Abstract
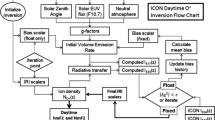
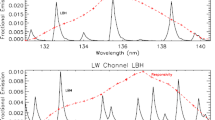
The NASA Ionospheric Connection Explorer Extreme Ultraviolet spectrograph, ICON EUV, images one-dimensional altitude profiles of the daytime extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) airglow between 54-88 nm. This spectral range contains several OII emission features derived from the photoionization of atomic oxygen by solar EUV. The primary target of the ICON EUV is the bright OII (4P – 4S) triplet emission spanning 83.2-83.4 nm that is used in combination with a dimmer but complementary feature (2P – 2D) spanning 61.6-61.7 nm that are jointly analyzed with an algorithm that uses discrete inverse theory to optimize a forward model of these emissions to infer the best-fit solution of ionospheric O+ density profile between 150-450 km. From this result, the daytime ionospheric F-region peak electron density and height, NmF2 and hmF2 respectively, are inferred. The science goals of ICON require these measurements be made in the regions of interest with a vertical resolution in hmF2 of 20 km and a 20% precision in NmF2 within a 60-second integration corresponding to a 500 km sampling along the orbit track. This paper describes the results from the ICON EUV over the first year of the mission, which occurred primarily under solar minimum conditions. It describes adjustments made to the algorithm to improve not only the quality of data products during this time, but also to improve speed and performance while simultaneously meeting the ICON measurement requirements. It also provides examples of results and an overview of key features and limitations to consider when using these products for scientific studies.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This analysis used version 03 of the Level 2.6 ICON-EUV data which are available from the ICON website (https://icon.ssl.berkeley.edu/Data) and NASA’s Space Physics Data Facility (https://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/data/icon/).
References
Bevington PR, Robinson KR (1992) Data reduction and error analysis for the physical sciences. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York
Bilitza D, Reinisch BW (2008) International reference ionosphere 2007: improvements and new parameters. Adv Space Res 42:599–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.07.048
Bilitza D, Altadill D, Truhlik V, Shubin V, Galkin I, Reinisch B, Huang X (2017) International reference ionosphere 2016: from ionospheric climate to real-time weather predictions. Space Weather 15:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016SW001593
Emmert JT, Picone JM, Meier RR (2008) Thermospheric global average density trends, 1967–2007, derived from orbits of 5000 near-earth objects. Geophys Res Lett 35(5):L05101. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl032809
Hinteregger HE, Fukui K, Gilson BR (1981) Observational, reference and model data on solar EUV from measurements on AE-E. Geophys Res Lett 8:1147–1150. https://doi.org/10.1029/GL008i011p01147
Immel TJ, England SL, Mende SB, Heelis RA, Englert CR, Edelstein J et al. (2018) The ionospheric connection explorer mission: mission goals and design. Space Sci Rev 214(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0449-2
Korpela EJ, Sirk MM, Edelstein J, McPhate JB, Tuminello RM, Stephan AW et al (2022, submitted) In-flight performance of the ICON EUV spectrograph. Space Sci Rev
Lean JL, Woods TN, Eparvier FG, Meier RR, Strickland DJ, Correira JT, Evans JS (2011) Solar extreme ultraviolet irradiance: present, past, and future. J Geophys Res 116:A01102. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JA015901
Meier RR et al. (2015) Remote sensing of Earth’s limb by TIMED/GUVI: retrieval of thermospheric composition and temperature. Earth Space Sci 2:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014EA000035
Sirk MM, Korpela EJ, Ishikawa Y, Edelstein J, Wishnow EH, Smith C et al. (2017) Design and performance of the ICON EUV spectrograph. Space Sci Rev 212:631–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0384-2
Stephan AW, Finn SC, Cook TA, Geddes G, Chakrabarti S, Budzien SA (2019) Imaging of the daytime ionospheric equatorial arcs with extreme and far ultraviolet airglow. J Geophys Res Space Phys 124:6074–6086. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA026624
Stephan AW, Korpela EJ, Sirk MM, England SL, Immel TJ (2017) Daytime ionosphere retrieval algorithm for the Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON). Space Sci Rev 212:645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0385-1
Stephan AW (2016) Advances in remote sensing of the daytime ionosphere with EUV airglow. J Geophys Res Space Phys 121:9284–9292. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JA022629
Stephan AW, Picone JM, Budzien SA, Bishop RL, Christensen AB, Hecht JH (2012) Measurement and application of the O II 61.7 nm dayglow. J Geophys Res 117:A01316. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA016897
Wautelet G, Hubert B, Gérard J-C, Immel TJ, Sirk MM, Korpela EJ et al. (2022) Comparison of ICON-EUV F-peak characteristic parameters with external data sources. Space Sci Rev 218:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-022-00930-2
Acknowledgements
ICON is supported by the NASA Explorers Program through contracts NNG12FA45C and NNG12FA42I. We gratefully acknowledge the contributions from the entire ICON team, including Tori Fae and Irene Rosen in the ICON Science Data Center, and the ICON mission operations staff. AWS acknowledges R. R. Meier for his supporting contributions to the validation and testing of the algorithm, and Judith Lean for providing the alternate solar EUV flux model used for algorithm testing and validation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) Mission: First Results
Edited by David E. Siskind and Ruth S. Lieberman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephan, A.W., Sirk, M.M., Korpela, E.J. et al. Characterization of the Daytime Ionosphere with ICON EUV Airglow Limb Profiles. Space Sci Rev 218, 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-022-00933-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-022-00933-z