Abstract
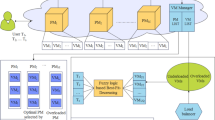
A hybrid of supervised (artificial neural network), unsupervised (clustering) machine learning, and soft computing (interval type 2 fuzzy logic system)-based load balancing algorithm, i.e., clustering-based multiple objective dynamic load balancing technique (CMODLB), is introduced to balance the cloud load in the present work. Initially, our previously introduced artificial neural network-based dynamic load balancing (ANN-LB) technique is implemented to cluster the virtual machines (VMs) into underloaded and overloaded VMs using Bayesian optimization-based enhanced K-means (BOEK-means) algorithm. In the second stage, the user tasks are scheduled for underloading VMs to improve load balance and resource utilization. Scheduling of tasks is supported by multi-objective-based technique of order preference by similarity to ideal solution with particle swarm optimization (TOPSIS-PSO) algorithm using different cloud criteria. To realize load balancing among PMs, the VM manager makes decisions for VM migration. VM migration decision is done based on the suitable conditions, if a PM is overloaded, and if another PM is minimum loaded. The former condition balances load, while the latter condition minimizes energy consumption in PMs. VM migration is achieved through interval type 2 fuzzy logic system (IT2FS) whose decisions are based on multiple significant parameters. Experimental results show that the CMODLB method takes 31.067% and 71.6% less completion time than TaPRA and BSO, respectively. It has maintained 65.54% and 68.26% less MakeSpan than MaxMin and R.R algorithms, respectively. The proposed method has achieved around 75% of resource utilization, which is highest compared to DHCI and CESCC. The use of novel and innovative hybridization of machine learning, multi-objective, and soft computing methods in the proposed algorithm offers optimum scheduling and migration processes to balance PMs and VMs.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sadiku NOM, Musa M, S, D Momoh, O, (2014) Cloud computing: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Potentials 3(1):34–36
Diaz M, Martin C, Rubio B (2016) State-of-the-art challenges, and open issues in an integration of internet of things and cloud computing. J Netw Comput Appl 67:99–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2016.01.010
Milani AS, Navimipour NJ (2016) Load balancing mechanisms and techniques in the cloud environments: systematic literature review and future trends. J Netw Comput Appl 71:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2016.06.003
Zhi-H Zhan, Xiao-F Liu, Yue-Jiao Gong, Zhang J (2015) Cloud computing resource scheduling and a survey of its evolutionary approaches. ACM Comput Surv 47(4):1–33. https://doi.org/10.1145/2788397
Hua H, Guangquan X, Shanchen P, Zenghua Z (2016) AMTS: adaptive multi-objective task scheduling strategy in cloud computing. China Commun 13(4):162–171. https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2016.7464133
Yuan H, Bi J, Tan W, Zhou M, Li BH, Li J (2017) TTSA: an effective scheduling approach for delay bounded tasks in hybrid clouds. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3658–3668. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2016.2574766
Zhong Z, Chen K, Zhai X, Zhou S (2016) Virtual machine-based task scheduling algorithm in a cloud computing environment. Tsinghua Sci Technol 21(6):660–667. https://doi.org/10.1109/TST.2016.7787008
Xu X, Cao L, Wang X (2016) Resource pre-allocation algorithms for low-energy task scheduling of cloud computing. J Syst Eng Electron 27(2):457–469. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEE.2016.00047
Sharma SCM, Rath AK (2017) Multi-Rumen Anti-Grazing approach of load balancing in cloud network. Int J Info Technol 9(2):129–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-017-0022-y
Singha A, Junejab D, Malhotra M (2015) Autonomous agent based load balancing algorithm in cloud computing. Procedia Comput Sci 45:832–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.03.168
Gutierrez-Garcia JO, Ramirez-Nafarrate A (2015) Agent-based load balancing in cloud data centers. Cluster Comput 18(3):1041–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0460-x
Chun-C L, Hui-H C, Der-J D (2014) Dynamic multiservice load balancing in cloud-based multimedia system. IEEE Syst J 8(1):225–234. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2013.2256320
Chitra DD, Uthariaraj VR (2016) Load balancing in cloud computing environment using improved weighted round robin algorithm for nonpreemptive dependent tasks. Sci World J 2016:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3896065
Tao D, Lin Z, Wang B (2017) Load feedback-based resource scheduling and dynamic migration-based data locality for virtual Hadoop clusters in OpenStack-based clouds. Tsinghua Sci Technol 22(2):149–159.https://doi.org/10.23919/TST.2017.7889637
Xie R, Wen Y, Jia X, Xie H (2015) Supporting seamless virtual machine migration via named data networking in cloud data center. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 26(12):3485–3497. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2014.2377119
Mosleh Mohammed AS, Radhamani G, Hazber Mohamed AG, Hasan SH (2016) Adaptive cost-based task scheduling in cloud environment. Sci Program 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8239239
Liu Y, Li C, Li L (2016) Distributed two-level cloud-based multimedia task scheduling. Automat Contr Comput Sci 50(3):41–150. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411616030044
Shi L, Zhang Z, Robertazzi T (2017) Energy-aware scheduling of embarrassingly parallel jobs and resource allocation in cloud. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 28(6):1607–1620. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2016.2625254
Li Y, Chen M, Dai W, Qiu M (2017) Energy optimization with dynamic task scheduling mobile cloud computing. IEEE Syst J 11(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2015.2442994
Keng-M C, Pang-W T, Chun-W T, Chu-S Y (2015) A hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm for VM scheduling with load balancing in cloud computing. Neural Comput Appl 26(6):297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1804-9
Eswaran S, Rajakannu M (2017) Multiservice load balancing with hybrid particle swarm optimization in cloud-based multimedia storage system with QoS provision. Mobile Netw Appl 22(4):760–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0840-y
Dhinesh Babu LD, Venkata Krishna P (2013) Honey bee behavior inspired load balancing of tasks in cloud computing environments. Appl Soft Comput 13:2292–2303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2013.01.025
Negi S, Panwar N, Vaisla K S, Rauthan MMS (2020) Artificial Neural Network Based Load Balancing in Cloud Environment. Advances in Data and Information Sciences. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 94. /https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0694-9_20.
Jeyakrishnan V, Sengottuvelan P (2017) A Hybrid Strategy for Resource Allocation and Load Balancing in Virtualized Data Centers Using BSO Algorithms. Wireless Pers Commun 94(4):2363–2375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3481-8
Polepally V K, Chatrapati K S (2017) Dragonfly optimization and constraint measure-based load balancing in cloud computing. Cluster Computing. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1056-4
Zhao J, Yang K, Wei X, Ding Y, Hu L, Xu G (2016) A Heuristic Clustering-based Task Deployment Approach for Load Balancing Using Bayes Theorem in Cloud Environment. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 27(2):305–316. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2015.2402655
Tsakalozos K, Verroios V, Roussopoulos M, Delis A (2017) Live VM Migration under Time-Constraints in Share-Nothing IaaS-Clouds. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 28(8):2285–2298. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2017.2658572
Kansal Nidhi J, Chana I (2016) Energy-aware Virtual Machine Migration for cloud computing—a firefly optimization approach. J Grid Comput 14(2):327–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-016-9364-0
Farahnakian F, Pahikkala T, Liljeberg P, Plosila J, TrungHieu N, Tenhunen H (2016) Energy-aware VM Consolidation in Cloud Data Centers Using Utilization Prediction Model. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing (99).https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2016.2617374
Patel G, Mehta R, Bhoi U (2015) Enhanced Load Balanced Min-Min algorithm for Static Meta-task Scheduling in Cloud Computing. Procedia Computer Science (Elsevier). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.385
Lakraa AV, Yadav DK (2015) Multi-Objective Tasks Scheduling Algorithm for Cloud Computing Throughput Optimization. Procedia Computer Science, Elsevier 48:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.04.158
Zhang P, Zhou Meng C (2017) Dynamic Cloud Task Scheduling Based on a Two-Stage Strategy. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 99:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2017.2693688
Zuo X, Zhang G, Tan W (2014) Self-Adaptive Learning PSO-Based Deadline Constrained Task Scheduling for Hybrid IaaS Cloud. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 11(2):564–573. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2013.2272758
Awada AI, El-Hefnawyb NA, Abdelkader HM (2015) Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization for Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing Environments. Procedia Comput Sci Elsevier 65:920–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.064
Panwar N, Negi S, Rauthan MMS, Vaisla KS (2019) TOPSIS–PSO inspired non-preemptive tasks scheduling algorithm in cloud environment. Clust Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02915-3
Pooranian Z, Shojafar M, Abawajy Jemal H, Abraham A (2013) An efficient meta-heuristic algorithm for grid computing. J Comb Optim, Springer 30(3):413–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-013-9644-6
Brochu E, Cora Vlad M, Freitas Nando D (2013) A Tutorial on Bayesian Optimization of Expensive Cost Functions with Application to Active User Modeling and Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning. https://arxiv.org/abs/1012.2599
Nyikosa F M, Osborne M A, Roberts S J (2018) Bayesian Optimization for Dynamic Problems. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.03432
Wagner C (2013) Juzzy – A Java based Toolkit for Type-2 Fuzzy Logic. IEEE. Symposium on Advances in Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems (T2FUZZ). https://doi.org/10.1109/T2FZZ.2013.6613298
Mendel JM, John RI, Liu F (2006) Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems Made Simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14(6):808–821
Kasper Fredenslund (2018) March 25. https://kasperfred.com/series/introduction-to-neural-networks/computational-complexity-of-neural-networks
Baptista R, Poloczek M (2018) Bayesian optimization of combinatorial structures. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, PMLR. 80. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.08838
Ren Q, Balazinski M, Baron L (2011) Type-2 TSK fuzzy logic system and its type-1 counterpart. Int J Comput Appl 20(6):0975–8887. https://doi.org/10.5120/2440-3292
Buyya R, Ranjan R, Calheiros R N (2019) Modeling and Simulation of Scalable Cloud Computing Environments and the CloudSim Toolkit: Challenges and Opportunities. High Performance Computing & Simulation HPCS’09. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/HPCSIM.2009.5192685
Shojafar M, Javanmardi S, Saeid A, Nicola C (2015) FUGE: a joint meta-heuristic approach to cloud job scheduling algorithm using fuzzy theory and a genetic method. Clust Comp 18(2):829–844
Chen Y (2019) Study on Centroid Type-Reduction of Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems Based on Noniterative Algorithms. Compl Hindwai 2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7325053
Mendel JM (2013) On KM algorithms for solving type-2 fuzzy set problems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21(3):426–446
Liang Q, Mendel J (2000) Interval Type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8:535–550
Singh H, Tyagi S, Kumar P (2020) Crow–penguin optimizer for multiobjective task scheduling strategy in cloud computing. Int J Commun Syst 33(5):e4467. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4467
Prassanna J, Venkataraman N (2019) Threshold based multi-objective memetic optimized round robin scheduling for resource efficient load balancing in cloud. Mobile Netw Appl 24:1214–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01259-x
Neelima P, Rama Mohan Reddy A (2020) An efficient load balancing system using adaptive dragonfly algorithm in cloud computing. Cluster Comput 23:2891–2899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03054-w
Acknowledgment
The first author (Sarita Negi) acknowledges Prof. Man Mohan Singh Ruthann, Dr. Rohit Mahar, and the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, H N B Garhwal University (Srinagar Garhwal), Uttarakhand, for their immense support and resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negi, S., Rauthan, M.M.S., Vaisla, K.S. et al. CMODLB: an efficient load balancing approach in cloud computing environment. J Supercomput 77, 8787–8839 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03601-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03601-7