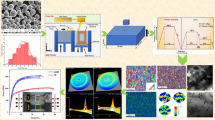
Squeeze casting is characterized by an applied pressure during solidification. It activates different physical processes which have metallurgical repercussions on the cast alloys. An experimental study showed the effect of the pressure levels on the microstructure and the mechanical behavior of an Al–13%Si alloy. The results showed that the applied pressure ranging from 0.1 to 100 MPa refined the microstructure, improved the tensile properties and increased the hardness Vickers in the specimen centers. Beyond 100 MPa until 150 MPa, the alloy has undergone a severe deformation in the presence of the high temperature, which generated a coarse micro-structure. Consequently, the tensile properties and the hardness decreased. The scanning electron microscopy fractographs show that the fracture mode of the squeeze cast specimens is more ductile up to 100 MPa pressure. This implies that the pressure is optimized to avoid degradation and segregation of the material during the elaboration process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Schmidt, J. Bast, M. Aitsuradze, and L. Arnberg, “Hollow castings produced by interrupted low pressure die casting,” Int. J. Cast. Met. Res., 23, 1–6 (2010).
Kh. A. Ragab, A. M. Samuel, A. M. A. Al-Ahmari, et al., “Influence of fluidized sand bed heat treatment on the performance of AlSi cast alloys,” Mater. Des., 32, 1177–1193 (2011).
C. M. Cepeda-Jiménez, J. M. Garcia-Infanta, A. P. Zhilyaev, et al., “Influence of the thermal treatment on the deformation-induced precipitation of a hypoeutectic Al–7 wt% Si casting alloy deformed by high-pressure torsion,” J. Alloys Compd., 509, Issue 3, 636–643 (2011).
Y. Zedana, F. H. Samuela, A. M. Samuela, and H. W. Doty, “Effects of Fe intermetallics on the machinability of heat-treated Al–(7–11)% Si alloys,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210, Issue 2, 245–257 (2010).
S. Nafisi and R. Ghomashchi, “Boron-based refiners: Advantages in semi-solid-metal casting of Al–Si alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 452-453, 437–444 (2007).
N. A. Belov, D. G. Eskin, and N. N. Avxentieva, “Constituent phase diagrams of the Al–Cu–Fe–Mg–Ni–Si system and their application to the analysis of aluminium piston alloys,” Acta Mater., 53, 4709–4722 (2005).
R. Ashiri, B. Niroumand, F. Karimzadeh, et al., “Effect of casting process on microstructure and tribological behavior of LM13 alloy,” J. Alloys Compd., 475, Issue 1-2, 321–327 (2009).
Rodrigo González, Dora I. Martinez, J. Alejandro González, et al., “Experimental investigation for fatigue strength of a cast aluminium alloy,” Int. J. Fatigue, 33, Issue 2, 273–278 (2011).
Choong Do Lee, “Variability in the tensile properties of squeeze-cast Al–Si– Cu–Mg alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 488, 296–302 (2008).
Choong Do Lee, “Effect of damage evolution of Si particles on the variability of the tensile ductility of squeeze-cast Al–10%Si–2%Cu–0.4%Mg alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 3144–3150 (2010).
X. Meng-Burany, T. A. Perry, A. K. Sachdev, and A. T. Alpas, “Subsurface sliding wear damage characterization in Al–Si alloys using focused ion beam and cross-sectional TEM techniques,” Wear, 270, 152–162 (2011).
S. W. Kim, D. Y. Kim, W. G. Kim, and K. D. Woo, “The study on characteristics of heat treatment of the direct squeeze cast 7075 wrought Al alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 304-306, 721–726 (2001).
S. W. Youn, C. G. Kang, and P. K. Seo, “Thermal fluid/solidification analysis of automobile part by horizontal squeeze casting process and experimental evaluation,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 146, 294–302 (2004).
Crystopher Cardoso De Brito, Fabricio Dias Magalhães, André Luiz de Morais Costa, and Cláudio Alves Siqueira, “Microstructural analysis and tensile properties of squeeze cast Al–7%Mg alloy,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 643, 119–123 (2010).
Ming Zhou, Henry Hu, Naiyi Li, and Jason Lo, “Microstructure and tensile properties of squeeze cast magnesium alloy AM50,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 14, No. 4, 539–545 (2005).
M. T. Abou El-khair, “Microstructure characterization and tensile properties of squeeze-cast AlSiMg alloys,” Mater. Lett., 59, 894–900 (2005).
Yanfei Bai and Haidong Zhao, “Tensile properties and fracture behavior of partial squeeze added slow shot die-cast A356 aluminum alloy,” Mater. Des., 31, Issue 9, 4237–4243 (2010).
S. Murali and M. S. Yong, “Liquid forging of thin Al–Si structures,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210, 1276–1281 (2010).
A. Maleki, B. Niroumand, and A. Shafyei, “Effects of squeeze casting parameters on density, macrostructure and hardness of LM13 alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 428, Issue 1-2, 135–140 (2006).
A. Maleki, A. Shafyei, and B. Niroumand, “Effects of squeeze casting parameters on the microstructure of LM13 alloy,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 209, Issue 8, 3790–3797 (2009).
C. H. Fan, Z. H. Chen, W. Q. He, et al., “Effects of the casting temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of the squeeze-cast Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy,” J. Alloys Compd., 504, Issue 2, L42–L45 (2010).
ASM Handbook, Vol. 9: Metallography and Microstructures, Materials Park, OH (1986), pp. 334–435.
A. Boschetto, G. Costanza, F. Quadrini, and M. E. Tata, “Cooling rate inference in aluminum alloy squeeze casting,” Mater. Lett., 61, Issues 14–15, 2969–2972 (2007).
Ming Zhang, Wei-wen Zhang, Hai-dong Zhao, et al., “Effect of pressure on microstructures and mechanical properties of Al–Cu-based alloy prepared by squeeze casting,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 17, No. 3, 496–501 (2007).
M. R. Ghomashchi and A. Vikhrov, Squeeze casting: an overview, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 101, Issues 1–3, 1–9 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Problemy Prochnosti, No. 3, pp. 156 – 167, May – June, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souissi, S., Amar, M.B. & Bradai, C. Experimental investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of direct squeeze cast Al–13%Si alloy. Strength Mater 44, 337–345 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-012-9387-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-012-9387-0