Abstract
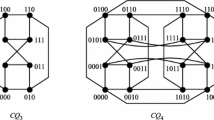
In many parallel and distributed multiprocessor systems, the processors are connected based on different types of interconnection networks. The topological structure of an interconnection network is typically modeled as a graph. Among the many kinds of network topologies, the crossed cube is one of the most popular. In this paper, we investigate the panpositionable panconnectedness problem with respect to the crossed cube. A graph G is r-panpositionably panconnected if for any three distinct vertices x, y, z of G and for any integer \(l_1\) satisfying \(r \le l_1 \le |V(G)| - r - 1\), there exists a path \(P = [x, P_1, y, P_2, z]\) in G such that (i) \(P_1\) joins x and y with \(l(P_1) = l_1\) and (ii) \(P_2\) joins y and z with \(l(P_2) = l_2\) for any integer \(l_2\) satisfying \(r \le l_2 \le |V(G)| - l_1 - 1\), where |V(G)| is the total number of vertices in G and \(l(P_1)\) (respectively, \(l(P_2)\)) is the length of path \(P_1\) (respectively, \(P_2\)). By mathematical induction, we demonstrate that the n-dimensional crossed cube \(CQ_n\) is n-panpositionably panconnected. This result indicates that the path embedding of joining x and z with a mediate vertex y in \(CQ_n\) is extremely flexible. Moreover, applying our result, crossed cube problems such as panpositionable pancyclicity, panpositionably Hamiltonian connectedness, and panpositionable Hamiltonicity can be solved.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi Y, Williamson JE (1975) Panconnected graphs. Stud Sci Math Hung 10:19–22
Arabnia HR, Oliver MA (1987) A transputer network for the arbitrary rotation of digitised images. Comput J 30:425–432
Arabnia HR, Oliver MA (1989) A transputer network for fast operations on digitised images. Int J Eurograph Assoc (Computer Graphics Forum) 8:3–11
Arabnia HR, Smith JW (1993) A reconfigurable interconnection network for imaging operations and its implementation using a multi-stage switching box. In: Proceedings of the 7th Annual International High Performance Computing Conference. The 1993 High Performance Computing: New Horizons Supercomputing Symposium, Calgary, pp 349–357
Bhandarkar SM, Arabnia HR (1995) The hough transform on a reconfigurable multi-ring network. J Parallel Distrib Comput 24:107–114
Bhandarkar SM, Arabnia HR, Smith JW (1995) A reconfigurable architecture for image processing and computer vision. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 9:201–229
Bhandarkar SM, Arabnia HR (1995) The REFINE multiprocessor: theoretical properties and algorithms. Parallel Comput 21:1783–1805
Bondy JA (1971) Pancyclic graphs. J Comb Theory Ser B 11:80–84
Chen H-C (2017) A data verification report on the panpositionable panconnectedness of crossed cubes. http://mis.web2.ncut.edu.tw/ezfiles/19/1019/img/1258/CHENHC2.htm. Accessed 1 July 2017
Chen H-C, Kung T-L, Hsu L-H (2011) Embedding a Hamiltonian cycle in the crossed cube with two required vertices in the fixed positions. Appl Math Comput 217:10058–10065
Chen H-C, Kung T-L, Hsu L-Y (2015) 2-Disjoint-path-coverable panconnectedness of crossed cubes. J Supercomput 71:2767–2782
Chen H-C, Kung T-L, Zou Y-H, Mao H-W (2015) The fault-tolerant Hamiltonian problems of crossed cubes with path faults. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E98–D:2116–2122
Chen H-C, Zou Y-H, Wang Y-L, Pai K-J (2017) A note on path embedding in crossed cubes with faulty vertices. Inf Process Lett 121:34–38
Chen X-B (2013) The 2-path-bipanconnectivity of hypercubes. Inf Sci 239:283–293
Chen X-B (2014) Panconnectivity and edge-pancyclicity of multidimensional torus networks. Discrete Appl Math 178:33–45
Choudum SA, Sunitha V (2002) Augmented cubes. Networks 40:71–84
Efe K (1992) The crossed cube architecture for parallel computing. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 3:513–524
Fan J, Jia X, Lin X (2006) Complete path embeddings in crossed cubes. Inf Sci 176:3332–3346
Fan J, Lin X, Jia X (2005) Node-pancyclicity and edge-pancyclicity of crossed cubes. Inf Process Lett 93:133–138
Fan J, Lin X, Jia X (2005) Optimal path embeddings in crossed cubes. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 16:1190–1200
Golumbic MC (1980) Algorithmic graph theory and perfect graphs. Academic Press, New York
Huang W-T, Chuang Y-C, Tan JJM, Hsu L-H (2002) On the fault-tolerant hamiltonicity of faulty crossed cubes. IEICE Trans Fundam Electron Commun Comput Sci E85–A:1359–1370
Hsu L-H, Lin C-K (2008) Graph theory and interconnection networks. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kulasinghe P, Bettayeb S (1995) Embedding binary trees into crossed cubes. IEEE Trans Comput 44:923–929
Kung T-L (2013) Flexible cycle embedding in the locally twisted cube with nodes positioned at any prescribed distance. Inf Sci 242:92–102
Kung T-L, Teng Y-H, Hsu L-H (2010) The panpositionable panconnectedness of augmented cubes. Inf Sci 180:3781–3793
Lai P-L, Hsu H-C (2008) The two-equal-disjoint path cover problem of matching composition network. Inf Process Lett 107:18–23
Li J, Wang S, Yang Y (2014) Panconnectivity and pancyclicity of the 3-ary \(n\)-cube network under the path restrictions. Appl Math Comput 243:339–348
Lin T-J, Hsieh S-Y, Juan JS-T (2012) Embedding cycles and paths in product networks and their applications to multiprocessor systems. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 23:1081–1089
Saad Y, Shultz MH (1988) Topological properties of hypercubes. IEEE Trans Comput 37:867–872
Teng Y-H, Tan JJM, Hsu L-H (2008) Panpositionable hamiltonicity and panconnectivity of the arrangement graphs. Appl Math Comput 198:414–432
Teng Y-H, Tan JJM, Hsu L-H (2007) Panpositionable hamiltonicity of the alternating group graphs. Networks 50:146–156
Yang X, Evans DJ, Megson GM (2005) The locally twisted cubes. Int J Comput Math 82:401–413
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express his gratitude to the anonymous referees and the editor for their valuable suggestions for improving the clarity and style of this work. This work is supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under Contract MOST103-2221-E-167-022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HC. The panpositionable panconnectedness of crossed cubes. J Supercomput 74, 2638–2655 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2295-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2295-8