Abstract
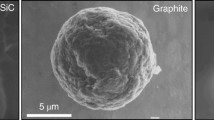
Small amounts of pre-solar “stardust” grains have survived in the matrices of primitive meteorites and interplanetary dust particles. These grains—formed directly in the outflows of or from the ejecta of stars—include thermally and chemically refractory carbon materials such as diamond, graphite and silicon carbide; as well as refractory oxides and nitrides. Pre-solar silicates, which have only recently been identified, are the most abundant type except for possibly diamond. The detailed study with modern analytical tools, of isotopic signatures in particular, provides highly accurate and detailed information with regard to stellar nucleosynthesis and grain formation in stellar atmospheres. Important stellar sources are Red Giant (RG) and Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars, with supernova contributions apparently small. The survival of those grains puts constraints on conditions they were exposed to in the interstellar medium and in the early solar system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Amari, P. Hoppe, E. Zinner, R.S. Lewis, Meteoritics 30, 679–693 (1995)
S. Amari, L.R. Nittler, E. Zinner, K. Lodders, R.S. Lewis, Astrophys. J. 559, 463–483 (2001a)
S. Amari, L.R. Nittler, E. Zinner, R. Gallino, M. Lugaro, R.S. Lewis, Astrophys J. 546, 248–266 (2001b)
E. Anders, E. Zinner, Meteoritics 28, 490–514 (1993)
T.J. Bernatowicz, S. Messenger, O. Pravdivtseva, P. Swan, R.M. Walker, Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 67, 4679–4691 (2003)
M. Busso, R. Gallino, G.J. Wasserburg, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 37, 239–309 (1999)
M. Chaussidon, F. Robert, K.D. McKeegan, Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 70, 224–245 (2006)
D.D. Clayton, Astrophys. J. 334, 191–195 (1988)
T.K. Croat, F.J. Stadermann, T.J. Bernatowicz, Astrophys. J. 631, 976–987 (2005)
S.J. Desch, H.C. Connolly Jr., G. Srinivasan, Astrophys. J. 602, 528–542 (2004)
B.T. Draine, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 41, 241–289 (2003)
T. Henning, F. Salama, Science 282, 2204–2210 (1998)
M. Gounelle, F.H. Shuh, H. Shang, A.E. Glassgold, K.E. Rehm, T. Lee, Astrophys. J. 548, 1051–1070 (2001)
P. Hoppe, Nucl. Phys. A688, 94c–101c (2001)
P. Hoppe, U. Ott, in: Astrophysical Implications of the Laboratory Study of Presolar Materials, ed. by T.J. Bernatowicz, E. Zinner (American Institute of Physics, Woodbury 1997) pp. 27–58
P. Hoppe, E. Zinner, Geophys. Res. 105, 10371–10385 (2000)
P. Hoppe, P. Annen, R. Strebel, R. Eberhardt, P. Gallino, M. Lugaro, S. Amari, R.S. Lewis, Astrophys. J. 487, L101–L104 (1997)
P. Hoppe, U. Ott, G.W. Lugmair, New Ast. Rev. 48, 171–176 (2004)
G.R. Huss, R.S. Lewis, Meteoritics 29, 791–810 (1994)
A.P. Koscheev, M.D. Gromov, R.K. Mohapatra, U. Ott, Nature 412, 615–617 (2001)
K. Lodders, B. Fegley Jr., Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 33, 871–880 (1998)
R.D. Loss, G.W. Lugmair, A.M. Davis, G.J. MacPherson, Astrophys. J. 436, L193–L196 (1994)
B.S. Meyer, D.D. Clayton, The L.-S., Astrophys. J. 540, L49–L52 (2000)
L.R. Nittler, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 209, 259–273 (2003)
L.R. Nittler, C.M.O’D. Alexander, X. Gao, R.M. Walker, E. Zinner, Astrophys. J. 483, 475–495 (1997)
U. Ott, Nature 364, 25–33 (1993)
U. Ott, New Ast. Rev. 46, 513–518 (2002)
U. Ott, M. Altmaier, U. Herpers, J. Kuhnhenn, S. Merchel, R. Michel, R.K. Mohapatra, Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 40, 1635–1652 (2005)
T. Owen, P.R. Mahaffy, H.B. Niemann, S. Atreya, M. Wong, Astrophys. J. 553, L77–L79 (2001)
S. Richter, U. Ott, F. Begemann, Lunar Planet. Sci. XXVIII, 1163–1164 (1997)
S.S. Russell, J.W. Arden, C.T. Pillinger, Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 31, 343–355 (1996)
A.K. Speck, A.M. Hofmeister, M.J. Barlow, Astrophys. J. 513, L87–L90 (1999)
F.X. Timmes, D.D. Clayton, Astrophys. J. 472, 723–741 (1996)
A.B. Verchovsky, A.V. Fisenko, L.F. Semjonova, I.P. Wright, M.R. Lee, C.T. Pillinger, Science 281, 1165–1168 (1998)
A.B. Verchovsky, I.P. Wright, C.T. Pillinger, Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 20, 329–336 (2003)
A.B. Verchovsky, A.V. Fisenko, L.F. Semjonova, J. Bridges, M.R. Lee, I.P. Wright, Astrophys. J. 651, 481–490 (2006)
D.C.B. Whittet, Dust in the Galactic Environment (Inst. Phys., New York, 1992), 295 pp.
Q.-Z. Yin, C.-T.A. Lee, U. Ott, Astrophys. J. 647, 676–684 (2006)
E. Zinner, Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 26, 147–188 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ott, U. Presolar Grains in Meteorites and Their Compositions. Space Sci Rev 130, 87–95 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-007-9159-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-007-9159-5