Abstract
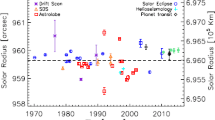
Solar oblateness is a key parameter that provides a strong constraint for understanding the variations in total solar irradiance as well as the differential rotation of the Sun. Furthermore, it takes part in the evaluation of General Relativity theory. In this paper, we propose a procedure to measure solar flattening based on modeling the light curve during a solar eclipse observed from the ground or from Earth orbit. We apply this procedure to synthetic data corresponding to the solar eclipse observed from Lakeland (Queensland, North Australia) on November 13, 2012. The results show that accurate measurements of the solar equator-to-polar radius difference can reach 1 km when based on the current DE430 ephemeris and the LRO DEM data (equivalent to \(1.4 \times 10^{-6}\) in solar oblateness).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antia, H.M., Basu, S., Chitre, S.M.: 2008, Solar rotation rate and its gradients during cycle 23. Astrophys. J. 681(1), 680.
Armstrong, J., Kuhn, J.R.: 1999, Interpreting the solar limb shape distortions. Astrophys. J. 525(1), 533.
Chandrasekhar, S.: 1933, The equilibrium of distorted polytopes: (I). The rotational problem. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 93, 390.
Chapman, G.A.: 2008, Aspects of our Sun. Science 322(5901), 535.
Damiani, C., Rozelot, J.P., Lefebvre, S., Kilcik, A., Kosovichev, A.G.: 2011, A brief history of the solar oblateness. A review. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73(2 – 3), 241. DOI.
Einstein, A.: 1916, Die Grundlage der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie. Ann. Phys. 354, 769.
Emilio, M., Bush, R.I., Kuhn, J., Scherrer, P.: 2007, A changing solar shape. Astrophys. J. 660(2), L161. DOI.
Eren, S., Rozelot, J.P.: 2023, Exploring the temporal variation of the solar quadrupole moment \(J_{2}\). Astrophys. J. 942(2), 90.
Fivian, M.D., Hudson, H.S., Lin, R.P., Zahid, H.J.: 2008, A large excess in apparent solar oblateness due to surface magnetism. Science 322(5901), 560. DOI.
Irbah, A., Meftah, M., Hauchecorne, A., Djafer, D., Corbard, T., Bocquier, M., et al.: 2014, New space value of the solar oblateness obtained with PICARD. Astrophys. J. 785(2), 89. DOI.
Irbah, A., Mecheri, R., Damé, L., Djafer, D.: 2019, Variations of solar oblateness with the 22 yr magnetic cycle explain apparently inconsistent measurements. Astrophys. J. Lett. 875(2), L26. DOI.
Kitiashvili, I.N., Kosovichev, A.G., Wray, A.A., Sadykov, V.M., Guerrero, G.: 2023, Leptocline as a shallow substructure of near-surface shear layer in 3D radiative hydrodynamic simulations. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 518(1), 504. DOI.
Klein, P.P.: 2012, On the ellipsoid and plane intersection equation. Appl. Math. 3(11), 1634.
Kuhn, J.R., Bush, R., Emilio, M., Scholl, I.F.: 2012, The precise solar shape and its variability. Science 337(6102), 1638. DOI.
Le Verrier, U.: 1846, Rapport à l’Académie des Sciences le 31 août 1846 et 1859. Ann. Obs. Paris 5, 104.
Mecheri, R., Abdelatif, T., Irbah, A., Provost, J., Berthomieu, G.: 2004, New values of gravitational moments \(J_{2}\) and \(J_{4}\) deduced from helioseismology. Solar Phys. 222(2), 191. DOI.
Meftah, M., Hauchecorne, A., Irbah, A., Corbard, T., Ikhlef, R., Morand, F., et al.: 2015a, On the constancy of the diameter of the Sun during the rising phase of solar cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 808(1), 4. DOI.
Meftah, M., Irbah, A., Hauchecorne, A., Corbard, T., Turck-Chièze, S., Hochedez, J.-F., et al.: 2015b, On the determination and constancy of the solar oblateness. Solar Phys. 290(3), 673. DOI.
Meftah, M., Hauchecorne, A., Bush, R.I., Irbah, A.: 2016, On HMI solar oblateness during solar cycle 24 and impact of the space environment on results. Adv. Space Res. 58(7), 1425. DOI.
Newcomb, S.: 1895, The Elements of the Four Inner Planets and the Fundamental Constants of Astronomy, US Government Printing Office.
Pireaux, S., Rozelot, J.P.: 2003, Solar quadrupole moment and purely relativistic gravitation contributions to Mercury’s perihelion advance. Astrophys. Space Sci. 284(4), 1159.
Pitjeva, E.V.: 1993, Experimental testing of relativistic effects, variability of the gravitational constant and topography of Mercury surface from radar observations 1964 – 1989. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 55(4), 313.
Reis Neto, E., Andrei, A.H., Penna, J.L., Jilinski, E.G., Puliaev, S.P.: 2003, Observed variations of the solar diameter in 1998/2000. Solar Phys. 212(1), 7. DOI.
Rozelot, J.P., Damiani, C.: 2011, History of solar oblateness measurements and interpretation. Eur. Phys. J. H 36(3), 407.
Rozelot, J.P., Damiani, C., Pireaux, S.: 2009, Probing the solar surface: the oblateness and astrophysical consequences. Astrophys. J. 703(2), 1791.
Rozelot, J.P., Eren, S.: 2020, Exploring the temporal variation of the solar quadrupole moment from relativistic gravitation contributions: a fortuitous circumstance? Adv. Space Res. 65(12), 2821.
Sofia, S., Girard, T.M., Sofia, U.J., Twigg, L., Heaps, W., Thuillier, G.: 2013, Variation of the diameter of the Sun as measured by the Solar Disk Sextant (SDS). Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 436(3), 2151. DOI.
Sturrock, P.A., Gilvarry, J.J.: 1967, Solar oblateness and magnetic field. Nature 216(5122), 1280.
Wang, Y.B., Yan, J.G., Ye, M., Yang, Y.-Z., Li, F., Barriot, J.-P.: 2021, Computation of the atmosphere-less light intensity curve during a total solar eclipse by using Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter topography data and the DE430 astronomical ephemeris. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 21(1), 011. DOI.
Wu, J., Yuan, Y., Gong, H., Tseng, T.L.: 2018, Inferring 3D ellipsoids based on cross-sectional images with applications to porosity control of additive manufacturing. IISE Trans. 50(7), 570. DOI.
Acknowledgments
The J2000 frame data provided by SPICE system and ephemeris/topography data provided by JPL/NASA. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42030110, U1831132); Jean-Pierre Barriot is supported by a DAR fund in planetology from the French Space Agency (CNES). The Lakeland photometric data were acquired with special funding from CNES as part of the “ground-truth” of the PICARD satellite mission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jean-Pierre Barriot and Jianguo Yan conceived of the presented idea. Jean-Pierre Barriot and Yunbo Wang developed the theory and performed the computations. Yunbo Wang wrote the main manuscript text with support from Jean-Pierre Barriot and Jianguo Yan. Jianguo Yan and Jean-Pierre Barriot helped supervise the project. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yan, J. & Barriot, JP. On the Possibility of Measuring Solar Flattening from Photometry Measurements Taken during Solar Eclipses Seen from the Earth’s Surface or Earth Orbit. Sol Phys 298, 76 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02172-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02172-z