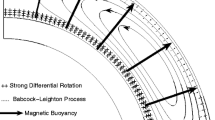
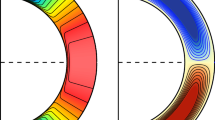
Abstract
Over the past several decades, Flux-Transport Dynamo (FTD) models have emerged as a popular paradigm for explaining the cyclic nature of solar magnetic activity. Their defining characteristic is the key role played by the mean meridional circulation in transporting magnetic flux and thereby regulating the cycle period. Most FTD models also incorporate the so-called Babcock-Leighton (BL) mechanism in which the mean poloidal field is produced by the emergence and subsequent dispersal of bipolar active regions. This feature is well grounded in solar observations and provides a means for assimilating observed surface flows and fields into the models in order to forecast future solar activity, to identify model biases, and to clarify the underlying physical processes. Furthermore, interpreting historical sunspot records within the context of FTD models can potentially provide insight into why cycle features such as amplitude and duration vary and what causes extreme events such as Grand Minima. Though they are generally robust in a modeling sense and make good contact with observed cycle features, FTD models rely on input physics that is only partially constrained by observation and that neglects the subtleties of convective transport, convective field generation, and nonlinear feedbacks. Here we review the formulation and application of FTD models and assess our current understanding of the input physics based largely on complementary 3D MHD simulations of solar convection, dynamo action, and flux emergence.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that Balbus and Schaan (2012) attribute the solar differential rotation to a meridional flow induced by centrifugal distortion of the base of the CZ. However, though this can influence the Ω profile, it cannot establish the equatorward Ω gradient observed in the Sun. For a discussion of this issue see the Appendix of Miesch et al. (2012).
References
K.C. Augustson, A.S. Brun, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Cycling dynamo in a young sun: grand minima and equatorward propagation. Astrophys. J. (2014 submitted)
H.W. Babcock, The topology of the sun’s magnetic field and the 22-year cycle. Astrophys. J. 133, 572 (1961)
S.A. Balbus, E. Schaan, The stability of stratified, rotating systems and the generation of vorticity in the sun. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 426, 1546–1557 (2012)
S.A. Balbus, J. Bonart, H.N. Latter, N.O. Weiss, Differential rotation and convection in the sun. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 400, 176–182 (2009)
S.A. Balbus, H. Latter, N. Weiss, Global model of differential rotation in the sun. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 420, 2457–2466 (2012)
T. Baranyi, L. Gyori, A. Ludmány, H.E. Coffey, Comparison of sunspot area data bases. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 323, 223–230 (2001)
A.J. Barker, L.J. Silvers, M. Proctor, N. Weiss, Magnetic buoyancy instabilities in the presence of magnetic flux pumping at the base of the solar convection zone. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 424, 115–127 (2012)
I. Baumann, D. Schmitt, M. Schüssler, S.K. Solanki, Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field on the solar surface: a parameter study. Astron. Astrophys. 426, 1075–1091 (2004)
P. Beaudoin, P. Charbonneau, E. Racine, P.K. Smolarkiewicz, Torsional oscillations in a global solar dynamo. Sol. Phys. 282, 335–360 (2013)
J. Beer, S. Tobias, N.O. Weiss, An active sun throughout the Maunder minimum. Sol. Phys. 181, 237–249 (1998)
A. Brandenburg, K. Subramanian, Astrophysical magnetic fields and nonlinear dynamo theory Phys. Rep. 417, 1–209 (2005)
A. Brandenburg, F. Krause, R. Meinel, D. Moss, I. Tuominen, The stability of nonlinear dynamos and the limited role of kinematic growth rates. Astron. Astrophys. 213, 411–422 (1989)
A. Brandenburg, D. Moss, I. Tuominen, Turbulent pumping in the solar dynamo, in The Solar Cycle, vol. 27 (1992), p. 536
A. Brandenburg, N. Kleeorin, I. Rogachevskii, Large-scale magnetic flux concentrations from turbulent stresses. Astron. Nachr. 331, 5–13 (2010)
A. Brandenburg, K. Koen, N. Kleeorin, I. Rogachevskii, The negative effective magnetic pressure in stratified forced turbulence. Astrophys. J. 749, 179 (2012)
B.P. Brown, M.K. Browning, A.S. Brun, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Persistent magnetic wreathes in a rapidly rotating sun. Astrophys. J. 711, 424–438 (2010)
B.P. Brown, M.S. Miesch, M.K. Browning, A.S. Brun, J. Toomre, Magnetic cycles in a convective dynamo simulation of a young solar-type star. Astrophys. J. 731, 69 (2011)
M.K. Browning, M.S. Miesch, A.S. Brun, J. Toomre, Dynamo action in the solar convection zone and tachocline: pumping and organization of toroidal fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 648, L157–L160 (2006)
A.S. Brun, J. Toomre, Turbulent convection under the influence of rotation: sustaining a strong differential rotation. Astrophys. J. 570, 865–885 (2002)
A.S. Brun, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Modeling the dynamical coupling of the solar convection zone to the radiative interior. Astrophys. J. 742, 79 (2011)
P. Caligari, F. Moreno-Insertis, M. Schüssler, Emerging flux tubes in the solar convection zone. 1: Asymmetry, tilt, and emergence latitude. Astrophys. J. 441, 886–902 (1995)
R. Cameron, M. Schüssler, Solar cycle prediction using precursors and flux transport models. Astrophys. J. 659, 801–811 (2007)
R.H. Cameron, D. Schmitt, J. Jiang, E. Işık, Surface flux evolution constraints for flux transport dynamos. Astron. Astrophys. 542, A127 (2012)
R.H. Cameron, M. Dasi-Espuig, J. Jiang, E. Işık, D. Schmitt, M. Schüssler, Limits to solar cycle predictability: cross-equatorial flux plumes. Astron. Astrophys. 557, A141 (2013)
S. Chakraborty, P. Chatterjee, A.R. Choudhuri, Why does the sun’s torsional oscillation begin before the sunspot cycle? Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 041102 (2009)
P. Charbonneau, Multiperiodicity, chaos and intermittency in a reduced model of the solar cycle. Sol. Phys. 199, 385 (2001)
P. Charbonneau, Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 7, 3 (2010)
P. Charbonneau, Where is the solar dynamo? J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 440, 012014 (2013)
P. Charbonneau, M. Dikpati, Stochastic fluctuations in a Babcock-Leighton model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 543, 1027–1043 (2000)
P. Charbonneau, G. Blais-Laurier, C. St-Jean, Intermittency and phase persistence in a Babcock-Leighton model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 616, L183–L186 (2004)
P. Charbonneau, C. St-Jean, P. Zacharias, Fluctuations in Babcock-Leighton dynamos. I. Period doubling and transition to chaos. Astrophys. J. 619, 613–622 (2005)
P. Charbonneau, G. Beaubien, C. St-Jean, Fluctuations in Babcock-Leighton dynamos. II. Revisiting the Gnevyshev-Ohl rule. Astrophys. J. 658, 657–662 (2007)
P. Chatterjee, A.R. Choudhuri, On magnetic coupling between the two hemispheres in solar dynamo models. Sol. Phys. 239, 29–39 (2006)
P. Chatterjee, D. Nandy, A.R. Choudhuri, Full-sphere simulations of a circulation-dominated solar dynamo: exploring the parity issue. Astron. Astrophys. 427, 1019–1030 (2004)
M. Cheung, M. Rempel, A.M. Title, M. Schüssler, Simulation of the formation of a solar active region. Astrophys. J. 720, 233–244 (2010)
D.-Y. Chou, D.-C. Dai, Solar cycle variations of subsurface meridional flows in the sun. Astrophys. J. 559, L175–L178 (2001)
A.R. Choudhuri, The evolution of loop structures in flux rings within the solar convection zone. Sol. Phys. 123, 217–239 (1989)
A.R. Choudhuri, A correction to Spruit’s equation for the dynamics of thin flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 239, 335–339 (1990)
A.R. Choudhuri, Stochastic fluctuations of the solar dynamo. Sol. Phys. 253, 277–285 (1992)
A.R. Choudhuri, The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas: An Introduction for Astrophysicists (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998). QB466.F58 C46
A.R. Choudhuri, On the connection between mean field dynamo theory and flux tubes. Sol. Phys. 215, 31–55 (2003)
A.R. Choudhuri, The origin of the solar magnetic cycle. Pramana 77, 77–96 (2011)
A.R. Choudhuri, P.A. Gilman, The influence of the Coriolis force on flux tubes rising through the solar convection zone. Astrophys. J. 316, 788–800 (1987)
A.R. Choudhuri, B.B. Karak, A possible explanation of the Maunder minimum from a flux transport dynamo model. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 953–958 (2009)
A.R. Choudhuri, B.B. Karak, Origin of grand minima in sunspot cycles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 171103 (2012)
A.R. Choudhuri, M. Schüssler, M. Dikpati, The solar dynamo with meridional circulation. Astron. Astrophys. 303, L29 (1995)
A.R. Choudhuri, D. Nandy, P. Chatterjee, Reply to the comments of Dikpati et al.. Astron. Astrophys. 437, 703–704 (2005)
A.R. Choudhuri, P. Chatterjee, J. Jiang, Predicting solar cycle 24 with a solar dynamo model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 131103 (2007)
J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, Helioseismology. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 1073–1129 (2002)
C. Cincunegui, R.F. Diaz, P.J.D. Mauas, A possible activity cycle in Proxima Centauri. Astron. Astrophys. 461, 1107–1113 (2007)
M. Dasi-Espuig, S.K. Solanki, N.A. Krivova, R. Cameron, K. Peñuela, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 518, A7 (2010)
M. Dikpati, Generating the suns global meridional circulation from differential rotation and turbulent Reynolds stresses. Astrophys. J. 438, 2380–2394 (2014)
M. Dikpati, P. Charbonneau, A Babcock-Leighton flux transport dynamo with solar-like differential rotation. Astron. Astrophys. 518, 508–520 (1999)
M. Dikpati, A.R. Choudhuri, On the large-scale diffuse magnetic field of the sun. Sol. Phys. 161, 9–27 (1995)
M. Dikpati, P.A. Gilman, Simulating and predicting solar cycles using a flux-transport dynamo. Astrophys. J. 649, 498–514 (2006)
M. Dikpati, G. de Toma, P.A. Gilman, C.N. Arge, O.R. White, Diagnostics of polar field reversal in solar cycle 23 using a flux transport dynamo model. Astrophys. J. 601, 1136–1151 (2004)
M. Dikpati, G. de Toma, P.A. Gilman, Predicting the strength of solar cycle 24 using a flux-transport dynamo-based tool. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, 5102 (2006)
S. D’Silva, A.R. Choudhuri, A theoretical model for tilts of bipolar magnetic regions. Astron. Astrophys. 272, 621 (1993)
B.R. Durney, On a Babcock-Leighton dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field. Sol. Phys. 160, 213–235 (1995)
B.R. Durney, On a Babcock-Leighton solar dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field. IV. Astrophys. J. 724, 1065 (1997)
B.R. Durney, On the differences between odd and even solar cycles. Sol. Phys. 196, 421 (2000)
J.R. Elliott, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Turbulent solar convection and its coupling with rotation: the effect of Prandtl number and thermal boundary conditions on the resulting differential rotation. Astrophys. J. 533, 546–556 (2000)
Y. Fan, Magnetic fields in the solar convection zone. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 6, 4 (2009). http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-4
Y. Fan, F. Fang, A simulation of convective dynamo in the solar convective envelope: maintenance of the solar-like differential rotation and emerging flux. Astrophys. J. 789, 35 (2014)
Y. Fan, G.H. Fisher, E.E. Deluca, The origin of morphological asymmetries in bipolar active regions. Astrophys. J. 405, 390–401 (1993)
N.A. Featherstone, M.S. Miesch, Meridional circulation in solar and stellar convection zones. Astrophys. J. (2014 submitted)
A. Ferriz-Mas, M. Schüssler, Instabilities of magnetic flux tubes in a stellar convection zone II. Flux rings outside the equatorial plane. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 81, 233–265 (1995)
P. Foukal, An explanation of the differences between the sunspot area scales of the Royal Greenwich and Mt. Wilson Observatories, and the SOON program. Sol. Phys. 289(5), 1517–1529 (2014)
D.J. Galloway, N.O. Weiss, Convection and magnetic fields in stars. Astrophys. J. 243, 945–953 (1981)
T. Gastine, J. Wicht, J.M. Aurnou, Zonal flow regimes in rotating anelastic spherical shells: an application to giant planets. Icarus 225, 156–172 (2013)
M. Ghizaru, P. Charbonneau, P.K. Smolarkiewicz, Magnetic cycles in global large-eddy simulations of solar convection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 715, L133–L137 (2010)
P.A. Gilman, Dynamically consistent nonlinear dynamos driven by convection in a rotating spherical shell. II—Dynamos with cycles and strong feedbacks. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 53, 243–268 (1983)
P.A. Gilman, M. Miesch, Limits to penetration of meridional circulation below the solar convection zone. Astrophys. J. 611, 568–574 (2004)
L. Gizon, Helioseismology of time-varying flows through the solar cycle. Sol. Phys. 224, 217–228 (2004)
G.A. Glatzmaier, Numerical simulations of stellar convective dynamos. I. The model and method. J. Comput. Phys. 55, 461–484 (1984)
G.A. Glatzmaier, Numerical simulations of stellar convective dynamos. II. Field propagation in the convection zone. Astrophys. J. 291, 300–307 (1985)
G.A. Glatzmaier, P.H. Roberts, A three-dimensional convective dynamo solution with rotating and finitely conducting inner core and mantle. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 91, 63–75 (1995)
A. Goel, A.R. Choudhuri, The hemispheric asymmetry of solar activity during the last century and the solar dynamo. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 115–126 (2009)
I. González-Hernandez, R. Komm, F. Hill, R. Howe, T. Corbard, D.A. Haber, Meridional circulation variability from large-aperture ring-diagram analysis of global oscillation network group and Michelson Doppler Imager data. Astrophys. J. 638, 576–583 (2006)
G.A. Guerrero, E.M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, Turbulent magnetic pumping in a Babcock-Leighton solar dynamo model. Astron. Astrophys. 485, 267–273 (2008)
G.A. Guerrero, J.D. Muñoz, Kinematic solar dynamo models with a deep meridional flow. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 350, 317–322 (2004)
S.M. Hanasoge, T. Duvall, M.L. DeRosa, Seismic constraints on interior solar convection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 712, L98–L102 (2010)
S.M. Hanasoge, T. Duvall, K.R. Sreenivasan, Anomalously weak solar convection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (2012). doi:10.1073/pnas.1206570109
D.H. Hathaway, The solar cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 7, 1 (2010)
D.H. Hathaway, Supergranules as probes of the sun’s meridional circulation. Astrophys. J. 760, 84 (2012), 6pp.
D.H. Hathaway, L. Rightmire, Variations in the sun’s meridional flow over a solar cycle. Science 327, 1350 (2010)
D.H. Hathaway, L. Rightmire, Variations in the axisymmetric transport of magnetic elements on the sun: 1996–2010. Astrophys. J. 729, 80 (2011)
P.H. Haynes, C.J. Marks, M.E. McIntyre, T.G. Shepherd, K.P. Shine, On the downward control of extratropical diabatic circulations by eddy-induced mean zonal flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 651–678 (1991)
G. Hazra, B.B. Karak, A.R. Choudhuri, Is a deep one-cell meridional circulation essential for the flux transport solar dynamo? Astrophys. J. 782, 93 (2014)
H. Hotta, T. Yokoyama, Solar parity issue with flux-transport dynamo. Astrophys. J. 714, L308–L312 (2010)
H. Hotta, M. Rempel, T. Yokoyama, High-resolution calculation of the solar global convection with the reduced sound speed technique: II. Near surface shear layer with the rotation. Astrophys. J. 786, 24 (2014)
R. Howe, Solar interior rotation and its variation. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 6, 1 (2009). http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-1
R. Howe, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, F. Hill, R.W. Komm et al., Dynamic variations at the base of the solar convection zone. Science 287, 2456–2460 (2000)
P. Hoyng, Turbulent transport of magnetic fields. III. Stochastic excitation of global magnetic modes. Astrophys. J. 332, 857–871 (1988)
P. Hoyng, Helicity fluctuations in mean field theory: an explanation for the variability of the solar cycle? Astron. Astrophys. 272, 321 (1993)
J. Jiang, P. Chatterjee, A.R. Choudhuri, Solar activity forecast with a dynamo model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 381, 1527–1542 (2007)
J. Jiang, R.H. Cameron, D. Schmitt, E. Işık, Modeling solar cycles 15 to 21 using a flux transport dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 553, A128 (2013)
J. Jiang, R.H. Cameron, M. Schüssler, Effects of the scatter in sunspot group tilt angles on the large-scale magnetic field at the solar surface. Astrophys. J. 791, 5 (2014a)
J. Jiang, D.H. Hathaway, R.H. Cameron, S.K. Solanki, L. Upton, Magnetic flux transport at the solar surface. Space Sci. Rev. (2014b). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0083-1
L. Jouve, A.S. Brun, On the role of meridional flows in flux transport dynamo models. Astron. Astrophys. 474, 239–250 (2007)
P.J. Käpyla, M.J. Mantere, A. Brandenburg, Cyclic magnetic activity due to turbulent convection in spherical wedge geometry. Astrophys. J. 755, L22 (2012)
P.J. Käpylä, M.J. Mantere, E. Cole, J. Warnecke, A. Brandenburg, Effects of enhanced stratification on equatorward dynamo wave propagation. Astrophys. J. 778, 41 (2013)
P.J. Käpylä, M. Mantere, A. Brandenburg, Confirmation of bistable stellar differential rotation profiles. Astron. Astrophys. (2014 accepted)
B.B. Karak, Importance of meridional circulation in flux transport dynamo: the possibility of a Maunder-like grand minimum. Astrophys. J. 724, 1021–1029 (2010)
B.B. Karak, A.R. Choudhuri, The Waldmeier effect and the flux transport solar dynamo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 410, 1503–1512 (2011)
B.B. Karak, A.R. Choudhuri, Quenching of meridional circulation in flux transport dynamo models. Sol. Phys. 278, 137–148 (2012)
B.B. Karak, A.R. Choudhuri, Studies of grand minima in sunspot cycles by using a flux transport solar dynamo model. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 13, 1339–1357 (2013)
B.B. Karak, D. Nandy, Turbulent pumping of magnetic flux reduces solar cycle memory and thus impacts predictability of the sun’s activity. Astrophys. J. 761, L13 (2012)
B.B. Karak, P.J. Käpyla, M.J. Käpyla, A. Brandenburg, Magnetically controlled stellar differential rotation near the transition from solar to anti-solar profiles. Astron. Astrophys. (2014a submitted). arXiv:1407.0984
B.B. Karak, M. Rheinhardt, A. Brandenburg, P.J. Käpylä, M.J. Käpylä, Quenching and anisotropy of hydromagnetic turbulent transport. Astrophys. J. (2014b accepted). arXiv:1406.4521
K. Kemel, A. Brandenburg, N. Kleeorin, D. Mitra, I. Rogachevskii, Active region formation through the negative effective magnetic pressure instability. Sol. Phys. 287, 293–313 (2013)
L.L. Kitchatinov, Turbulent transport of magnetic fields in a highly conducting rotating fluid and the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 243, 483–491 (1991)
L.L. Kitchatinov, Theory of differential rotation and meridional circulation, in Solar and Astrophysical Dynamos and Magnetic Activity, ed. by A.G. Kosovichev, E.M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, Y. Yan. Proc. IAU Symposium, vol. 294 (2013), pp. 399–410
L.L. Kitchatinov, S.V. Olemskoy, Does the Babcock-Leighton mechanism operate on the sun? Astron. Lett. 37, 656–658 (2011)
L.L. Kitchatinov, G. Rüdiger, Differential rotation in solar-type stars: revisiting the Taylor-number puzzle. Astron. Astrophys. 299, 446–452 (1995)
F. Krause, R. Meinel, Stability of simple nonlinear 2-dynamos. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 43, 95–117 (1988)
M. Küker, G. Rüdiger, M. Schultz, Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha-effect. Astron. Astrophys. 374, 301–308 (2001)
R.B. Leighton, A magneto-kinematic model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 156, 1–26 (1969)
D.W. Longcope, A.R. Choudhuri, The orientational relaxation of bipolar active regions. Astrophys. J. 205, 63–92 (2002)
I. Lopes, D. Passos, Solar variability induced in a dynamo code by realistic meridional circulation variations. Sol. Phys. 257, 1–12 (2009)
M.S. Miesch, The solar dynamo. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 370, 3049–3069 (2012)
M.S. Miesch, B.P. Brown, Convective Babcock-Leighton dynamo models. Astrophys. J. Lett. 746, L26 (2012)
M.S. Miesch, M. Dikpati, A three-dimensional Babcock-Leighton solar dynamo model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 785, L8 (2014), 5pp
M.S. Miesch, B.W. Hindman, Gyroscopic pumping in the solar near-surface shear layer. Astrophys. J. 743, 79 (2011)
M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Turbulence, magnetism and shear in stellar interiors. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 41, 317–345 (2009)
M.S. Miesch, A.S. Brun, J. Toomre, Solar differential rotation influenced by latitudinal entropy variations in the tachocline. Astrophys. J. 641, 618–625 (2006)
M.S. Miesch, N.A. Featherstone, M. Rempel, R. Trampedach, On the amplitude of convective velocities in the deep solar interior. Astrophys. J. 757, 128 (2012)
H.K. Moffatt, Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1978)
D. Moss, A. Brandenburg, R. Tavakol, I. Tuominen, Stochastic effects in mean-field dynamos. Astron. Astrophys. 265, 843–849 (1992)
A. Muñoz-Jaramillo, D. Nandy, P.C.H. Martens, A.R. Yeates, A double-ring algorithm for modeling solar active regions: unifying kinematic dynamo models and flux transport simulations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 720, L20–25 (2010)
A. Munoz-Jaramillo, D. Nandy, P.C.H. Martens, Magnetic quenching of turbulent diffusivity: reconciling mixing-length theory estimates with kinematic dynamo models of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. Lett. 727, L23 (2011)
A. Muñoz-Jaramillo, N.R. Sheeley Jr., J. Zhang, E.E. DeLuca, Calibrating 100 years of polar faculae measurements: implications for the evolution of the heliospheric magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 753, 146 (2012)
D. Nandy, A.R. Choudhuri, Toward a mean field formulation of the Babcock-Leighton type solar dynamo. I. α-Coefficient versus Durney’s double-ring approach. Astrophys. J. 551, 576–585 (2001)
D. Nandy, A.R. Choudhuri, Explaining the latitudinal distribution of sunspots with deep meridional flow. Science 296, 1671–1673 (2002)
N.J. Nelson, M.S. Miesch, Generating buoyant magnetic flux ropes in solar-like convective dynamos. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56, 064004 (2014)
N.J. Nelson, B.P. Brown, A.S. Brun, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Buoyant magnetic loops generated by global convective dynamo action. Sol. Phys. 289, 441–458 (2013a)
N.J. Nelson, B.P. Brown, A.S. Brun, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, Magnetic wreathes and cycles in convective dynamos. Astrophys. J. 762, 73 (2013b)
A.A. Norton, P. Charbonneau, D. Passos, Hemispheric coupling: comparing dynamo simulations and observations. Space Sci. Rev. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0100-4
S.V. Olemskoy, L.L. Kitchatinov, Grand minima and North-South asymmetry of solar activity. Astrophys. J. 777, 71 (2013)
S.V. Olemskoy, A.R. Choudhuri, L.L. Kitchatinov, Fluctuations in the alpha-effect and grand solar minima. Astron. Rep. 57, 458–468 (2013)
A.J.H. Ossendrijver, P. Hoyng, D. Schmitt, Stochastic excitation and memory of the solar dynamo. Astrophys. J. 313, 938–948 (1996)
A.J.H. Ossendrijver, M. Stix, A. Brandenburg, G. Rüdiger, Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients. Dependence of the alpha effect on rotation and magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 376, 713–726 (2001)
A.J.H. Ossendrijver, M. Stix, A. Brandenburg, G. Rüdiger, Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients. II. Field-direction dependent pumping of magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 394, 735–745 (2002)
E.N. Parker, Hydromagnetic dynamo models. Astrophys. J. 122, 293–314 (1955)
E.N. Parker, Solar magnetism: the state of our knowledge and ignorance. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 15–24 (2009)
D. Passos, P. Charbonneau, Characteristics of magnetic solar-like cycles in a 3D MHD simulation of solar convection. Astron. Astrophys. 568, A113 (2014)
D. Passos, I. Lopes, A low-order solar dynamo model: inferred meridional circulation variations since 1750. Astrophys. J. 686, 1420–1425 (2008)
D. Passos, I. Lopes, Grand minima under the light of a low order dynamo model. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 73, 191–197 (2011)
D. Passos, P. Charbonneau, P. Beaudoin, An exploration of non-kinematic effects in flux transport dynamos. Sol. Phys. 279, 1–22 (2012)
D. Passos, D. Nandy, S. Hazra, I. Lopes, A solar dynamo model driven by mean-field alpha and Babcock-Leighton sources: fluctuations, grand-minima-maxima, and hemispheric asymmetry in sunspot cycles. Astron. Astrophys. 563, A18 (2014)
J. Pedlosky, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 1987)
K. Petrovay, Topological pumping in the lower overshoot layer, in IAU Colloq. 130: The Sun and Cool Stars. Activity, Magnetism, Dynamos, ed. by I. Tuominen, D. Moss, G. Rüdiger. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol. 380 (Springer, Berlin, 1991), p. 67
M. Priyal, D. Banerjee, B.B. Karak, A. Muñoz-Jaramillo, B. Ravindra, A.R. Choudhuri, J. Singh, Polar network index as a magnetic proxy for the solar cycle studies. Astrophys. J. 793, L4 (2014)
E. Racine, P. Charbonneau, M. Ghizaru, A. Bouchat, P.K. Smolarkiewicz, On the mode of dynamo action in a global large-eddy simulation of solar convection. Astrophys. J. 735, 46 (2011)
K.H. Rädler, On the electrodynamics of conducting fluids in turbulent motion. II. Turbulent conductivity and turbulent permeability. Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, Phys. Phys. Chem. Kosmophys. 23, 1851–1860 (1968)
M. Rempel, Solar differential rotation and meridional flow: the role of a subadiabatic tachocline for the Taylor-Proudman balance. Astrophys. J. 622, 1320–1332 (2005)
M. Rempel, Flux-transport dynamos with Lorentz force feedback on differential rotation and meridional flow: saturation mechanism and torsional oscillations. Astrophys. J. 647, 662–667 (2006)
M. Rempel, Subsurface magnetic field and flow structure of simulated sunspots. Astrophys. J. 740, 15 (2011)
M. Rempel, M. Schüssler, Intensification of magnetic fields by conversion of potential energy. Astrophys. J. 552, L171–L174 (2001)
F.J. Robinson, K.L. Chan, A large-eddy simulation of turbulent compressible convection: differential rotation in the solar convection zone. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 321, 723–732 (2001)
I. Rogachevskii, N. Kleeorin, Magnetic fluctuations and formation of large-scale inhomogeneous magnetic structures in a turbulent convection. Phys. Rev. E 76, 056307 (2007)
G. Rüdiger, L.L. Kitchatinov, R. Arlt, The penetration of meridional flow into the tachocline and its meaning for the solar dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 444, L53–L56 (2005)
A. Schad, J. Timmer, M. Roth, Global helioseismic evidence for a deeply penetrating solar meridional flow consisting of multiple flow cells. Astrophys. J. Lett. 778, L38 (2013)
J. Schou, R. Howe, S. Basu, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard et al., A comparison of solar p-mode parameters from the Michelson Doppler Imager and the global oscillation network group: splitting coefficients and rotation inversions. Astrophys. J. 567, 1234–1249 (2002)
C. Simard, P. Charbonneau, A. Bouchat, Magnetohydrodynamics simulation-driven kinematic mean-field models of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 768, 16 (2013)
H.C. Spruit, Motion of magnetic flux tubes in the solar convection zone and chromosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 98, 155–160 (1981). In: The Sun, the Solar Wind, and the Heliosphere: Proc. IAGA
M. Steenbeck, F. Krause, On the dynamo theory of stellar and planetary magnetic fields. I. AC dynamos of solar type. Astron. Nachr. 291, 49–84 (1969)
M. Steenbeck, F. Krause, K.-H. Rädler, Berechnung der mittleren Lorentz-Feldstärke v×B Für ein elektrisch leitendes medium in turbulenter, durch Coriolis-Kräfte beeinflußter bewegung Z(0). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, Phys. Phys. Chem. Kosmophys. 21, 369 (1966)
R.F. Stein, A. Nordlund, On the formation of active regions. Astrophys. J. 753, L13 (2012)
J.O. Stenflo, A.G. Kosovichev, Bipolar magnetic regions on the sun: global analysis of the SOHO/MDI data set. Astrophys. J. 745, 129 (2012)
M. Stix, Differential rotation and the solar dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 47, 243–254 (1976)
J.L. Tassoul, Theory of Rotating Stars (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1978)
M.J. Thompson, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, M.S. Miesch, J. Toomre, The internal rotation of the sun. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 41, 599–643 (2003)
A.G. Tlatov, V.V. Vasil’eva, A.A. Pevtsov, Distribution of magnetic bipoles on the sun over three solar cycles. Astrophys. J. 717, 357–362 (2010)
S.M. Tobias, N.H. Brummell, T.L. Clune, J. Toomre, Transport and storage of magnetic field by overshooting turbulent compressible convection. Astrophys. J. 549, 1183–1203 (2001)
S.M. Tobias, F. Cattaneo, S. Boldyrev, MHD dynamos and turbulence, in Ten Chapters in Turbulence, ed. by P. Davidson, Y. Kaneda, K. Sreenivasan (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2013)
R. Trampedach, R.F. Stein, The mass mixing length in convective stellar envelopes. Astrophys. J. 731, 78 (2011)
R.K. Ulrich, Solar meridional circulation from Doppler shifts of the FeI line at 5250 a as measured by the 150-foot solar tower telescope at the Mt. Wilson Observatory. Astrophys. J. 725, 658–669 (2010)
I.G. Usoskin, S.K. Solanki, G.A. Kovaltsov, Grand minima and maxima of solar activity: new observational constraints. Astron. Astrophys. 471, 301–309 (2007)
A.A. van Ballegooijen, The overshoot layer at the base of the solar convection zone and the problem of magnetic flux storage. Astron. Astrophys. 113, 99–112 (1982)
G. Vasil, N. Brummell, Constraints on the magnetic buoyancy instabilities of a shear-generated magnetic layer. Astrophys. J. 690, 783–794 (2009)
M. Waldmeier, Mitt. Eidgenöss. Sternwarte Zür. 14, 105 (1935)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Magnetic flux transport and the sun’s dipole moment—new twists to the Babcock-Leighton model. Astrophys. J. 375, 761–770 (1991)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., The solar wind and interplanetary field during very low amplitude sunspot cycles. Astrophys. J. 764, 90 (2013)
Y.-M. Wang, A.G. Nash, N.R. Sheeley Jr., Magnetic flux transport on the sun. Science 245, 712–718 (1989)
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., A.G. Nash, A new solar cycle model including meridional circulation. Astrophys. J. 383, 431–442 (1991)
M.A. Weber, Y. Fan, M.S. Miesch, The rise of active region flux tubes in the turbulent solar convective envelope. Astrophys. J. 741, 11 (2011)
N.O. Weiss, Modulation of the sunspot cycle. Astron. Geophys. 51, 3.09–3.15 (2010)
A.R. Yeates, A. Muñoz-Jaramillo, Kinematic active region formation in a three-dimensional solar dynamo model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 436, 3366–3379 (2013)
A.R. Yeates, D. Nandy, D.H. Mackay, Exploring the physical basis of solar cycle predictions: flux transport dynamics and the persistence of memory in advection versus diffusion dominated solar convection zones. Astrophys. J. 673, 544–556 (2008)
H. Yoshimura, Solar-cycle dynamo wave propagation. Astrophys. J. 201, 740–748 (1975)
J. Zhao, A.G. Kosovichev, Torsional oscillation, meridional flows, and vorticity inferred in the upper convection zone of the sun by time-distance helioseismology. Astrophys. J. 603, 776–784 (2004)
J. Zhao, R.S. Bogart, A.G. Kosovichev, T.L. Duvall, T. Hartlep, Detection of equatorward meridional flow and evidence of double-cell meridional circulation inside the sun. Astrophys. J. Lett. 774, L29 (2013)
U. Ziegler, G. Rüdiger, Box simulations of rotating magnetoconvection. Effects of penetration and turbulent pumping. Astron. Astrophys. 401, 433–442 (2003)
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank ISSI and its staff for their hospitality and a most stimulating workshop in November 2013. J.J. acknowledges the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 11173033). M.S.M. is supported in part through grants MMH09AK14I, NNX11AJ36G, and NNX13AG18G. The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the National Science Foundation of the U.S.A. P.C. is supported by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. The research of A.R.C. is supported by a JC Bose Fellowship awarded by the Department of Science and Technology of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karak, B.B., Jiang, J., Miesch, M.S. et al. Flux Transport Dynamos: From Kinematics to Dynamics. Space Sci Rev 186, 561–602 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0099-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-014-0099-6