Abstract
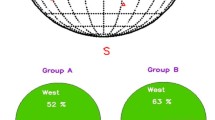
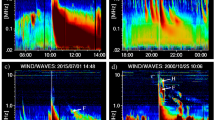
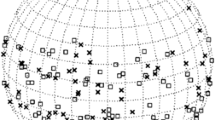
We present the characteristics of DH type II bursts for the Solar Cycles 23 and 24. The bursts are classified according to their end frequencies into three categories: Low-Frequency Group (LFG; 20 kHz ≤ f ≤ 200 kHz), Medium-Frequency Group (MFG; 200 kHz \(< f \leq 1\) MHz), and High-Frequency Group (HFG; 1 MHz \(< f \le 16\) MHz). We find that the sources for LFG, MFG, and HFG events are homogeneously distributed over the active region belt. Our analysis shows a drastic reduction of the DH type II events during Solar Cycle 24, which includes only 35% of the total events (i.e., 179 out of 514). Despite having smaller number of DH type II events in the Solar Cycle 24, it contains a significantly higher fraction of LFG events compared to the previous cycle (32% versus 24%). However, within the LFG group, the cycle 23 exhibits significant dominance of type II bursts that extend below 50 kHz, suggesting rich population of powerful CMEs traveling beyond half of the Sun–Earth distance. The events of LFG group display strongest association with faster and wider (more than 82% events are halo) CMEs, whereas at the source location, they predominantly trigger large M/X class flares (in more than 83% cases). Our analysis also indicates that CME initial speed or flare energetics is partly related to the duration of type II burst and that survival of CME-associated shock is determined by multiple factors/parameters related to CMEs, flares, and state of coronal and interplanetary medium. The profiles relating CME heights with respect to the end frequencies of DH type II bursts suggest that for HFG and MFG categories, the location for majority of CMEs (≈ 65%–70%) is in well compliance with ten-fold Leblanc coronal density model, whereas for LFG events, a lower value of density multiplier (≈ 3) seems to be compatible.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Source: WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels.
Source: Royal Observatory, Greenwich–USAF/NOAA Sunspot Data.
References
Bougeret, J.-L., Kaiser, M.L., Kellogg, P.J., Manning, R., Goetz, K., Monson, S.J., Monge, N., Friel, L., Meetre, C.A., Perche, C., Sitruk, L., Hoang, S.: 1995, Waves: the radio and plasma wave investigation on the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 231. DOI. ADS.
Bougeret, J.L., Goetz, K., Kaiser, M.L., Bale, S.D., Kellogg, P.J., Maksimovic, M., Monge, N., Monson, S.J., Astier, P.L., Davy, S., Dekkali, M., Hinze, J.J., Manning, R.E., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Bonnin, X., Briand, C., Cairns, I.H., Cattell, C.A., Cecconi, B., Eastwood, J., Ergun, R.E., Fainberg, J., Hoang, S., Huttunen, K.E.J., Krucker, S., Lecacheux, A., MacDowall, R.J., Macher, W., Mangeney, A., Meetre, C.A., Moussas, X., Nguyen, Q.N., Oswald, T.H., Pulupa, M., Reiner, M.J., Robinson, P.A., Rucker, H., Salem, C., Santolik, O., Silvis, J.M., Ullrich, R., Zarka, P., Zouganelis, I.: 2008, S/WAVES: the radio and plasma wave investigation on the STEREO mission. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 487. DOI. ADS.
Cane, H.V., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A.: 1987, Energetic interplanetary shocks, radio emission, and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 9869. DOI. ADS.
Cho, K.-S., Bong, S.-C., Kim, Y.-H., Moon, Y.-J., Dryer, M., Shanmugaraju, A., Lee, J., Park, Y.D.: 2008, Low coronal observations of metric type II associated CMEs by MLSO coronameters. Astron. Astrophys. 491, 873. DOI. ADS.
Cho, K.-S., Bong, S.-C., Moon, Y.-J., Shanmugaraju, A., Kwon, R.-Y., Park, Y.D.: 2011, Relationship between multiple type II solar radio bursts and CME observed by STEREO/SECCHI. Astron. Astrophys. 530, A16. DOI. ADS.
Cliver, E.W., Kahler, S.W., Reames, D.V.: 2004, Coronal shocks and solar energetic proton events. Astrophys. J. 605, 902. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, Coronal Mass Ejections and Type II Radio Bursts. Geophysical Monograph Series 165, American Geophysica Union, Washington, 207. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2010, Corona mass ejections: a summary of recent results. In: Dorotovic, I. (ed.) 20th National Sol. Phys. Meeting 20, 108. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2011, Coronal mass ejections and solar radio emissions. In: Rucker, H.O., Kurth, W.S., Louarn, P., Fischer, G. (eds.) Planetary, Solar and Heliospheric Radio Emissions (Phys. Rev. E VII), 325. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Makela, P.A.: 2018, Properties of DH Type II Radio Bursts and Their Space Weather Implications. arXiv e-prints, arXiv. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S.: 2019, A catalog of type II radio bursts observed by Wind/WAVES and their statistical properties. Sun Geosph. 14, 111. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Characteristics of coronal mass ejections associated with long-wavelength type II radio bursts. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29219. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Yashiro, S., Nunes, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Type II radio bursts and energetic solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S07. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Michalek, G.: 2014, Anomalous expansion of coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 24 and its space weather implications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 2673. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2015, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 9221. DOI. ADS.
Harvey, K.L., Zwaan, C.: 1993, Properties and emergence patterns of bipolar active regions—part one. Solar Phys. 148, 85. DOI. ADS.
Joshi, B., Pant, P.: 2005, Distribution of H\(\alpha \) flares during solar cycle 23. Astron. Astrophys. 431, 359. DOI. ADS.
Joshi, B., Pant, P., Manoharan, P.K.: 2006, Periodicities in sunspot activity during solar cycle 23. Astron. Astrophys. 452, 647. DOI. ADS.
Joshi, B., Ibrahim, M.S., Shanmugaraju, A., Chakrabarty, D.: 2018, A major geoeffective CME from NOAA 12371: initiation, CME-CME interactions, and interplanetary consequences. Solar Phys. 293, 107. DOI. ADS.
Kharayat, H., Joshi, B., Chandra, R.: 2021, Radio-loud and radio-quiet CMEs: solar cycle dependency, influence on cosmic ray intensity, and geo-effectiveness. Astrophys. Space Sci. 366, 24. DOI. ADS.
Knock, S.A., Cairns, I.H., Robinson, P.A., Kuncic, Z.: 2003, Theoretically predicted properties of type II radio emission from an interplanetary foreshock. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1126. DOI. ADS.
Leblanc, Y., Dulk, G.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 1998, Tracing the electron density from the corona to 1 AU. Solar Phys. 183, 165. DOI. ADS.
Mann, G.: 1995, In: Benz, A.O., Krüger, A. (eds.) Theory and Observations of Coronal Shock Waves 444, 183. DOI. ADS.
Manoharan, P.K., Maia, D., Johri, A., Induja, M.S.: 2016, Interplanetary consequences of coronal mass ejection events occurred during 18-25 June 2015. In: Dorotovic, I., Fischer, C.E., Temmer, M. (eds.) Coimbra Sol. Phys. Meeting: Ground-Based Solar Observations in the Space Instrumentation Era, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series 504, 59. ADS.
Nelson, G.J., Melrose, D.B.: 1985, In: McLean, D.J., Labrum, N.R. (eds.) Type II Bursts, 333. ADS.
Owens, M.J., Forsyth, R.J.: 2013, The heliospheric magnetic field. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 10, 5. DOI. ADS.
Pohjolainen, S., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Culhane, J.L., Manoharan, P.K., Elliott, H.A.: 2007, CME propagation characteristics from radio observations. Solar Phys. 244, 167. DOI. ADS.
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN. The Art of Scientific Computing. ADS.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L.: 1999, High-frequency type II radio emissions associated with shocks driven by coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 16979. DOI. ADS.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Radio signatures of the origin and propagation of coronal mass ejections through the solar corona and interplanetary medium. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29989. DOI. ADS.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2007, Coronal and interplanetary propagation of CME/shocks from radio, in situ and white-light observations. Astrophys. J. 663, 1369. DOI. ADS.
Shanmugaraju, A., Suresh, K., Vasanth, V., Selvarani, G., Umapathy, S.: 2018, Interplanetary type II radio bursts and their association with CMEs and flares. Astrophys. Space Sci. 363, 126. DOI. ADS.
Suresh, K., Prasanna Subramanian, S., Shanmugaraju, A., Vršnak, B., Umapathy, S.: 2019, Study of interplanetary CMEs/shocks during solar cycle 24 using drag-based model: the role of solar wind. Solar Phys. 294, 47. DOI. ADS.
Syed Ibrahim, M., Joshi, B., Cho, K.-S., Kim, R.-S., Moon, Y.-J.: 2019, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycles 23 and 24: Sun–Earth propagation characteristics and consequences at the near-Earth region. Solar Phys. 294, 54. DOI. ADS.
Vizoso, G., Ballester, J.L.: 1990, The North-South asymmetry of sunspots. Astron. Astrophys. 229, 540. ADS.
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Falkenberg, T.V., Möstl, C., Vennerstrom, S., Vrbanec, D.: 2010, The role of aerodynamic drag in propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 512, A43. DOI. ADS.
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Vrbanec, D., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A., Čalogović, J., Dumbović, M., Lulić, S., Moon, Y.-J., Shanmugaraju, A.: 2013, Propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: the drag-based model. Solar Phys. 285, 295. DOI. ADS.
Wild, J.P., Smerd, S.F., Weiss, A.A.: 1963, Solar bursts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1, 291. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the WIND/WAVES type II burst catalog, which forms the basis for the present study. The LASCO CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. We further acknowledge the SOHO, STEREO, GOES, and Wind missions for their open data policy. We are grateful to the anonymous referee of the paper for providing constructive comments and suggestions that have significantly enhanced the quality and presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, B.D., Joshi, B., Cho, KS. et al. DH Type II Radio Bursts During Solar Cycles 23 and 24: Frequency-Dependent Classification and Their Flare-CME Associations. Sol Phys 296, 142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01890-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01890-6