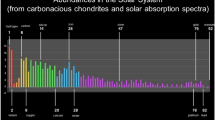
Abstract
The galactic cosmic rays arriving near Earth, which include both stable and long-lived nuclides from throughout the periodic table, consist of a mix of stellar nucleosynthesis products accelerated by shocks in the interstellar medium (ISM) and fragmentation products made by high-energy collisions during propagation through the ISM. Through the study of the composition and spectra of a variety of elements and isotopes in this diverse sample, models have been developed for the origin, acceleration, and transport of galactic cosmic rays. We present an overview of the current understanding of these topics emphasizing the insights that have been gained through investigations in the charge and energy ranges Z≲30 and E/M≲1 GeV/nuc, and particularly those using data obtained from the Cosmic Ray Isotope Spectrometer on NASA’s Advanced Composition Explorer mission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.R. Binns et al., in Cosmic Abundances of Matter, vol. CP183, ed. by C.J. Waddington (Amer. Instit. Phys., 1989), pp. 147–167
W.R. Binns et al., Astrophys. J. 634, 351–364 (2005)
W.R. Binns et al., Space Sci. Rev. (2007), this volume. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9195-1
G. Cescutti, F. Matteucci, P. François, C. Chiappini, Astron. Astrophys. 462, 943–951 (2007)
J.J. Connell, Space Sci. Rev. 99, 41–50 (2001)
A.J. Davis et al., in Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles Observed in the Heliosphere, vol. CP528, ed. by R.A. Mewaldt et al. (Amer. Instit. Phys., 2000), pp. 421–424
L.O’C. Drury, J. Korean Astron. Soc. 37, 393–398 (2004)
J.J. Engelmann et al., Astron. Astrophys. 233, 96–111 (1990)
J. Geiss, G. Gloeckler, C. Charbonnel, Astrophys. J. 578, 862–867 (2002)
J.S. George et al., in Solar and Galactic Composition, vol. CP598, ed. by R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (Amer. Instit. Phys., 2001), pp. 263–268
L.J. Gleeson, W.I. Axford, Astrophys. J. 154, 1011–1026 (1968)
M.L. Goldstein, L.A. Fisk, R. Ramaty, Phys. Rev. Lett. 25, 832–835 (1970)
J.C. Higdon, R.E. Lingenfelter, Astrophys. J. 628, 738–749 (2005)
K. Iwamoto et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 125, 439–462 (1999)
J.R. Jokipii, J. Kóta, Astrophys. Space Sci. 274, 77–96 (2000)
R.E. Lingenfelter, J.C. Higdon, Astrophys. J. 660, 330–335 (2007a)
R.E. Lingenfelter, J.C. Higdon, Space Sci. Rev. (2007b), this volume. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9172-8
K. Lodders, Astrophys. J. 591, 1220–1247 (2003)
M. Meneguzzi, J. Audouze, H. Reeves, Astron. Astrophys. 15, 337–359 (1971)
R.A. Mewaldt et al., in Solar and Galactic Composition, vol. CP598, ed. by R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (Amer. Instit. Phys., 2001), pp. 165–170
J.-P. Meyer, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 57, 173–204 (1985)
J.-P. Meyer, L.O’C. Drury, D.C. Ellison, Astrophys. J. 487, 182–196 (1997)
V.S. Ptuskin, A. Soutoul, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 225–238 (1998)
B.E. Reddy, J. Tomkin, D.L. Lambert, C.A. Prieto, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 340, 304–340 (2003)
L.M. Scott, Ph.D. thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, 2005
A. Soutoul, M. Cassé, E. Juliusson, Astrophys. J. 219, 753–755 (1978)
E.C. Stone et al., Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1–22 (1998a)
E.C. Stone et al., Space Sci. Rev. 86, 285–356 (1998b)
A.W. Strong, I.V. Moskalenko, V.S. Ptuskin, Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 57 (2007, in press) astro-ph/0701517
S.P. Swordy, Space Sci. Rev. 99, 85–94 (2001)
S.P. Swordy, D. Müller, P. Meyer, J. L’Heureux, J.M. Grunsfeld, Astrophys. J. 349, 625–633 (1999)
M.R. Thayer, Astrophys. J. 482, 792–795 (1997)
F.X. Timmes, S.E. Woosley, T.A. Weaver, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 98, 617–658 (1995)
C.J. Waddington, Space Sci. Rev. (2007), this volume. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9145-y
A.J. Westphal, J.P. Bradley, Astrophys. J. 617, 1131–1141 (2004)
J.Z. Wang et al., Astrophys. J. 564, 244–259 (2002)
W.R. Webber, A. Soutoul, J.C. Kish, J.M. Rockstroh, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 144, 153–167 (2003)
M.E. Wiedenbeck et al., Astrophys. J. (Lett.) 523, L61–L64 (1999)
M.E. Wiedenbeck et al., in Solar and Galactic Composition, vol. CP598, ed. by R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (Amer. Instit. Phys., 2001), pp. 269–274
S.E. Woosley, T.A. Weaver, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 101, 181–235 (1995)
N.E. Yanasak et al., Astrophys. J. 563, 768–792 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiedenbeck, M.E., Binns, W.R., Cummings, A.C. et al. An Overview of the Origin of Galactic Cosmic Rays as Inferred from Observations of Heavy Ion Composition and Spectra. Space Sci Rev 130, 415–429 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-007-9198-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-007-9198-y