin Nematologica 4 67–69
S.P. Stock H.Y. Choo H.K. Kaya (1997) ArticleTitleSteinernema monticolum sp. n. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), an entomopathogenic nematode from Korea with a key to other species. Nematologica 43 15–29
S.P. Stock J.F. Campbell S.A. Nadler (2001) ArticleTitlePhylogeny of SteinernemaTravassos, 1927 (Cephalobina: Steinernematidae) inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences and morphological characters Journal of Parasitology 87 877–889
S.A. Subbotin A. Vierstraete P. De Ley J. Rowe L. Waeyenberge M. Moens J.R. Vanfleteren (2001) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships within the cyst-forming nematodes (Nematoda, Heteroderidae) based on analysis of sequences from the ITS regions of ribosomal DNA Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 21 1–16
D.L. Swofford (1998) PAUP*.Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Version 4. Sinauer Sunderland, MA
T.C. Vrain D.A. Wakrchuk A.C. Levesque R.I. Hamilton (1992) ArticleTitleIntra specific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the Xiphinema americanum group Fundamental and Applied Nematology 15 563–574
G.F. White (1927) ArticleTitleA method for obtaining infective nematode larvae from cultures Science 66 302–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, L.K., Subbotin, S.A., Waeyenberge, L. et al. A new entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema robustispiculum n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), from Chumomray National Park in Vietnam. Syst Parasitol 60, 23–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-1373-x
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-1373-x