Abstract
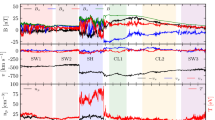
In this paper, using the measurements at the Sun–Earth first Lagrangian point (L1), the kinetic properties of the electron velocity distribution functions (EVDFs) during the passage of a typical halo coronal mass ejection (CME) has been analyzed. This CME was a front-sided, full halo CME, which erupted on 25 July 2004 (Carrington rotation 2019) from the active region NOAA AR 10652 (N04W30), and the CME reached at the L1 point ≈ 31 hours after the eruption. Solar wind electron measurements from the three-dimensional plasma (3DP) instrument onboard the WIND spacecraft and CME observations from the Large Angle and Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO) onboard the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) have been used for performing the present study. The velocity distributions of the electrons observed at the L1 point show distinct features representing the passage of the CME plasma and the associated magnetic cloud (MC). The relative enhancements in the core and the suprathermal electron populations were delineated from the EVDF measurements. This study shows that, relative to the ambient solar wind condition, the suprathermal electron population enhanced more than the core electron population during the CME passage at the spacecraft location. Following the CME sheath-shock plasma, a bidirectional electron streaming (BDE) representing a closed magnetic flux rope was observed. The Boltzmann entropy analysis of the event shows that the magnetic cloud held the largest share of the nonequilibrium Boltzmann entropy among all the CME sectors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bame, S., Asbridge, J., Feldman, W., Gosling, J., Zwickl, R.: 1981, Bi-directional streaming of solar wind electrons greater than 80 eV: ISEE evidence for a closed-field structure within the driver gas of an interplanetary shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 173. DOI.
Bothmer, V., Desai, M., Marsden, R., Sanderson, T., Trattner, K., Wenzel, K.-P., Gosling, J., Balogh, A., Forsyth, R., Goldstein, B.: 1996, Ulysses observations of open and closed magnetic field lines within a coronal mass ejection. Astron. Astrophys. 316, 493. ADS.
Brey, J.J., Santos, A.: 1992, Nonequilibrium entropy of a gas. Phys. Rev. A 45, 8566. DOI.
Brueckner, G., Howard, R., Koomen, M., Korendyke, C., Michels, D., Moses, J., Socker, D., Dere, K., Lamy, P., Llebaria, A., et al.: 1995, The large angle spectroscopic coronagraph (LASCO). In: The SOHO Mission, Springer, Berlin, 357. DOI. ADS.
Burlaga, L.F.: 1991, Magnetic clouds. In: Physics of the Inner Heliosphere II, Springer, Berlin, 1. DOI.
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 86, 6673. DOI. ADS.
Chen, F.F.: 2016, Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion. DOI. ADS.
Démoulin, P.: 2008, A review of the quantitative links between CMEs and magnetic clouds. In: Annales Geophysicae 26, 3113, Copernicus Publications, Germany. DOI. ADS.
Domingo, V., Fleck, B., Poland, A.I.: 1995, The SOHO mission: An overview. Solar Phys. 162, 1. DOI. ADS.
Dorelli, J.C., Scudder, J.D.: 1999, Electron heat flow carried by kappa distributions in the solar corona. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 3537. DOI. ADS.
Feldman, W., Asbridge, J., Bame, S., Montgomery, M.: 1974, Interpenetrating solar wind streams. Rev. Geophys. 12, 715. DOI. ADS.
Feldman, W., Asbridge, J., Bame, S., Montgomery, M., Gary, S.: 1975, Solar wind electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4181. DOI.
Feldman, W., Anderson, R., Asbridge, J., Bame, S., Gosling, J., Zwickl, R.: 1982, Plasma electron signature of magnetic connection to the Earth’s bow shock: ISEE 3. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 87, 632. DOI. ADS.
Feldman, W., Anderson, R., Bame, S., Gary, S., Gosling, J., McComas, D., Thomsen, M., Paschmann, G., Hoppe, M.: 1983, Electron velocity distributions near the Earth’s bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 88, 96. DOI.
Fitzenreiter, R., Ogilvie, K., Chornay, D., Keller, J.: 1998, Observations of electron velocity distribution functions in the solar wind by the WIND spacecraft: High angular resolution Strahl measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 249. DOI. ADS.
Gloeckler, G., Fisk, L.: 2006, Anisotropic beams of energetic particles upstream from the termination shock of the solar wind. Astrophys. J. Lett. 648, L63. DOI. ADS.
Gloeckler, G., Cain, J., Ipavich, F., Tums, E., Bedini, P., Fisk, L., Zurbuchen, T., Bochsler, P., Fischer, J., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R., et al.: 1998, Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pickup ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ace spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 497. DOI.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2007, Geoeffectiveness of halo coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112(A6), A06112. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.: 2010, A catalog of halo coronal mass ejections from SOHO. Sun Geosph. 5, 7. ADS.
Gosling, J.T.: 1990, Coronal Mass Ejections and Magnetic Flux Ropes in Interplanetary Space. Physics of Magnetic Flux Ropes 58, 343. DOI. ADS.
Gosling, J., Baker, D., Bame, S., Feldman, W., Zwickl, R., Smith, E.: 1987, Bidirectional solar wind electron heat flux events. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 8519. DOI.
Gosling, J., Bame, S., Feldman, W., McComas, D., Phillips, J., Goldstein, B.: 1993, Counterstreaming suprathermal electron events upstream of corotating shocks in the solar wind beyond 2 AU: Ulysses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 2335. DOI. ADS.
Gosling, J., McComas, D., Phillips, J., Weiss, L., Pizzo, V., Goldstein, B., Forsyth, R.: 1994, A new class of forward-reverse shock pairs in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 2271. DOI. ADS.
Halekas, J., Whittlesey, P., Larson, D., McGinnis, D., Maksimovic, M., Berthomier, M., Kasper, J., Case, A., Korreck, K., Stevens, M., et al.: 2020, Electrons in the young solar wind: First results from the Parker Solar Probe. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 246, 22. DOI. ADS.
Klein, L., Burlaga, L.: 1982, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 87, 613. ADS.
Lazar, M., Pomoell, J., Poedts, S., Dumitrache, C., Popescu, N.: 2014, Solar wind electron Strahls associated with a high-latitude CME: Ulysses observations. Solar Phys. 289, 4239. DOI. ADS.
Lemaire, J., Pierrard, V.: 2001, Kinetic models of solar and polar winds. Astrophys. Space Sci. 277, 169. DOI. ADS.
Lemaire, J., Scherer, M.: 1973, Kinetic models of the solar and polar winds. Rev. Geophys. 11, 427. DOI.
Lepping, R., Jones, J., Burlaga, L.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 95, 11957. DOI.
Lepping, R., Acũna, M., Burlaga, L., Farrell, W., Slavin, J., Schatten, K., Mariani, F., Ness, N., Neubauer, F., Whang, Y., et al.: 1995, The wind magnetic field investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207.
Leubner, M.: 2004a, Core-halo distribution functions: A natural equilibrium state in generalized thermostatistics. Astrophys. J. 604, 469. DOI. ADS.
Leubner, M.: 2004b, Fundamental issues on kappa-distributions in space plasmas and interplanetary proton distributions. Phys. Plasmas 11, 1308. DOI. ADS.
Leubner, M.: 2008, Consequences of entropy bifurcation in non-Maxwellian astrophysical environments. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 15, 531. DOI. ADS.
Leubner, M., Vörös, Z.: 2005, A nonextensive entropy path to probability distributions in solar wind turbulence. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 12, 171. DOI. ADS.
Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Lynch, B.J.: 2018, Magnetic clouds: Solar cycle dependence, sources, and geomagnetic impacts. Solar Phys. 293, 1. DOI.
Li, G., Zank, G., Desai, M., Mason, G., Rice, W.: 2005, Particle Acceleration and Transport at CME-Driven Shocks: A Case Study. Washington DC American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph Series 156, 51. DOI. ADS.
Lin, R., Anderson, K., Ashford, S., Carlson, C., Curtis, D., Ergun, R., Larson, D., McFadden, J., McCarthy, M., Parks, G., et al.: 1995, A three-dimensional plasma and energetic particle investigation for the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 125. DOI. ADS.
Maksimovic, M., Pierrard, V., Lemaire, J.: 1997, A kinetic model of the solar wind with kappa distribution functions in the corona. Astron. Astrophys. 324, 725. ADS.
Maksimovic, M., Pierrard, V., Riley, P.: 1997, Ulysses electron distributions fitted with kappa functions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 1151. DOI. ADS.
Maksimovic, M., Zouganelis, I., Chaufray, J.-Y., Issautier, K., Scime, E., Littleton, J., Marsch, E., McComas, D., Salem, C., Lin, R., et al.: 2005, Radial evolution of the electron distribution functions in the fast solar wind between 0.3 and 1.5 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110(A9), A09104. DOI. ADS.
Montgomery, M.D., Bame, S., Hundhausen, A.: 1968, Solar wind electrons: Vela 4 measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 4999. DOI. ADS.
Mueller, D., Marsden, R.G., Cyr, O.S., Gilbert, H.R.: 2013, Solar orbiter. Solar Phys. 285, 25. DOI.
Müller, D., Cyr, O.S., Zouganelis, I., Gilbert, H.R., Marsden, R., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Antonucci, E., Auchère, F., Berghmans, D., Horbury, T., et al.: 2020, The solar orbiter mission-science overview. Astron. Astrophys. 642, A1. DOI. ADS.
Neugebauer, M., Goldstein, R.: 1997, Particle and Field Signatures of Coronal Mass Ejections in the Solar Wind 99, 245. DOI.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Viñas, A.F.: 2008, Solar wind electron distribution functions inside magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113(A2), A02105. DOI. ADS.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Jian, L.K., Balmaceda, L., Vourlidas, A., dos Santos, L.F., Szabo, A.: 2019, Unraveling the internal magnetic field structure of the Earth-directed interplanetary coronal mass ejections during 1995–2015. Solar Phys. 294, 1. DOI.
Ogilvie, K., Scudder, J.D., Sugiura, M.: 1971, Electron energy flux in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 8165. DOI.
Ogilvie, K., Chornay, D., Fritzenreiter, R., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., Miller, G., Scudder, J., Sittler, E., Torbert, R., et al.: 1995, SWE, a comprehensive plasma instrument for the WIND spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55. DOI.
Pierrard, V.: 2012, Solar wind electron transport: Interplanetary electric field and heat conduction. Space Sci. Rev. 172, 315. DOI. ADS.
Pierrard, V., Lazar, M.: 2010, Kappa distributions: Theory and applications in space plasmas. Solar Phys. 267, 153. DOI.
Pierrard, V., Lemaire, J.: 1996, Lorentzian ion exosphere model. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 101, 7923. DOI. ADS.
Pierrard, V., Maksimovic, M., Lemaire, J.: 1999, Electron velocity distribution functions from the solar wind to the corona. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 104, 17021. DOI. ADS.
Pierrard, V., Maksimovic, M., Lemaire, J.: 2001, Core, halo and Strahl electrons in the solar wind. Astrophys. Space Sci. 277, 195. DOI. ADS.
Pierrard, V., Lazar, M., Poedts, S., Štverák, Š., Maksimovic, M., Trávníček, P.: 2016, The electron temperature and anisotropy in the solar wind. Comparison of the core and halo populations. Solar Phys. 291, 2165. DOI.
Pilipp, W., Miggenrieder, H., Montgomery, M., Mühlhäuser, K.-H., Rosenbauer, H., Schwenn, R.: 1987a, Characteristics of electron velocity distribution functions in the solar wind derived from the Helios plasma experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 92, 1075. DOI. ADS.
Pilipp, W., Miggenrieder, H., Montgomery, M., Mühlhäuser, K.-H., Rosenbauer, H., Schwenn, R.: 1987b, Unusual electron distribution functions in the solar wind derived from the Helios plasma experiment: Double-Strahl distributions and distributions with an extremely anisotropic core. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 92, 1093. DOI.
Pilipp, W., Miggenrieder, H., Mühlhäuser, K.-H., Rosenbauer, H., Schwenn, R., Neubauer, F.: 1987c, Variations of electron distribution functions in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 92, 1103. DOI. ADS.
Pilipp, W., Miggenrieder, H., Mühläuser, K.-H., Rosenbauer, H., Schwenn, R.: 1990, Large-scale variations of thermal electron parameters in the solar wind between 0.3 and 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 95, 6305. DOI.
Pinfield, D., Keenan, F., Mathioudakis, M., Phillips, K., Curdt, W., Wilhelm, K.: 1999, Evidence for non-Maxwellian electron energy distributions in the solar transition region: Si III line ratios from SUMER. Astrophys. J. 527, 1000. DOI. ADS.
Scudder, J.D.: 1992a, On the causes of temperature change in inhomogeneous low-density astrophysical plasmas. Astrophys. J. 398, 299. DOI. ADS.
Scudder, J.D.: 1992b, Why all stars should possess circumstellar temperature inversions. Astrophys. J. 398, 319. DOI. ADS.
Scudder, J.D.: 1994, Ion and electron suprathermal tail strengths in the transition region: Support for the velocity filtration model of the corona. Astrophys. J. 427, 446. DOI. ADS.
Shodhan, S., Crooker, N., Kahler, S., Fitzenreiter, R., Larson, D., Lepping, R., Siscoe, G., Gosling, J.: 2000, Counterstreaming electrons in magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 105, 27261. DOI. ADS.
Steed, K., Owen, C., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2011, Investigating the observational signatures of magnetic cloud substructure. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116(A1), A01106. DOI.
Steinberg, J., Gosling, J., Skoug, R., Wiens, R.: 2005, Suprathermal electrons in high-speed streams from coronal holes: Counterstreaming on open field lines at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110(A6), A06103. DOI. ADS.
Štverák, Š., Maksimovic, M., Trávníček, P.M., Marsch, E., Fazakerley, A.N., Scime, E.E.: 2009, Radial evolution of nonthermal electron populations in the low-latitude solar wind: Helios, Cluster, and Ulysses observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114(A5), A05104. DOI. ADS.
Tsallis, C.: 1995, Non-extensive thermostatistics: Brief review and comments. Physica A 221, 277. DOI.
Vasyliunas, V.M.: 1968, A survey of low-energy electrons in the evening sector of the magnetosphere with OGO 1 and OGO 3. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 2839. DOI. ADS.
Vocks, C., Mann, G.: 2003, Generation of suprathermal electrons by resonant wave-particle interaction in the solar corona and wind. Astrophys. J. 593, 1134. DOI. ADS.
Vocks, C., Mann, G., Rausche, G.: 2008, Formation of suprathermal electron distributions in the quiet solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 480, 527. DOI.
Webb, D., Cliver, E., Crooker, N., St. Cyr, O. Thompson, B.: 2000, Relationship of halo coronal mass ejections, magnetic clouds, and magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 105, 7491. DOI.
Weissman, P., McFadden, L.-A., Johnson, T.: 1998, Encyclopedia of the Solar System, Academic Press, San Diego.
Whittlesey, P.L., Larson, D.E., Kasper, J.C., Halekas, J., Abatcha, M., Abiad, R., Berthomier, M., Case, A., Chen, J., Curtis, D.W., et al.: 2020, The solar probe analyzers—electrons on the Parker solar probe. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 246, 74. DOI.
Wu, C., Lepping, R., Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, Relationships among magnetic clouds, CMEs, and geomagnetic storms. Solar Phys. 239, 449. DOI.
Yousef, S., El-Nazer, M.M., Bebars, A.: 2005, The successive ejection of several halo CMEs from NOAA AR. 652 July 2004, a physical study. In: Coronal and Stellar Mass Ejections (IAU S226) 226, 145. DOI. ADS.
Zouganelis, I.: 2008, Measuring suprathermal electron parameters in space plasmas: Implementation of the quasi-thermal noise spectroscopy with kappa distributions using in situ Ulysses/URAP radio measurements in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113(A8), A08111. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
The level zero data of the EVDFs from three-dimensional plasma instrument onboard WIND spacecraft is available directly from the Berkeley HTTP Site (url: http://sprg.ssl.berkeley.edu/wind3dp/data/wi/3dp/lz/). We thank the WIND project scientist Dr. Lynn B. Wilson III, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center for the 3DP LZ data. We thank Mr. Robert M. Candey and Dr. Natalia Papitashvili of Space Physics Data Facility (SPDF, CDA web), NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center for the solar wind data from WIND and ACE satellites (CDA Web, url: https://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html/). The CME data and images are from the SOHO LASCO CME catalog – cdaw data center – NASA (url: https://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/). This CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. We thank the ENLIL with cone model developer Dr. D. Odstrcil. We also thank the CCMC scientific staffs Anne Michelle Mendoza, Anna Chulaki, Lutz Rastaetter, Masha Kuznetsova for the model run on request from the CCMC website (url: https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov). We thank the WDC for Geomagnetism, Kyoto Dst index service for providing the Dst index data and images. The corresponding author thanks Dr. K. Rajeev, Director of SPL, VSSC, for providing the necessary resources for completing this work. The author also thanks Mr. Abhishek J.K., Scientist at SPL/VSSC, for providing access to the software tools used for the analysis of this work. We are also thankful to the reviewer and the editor for the valuable suggestions, which have helped to improve the quality of this article. The corresponding author Govind G. Nampoothiri is an ISRO Research Fellow at SPL, VSSC, and he is a registered PhD scholar at the Department of Physics, Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nampoothiri, G.G., Thampi, R.S., Thampi, S.V. et al. Nature and Variability of the Electron Velocity Distribution Functions and the Nonequilibrium Boltzmann Entropy in the Solar Wind at the First Lagrangian (L1) Point During the Halo CME Event on 25 July 2004. Sol Phys 296, 159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01900-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01900-7