Abstract
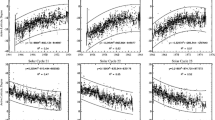
We analyzed the combined 142 years sunspot-group data from Greenwich Photoheliograpic Results (GPR) and Debrecen Photoheliographic Data (DPD) and determined the yearly mean residual rotation rate and the meridional velocity of sunspot groups in different \(5^{\circ }\) latitude intervals. We find that there exists a considerable latitude–time dependence in both the residual rotation and the meridional motion. The residual rotation rate is found to be −120 m s−1 to 80 m s−1. In a large number of solar cycles, the rotation is to some extent weaker during maxima than that of during minima. There exist alternate bands of equatorward and poleward meridional motions. The equatorward motion is dominant mostly around the maxima of solar cycles with velocity 8–12 m s−1, whereas the poleward motion is dominant mostly around the minima but with a relatively weak velocity, only 4–6 m s−1. The analysis of the data during Solar Cycles 12–24 that are folded according to the years from their respective epochs of maxima suggests the existence of equatorward migrating alternate bands of slower and faster than average rotation within the activity belt. This analysis suggests no clear equatorward or poleward migrating bands of meridional motions. A statistically significant anticorrelation exists between the meridional motion and residual rotation. The corresponding linear-least-squares best-fit is found to be reasonably good (slope, \(-0.028 \pm 0.008\), is about 3.5 times larger than its standard deviation). As per the sign convention used for the meridional motions, the significant negative value of the slope indicates the existence of a strong angular momentum transport toward the equator. The cross-correlation between the slopes determined from the data in 3-year moving time intervals and yearly mean sunspot number (SN) suggests that the slope leads SN by about 4 and 9 years. The Morlet wavelet spectrum of the slope suggests the existence of ≈11-year periodicity in the slope almost throughout the data window, but it was very weak during 1920–1940. We have also done cross-wavelet, wavelet-coherence, and wavelet-phase difference analyses of the slope and SN. Overall the results suggest there exists a strong relationship between the slope and amount of activity during a solar cycle. However, the correlation between the cycle-to-cycle modulations in the slope and the amplitude of solar cycle is found to be insignificant, indicating that there is no relationship between the slope and strength of activity on a long-time scale (longer than 11-year period).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antia, H.M.: 2002, In: Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H. (eds.) The Sun’s Rotation, Nova Science, New York, 81.
Balthasar, H., Vázquez, M., Wöhl, H.: 1986, Astron. Astrophys. 155, 87. ADS.
Baranyi, T., Győri, L., Ludmány, A.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 3081. DOI.
Brajša, R., Ruždjak, D., Wöhl, H.: 2006, Solar Phys. 237, 365. DOI.
Clette, F., Lefévre, L.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 2629. DOI.
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A.: 2006, Astrophys. J. 649, 498. DOI.
Gilman, P.A.: 1986, In: Sturrock, P.A., Holzer, T.E., Mihalas, D.M., Ulrich, R.K. (eds.) Physics of the Sun 1, Reidal, Dordrecht, 95.
Gilman, P.A., Howard, R.: 1984, Astrophys. J. 283, 385. DOI.
Godoli, G., Mazzuconi, F.: 1982, Astron. Astrophys. 116, 188.
Győri, L., Baranyi, T., Ludmány, A.: 2010, Proc. Int. Astron. Union 6, Symp. S273 2011, 403. DOI.
Győri, L., Ludmány, A., Baranyi, T.: 2017, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 465, 1259. DOI.
Hathaway, D.H.: 2015, Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12(4), 1. DOI.
Hathaway, D.H., Rightmire, L.: 2010, Science 327, 1350. DOI.
Howard, R.F.: 1991, Solar Phys. 135, 327. DOI.
Howard, R.F.: 1996, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 34, 75. DOI.
Howard, R., LaBonte, B.J.: 1980, Astrophys. J. 239, L33. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2003, Solar Phys. 212, 23. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2007, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 377, L34. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2013, Solar Phys. 287, 197.
Javaraiah, J.: 2020, Solar Phys. 295, 170. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H.: 1995, Solar Phys. 158, 173. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H.: 1997, Astron. Astrophys. 327, 795.
Javaraiah, J., Komm, R.W.: 1999, Solar Phys. 184, 41. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Komm, R.W.: 2002, In: Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H. (eds.) The Sun’s Rotation, Nova Science, New York, 23.
Javaraiah, J., Ulrich, R.K.: 2006, Solar Phys. 237, 245. DOI.
Komm, R.W., Howard, R.F., Harvey, J.W.: 1993a, Solar Phys. 147, 207. DOI.
Komm, R.W., Howard, R.F., Harvey, J.W.: 1993b, Solar Phys. 143, 19. DOI.
Komm, R.W., Howard, R.F., Harvey, J.W.: 1994, Solar Phys. 151, 15. DOI.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2020, Solar Phys. 295, 47. DOI.
Makarov, V.I., Tlatov, A.G., Callebaut, D.K.: 1997, Solar Phys. 170, 373. DOI.
Meunier, N.: 2005, Astron. Astrophys. 442, 693. DOI.
Meunier, N., Nesme-Ribes, E., Collin, B.: 1997, Astron. Astrophys. 319, 683.
Meunier, N., Zhao, J.: 2009, Space Sci. Rev. 144, 127. DOI.
Nesme-Ribes, E., Ferreira, E.N., Vince, I.: 1993, Astron. Astrophys. 276, 211.
Olemskoy, S.V., Kitchatinov, L.L.: 2005, Astron. Lett. 31, 706. DOI.
Paternó, I., Spadaro, D., Zappalá, R.A., Zuccarello, F.: 1991, Astron. Astrophys. 252, 337.
Pesnell, W.D.: 2018, Space Weather 16, 1997. DOI.
Schatten, K.H., Scherrer, P.H., Svalgaard, L., Wilcox, J.M.: 1978, Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 411. DOI.
Schröter, E.H.: 1985, Solar Phys. 100, 141. DOI.
Sivaraman, K.R., Sivaraman, H., Gupta, S.S., Howard, R.F.: 2010, Solar Phys. 266, 247. DOI.
Snodgrass, H.B.: 1987, Astrophys. J. 316, L91. DOI.
Snodgrass, H.B.: 1991, Astrophys. J. 383, L85. DOI.
Snodgrass, H.B.: 1992, In: Harvey, K.L. (ed.) The Solar Cycle, CS-27, Astron. Soc. Pac., San Francisco, 205.
Sudar, D., Skokić, I., Ruždjak, D., Brajsa, R., Wöhl, H.: 2014, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 439, 2377. DOI.
Sudar, D., Brajša, R., Skokić, I., Poljančć Beljan, I., Wöhl, H.: 2017, Solar Phys. 292, 86. DOI.
Švanda, M., Klvaňa, M., Sobotka, V., Bumba: 2008, Astron. Astrophys. 477, 285. DOI.
Ternullo, M.: 1990, Solar Phys. 127, 29. DOI.
Torrence, Ch., Compo, G.P.: 1998, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79, 61. DOI.
Tuominen, J., Tuominen, I., Kyöläinen, J.: 1983, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 205, 691. DOI.
Ward, F.: 1965, Astrophys. J. 141, 534. DOI.
Zhao, J., Kosovichev, A.G.: 2004, Astrophys. J. 603, 776. DOI.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the anonymous reviewer for useful comments and suggestions. The author acknowledges the work of all the people who contribute to and maintain the GPR and DPD Sunspot databases. The sunspot-number data are provided by WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels. The wavelet software was provided by C. Torrence and G. Compo and is available at paos.colorado.edu/research/wavelets.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
J. Javaraiah formerly working at Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru-560 034, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javaraiah, J. A Study of Variations in Correlation Between Rotation Residual and Meridional Velocity of Sunspot Groups. Sol Phys 296, 152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01883-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01883-5