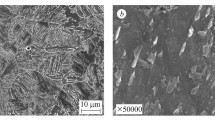
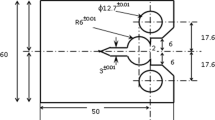
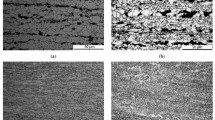
We evaluate, by means of fractographic analysis of fracture surfaces, changes in failure mechanism depending on the test temperature of ultra-hard low alloy steels ARMOX 500 T and ARMOX 600 T. Experimental investigation temperatures range was from −80 to 100°C, where the occurrence of a limit state in material is highly probable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISO 148–1:2009 – Metallic Materials – Charpy Pendulum Impact Test – Part 1: Test Method, Geneva (2009).
H. L. Yu and D. Y. Jeong, “Application of stress-triaxiality dependent fracture criteria for unnotched Charpy specimens,” in: G. C. Sih et al. (Eds.), Transferability and Applicability of Current Mechanics Approaches, ECUST, Shanghai (2009), pp. 41–51.
H. L. Yu and D. Y. Jeong, “Application of a stress triaxiality dependent fracture criterion in the finite element analysis of unnotched Charpy specimens,” Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech., 54, 54–62 (2010).
T. A. Baser, C. Leinenbach, and H. J. Schindlet, “Fracture behaviour of brazed soft martensitic stainless steel joints under cyclic loading,” in: L. G. Rosa and F. Margarido (Eds.), Advance Materials Forum V, TUL, Lisbon (2010), pp. 1490–1495.
C. Leinenbach, H. J. Schindlet, T. A. Baser, et al., “Quasistatic fracture behaviour and defect assessment of brazed soft martensitic stainless steel joints,” in: J. Pokluda et. al. (Eds.), Engineering Failure Analysis, ECF 17, Brno (2010), pp. 672–682.
J. Man, M. Valtr, A. Weidner, et al.,“AFM study of surface relief evolution in 316L steel fatigued at low and high temperatures,” in: P. Lukas (Ed.), Fatigue 2010, IPM ASCR, Prague (2010), pp. 1625–1633.
J. Polak, T. Kruml, K. Obrtlik, et al., “Short crack growth in polycrystalline materials,” in: P. Lukas (Ed.), Fatigue 2010, IPM ASCR, Prague (2010), pp. 883–892.
J. Hornikova, P. Sandera, J. Pokluda, “Linear-elastic and elastoplastic mode ii and iii crack tip stress–strain fields in cylindrical specimens with circumferential crack,” in: M. H. Aliabadi et al. (Eds.), Advances in Fracture and Damage Mechanics VIII, FDM 09, St. George (2010). pp. 321–324.
Acknowledgement
The work was supported by Ministry of Defence of the Czech Republic, Project No. FVT 0000404.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Problemy Prochnosti, No. 5, pp. 74 – 81, September – October, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binar, T., Kadlec, J., Rejzek, M. et al. Evaluation of the test temperature effect on failure mechanisms and notched impact strength characteristics of ultra-hard low alloy steels. Strength Mater 43, 537–542 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-011-9325-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-011-9325-6