Abstract
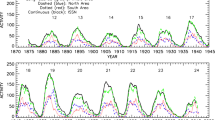
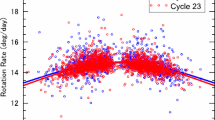
Studies of variations in the solar differential rotation are important for understanding the underlying mechanism of solar cycle and other variations of solar activity. We analyzed the sunspot-group daily data that were reported by Greenwich Photoheliographic Results (GPR) during the period 1874 – 1976 and Debrecen Photoheliographic Data (DPD) during the period 1977 – 2017. We determined the equatorial rotation rate [\(A\)] and the latitude gradient [\(B\)] components of the solar differential rotation by fitting the data in each of the 3-year moving time intervals (3-year MTIs) successively shifted by one year during the period 1874 – 2017 to the standard law of differential rotation. The values of \(A\) and \(B\) around the years of maxima and minima of Solar Cycles 12 – 24 are obtained from the 3-year MTIs series of \(A\) and \(B\) and studied the long-term cycle-to-cycle modulations in these coefficients. Here we have used the epochs of the maxima and minima of the Solar Cycles 12 – 24 that were recently determined from the revised Version-2 international sunspot-number series. We find that there exits a considerably significant secular decreasing-trend in \(A\) around the maxima of solar cycles. There exist no secular trends in both \(A\) and \(B\) around the minima of solar cycles. The secular trend in \(B\) around the maxima of solar cycles is also found to be statistically insignificant. We fitted a cosine function to the values of \(A\), and also to those of \(B\), after removing the corresponding linear trends. The cosine-fits suggest that there exist ≈54-year (≈94-year) and ≈82-year (≈79-year) periodicities in \(A\) (\(B\)) around the maxima and minima of solar cycles, respectively. The amplitude of the cosine-profile of \(A\) (\(B\)) around the minima of solar cycles is about 41% (65%) larger than that of \(A\) (\(B\)) around the maxima. In addition, the cosine profiles of \(A\) and \(B\) suggest a large (up to \(180^{\circ }\)) phase difference between the long-term variations of \(A\), and also between those of \(B\), around maxima and minima of solar cycles. Implications of all these results are discussed briefly.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H.W.: 1961, Astrophys. J. 133, 572. DOI.
Badalyan, O.G., Obridko, V.N.: 2017, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 466, 4535. DOI.
Balthasar, H., Vázquez, M., Wöhl, H.: 1986, Astron. Astrophys. 155, 87. ADS.
Baranyi, T., Győri, L., Ludmány, A.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 3081. DOI.
Brajša, R., Ruždjak, D., Wöhl, H.: 2006, Solar Phys. 237, 365. DOI.
Cameron, R.H., Dikpati, M., Brandenburg, A.: 2017, Space Sci. Rev. 210, 367. DOI.
Chandra, S., Vats, H.O., Iyer, K.N.: 2010, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 407, 1108. DOI.
Choudhuri, A.R., Gilman, P.A.: 1987, Astrophys. J. 316, 788. DOI.
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A.: 2006, Astrophys. J. 649, 498. DOI.
D’Silva, S., Howard, R.F.: 1994, Solar Phys. 151, 213. DOI.
Gao, P.X.: 2016, Astrophys. J. 830, 140. DOI.
Garcia, A., Mouradian, Z.: 1998, Solar Phys. 180, 495. DOI.
Gilman, P.A., Howard, R.: 1984, Astrophys. J. 283, 385. DOI.
Gupta, S.S., Sivaraman, K.R., Howard, R.: 1999, Solar Phys. 188, 225. DOI.
Győri, L., Baranyi, T., Ludmány, A.: 2010. In: Proc. Intern. Astron. Union 6, Sympo. S273 2011, 403. DOI.
Győri, L., Ludmány, A., Baranyi, T.: 2017, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 465, 1259. DOI.
Hathaway, D.H.: 2015, Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12, N0.4. DOI.
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M., Reichmann, E.J.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 22375. DOI.
Hiremath, K.M.: 2002, Astron. Astrophys. 386, 674. DOI.
Howard, R.: 1976, Astrophys. J. Lett. 93, L159. DOI.
Howard, R., Gilman, P.I., Gilman, P.A.: 1984, Astrophys. J. 283, 373. DOI.
Howard, R., LaBonte, B.J.: 1980, Astrophys. J. 239, L33. DOI.
Howe, R., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Hill, F., Komm, R.W., Larsen, R.M., Schou, J., Thompson, M.J., Toomre, J.: 2000, Astrophys. J. 533, L163. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2003, Solar Phys. 212, 23. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2005, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 362, 1311. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2011, Adv. Space Res. 48, 1032. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2013, Solar Phys. 287, 197. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2017, Solar Phys. 292, 172. DOI.
Javaraiah, J.: 2019, Solar Phys. 294, 64. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Bertello, L.: 2016, Solar Phys. 291, 3485. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Bertello, L., Ulrich, R.K.: 2005a, Article-I. Solar Phys. 232, 25. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Bertello, L., Ulrich, R.K.: 2005b, Astrophys. J. 626, 579. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H.: 1995, Solar Phys. 158, 173. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Gokhale, M.H.: 1997, Astron. Astrophys. 327, 795.
Javaraiah, J., Komm, R.W.: 1999, Solar Phys. 184, 41. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Ulrich, R.K.: 2006, Solar Phys. 237, 245. DOI.
Javaraiah, J., Ulrich, R.K., Bertello, L., Boyden, J.E.: 2009, Solar Phys. 257, 61. DOI.
Juckett, D.A.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 399, 731. DOI.
Kambry, M.A., Nishikawa, J.: 1990, Solar Phys. 126, 89. DOI.
Khutsishvili, E.V., Gigolashvili, M.Sh., Kvernadze, T.M.: 2002, Solar Phys. 206, 219. DOI.
Komitov, B., Sello, S., Duchlev, P., Dechev, M., Penev, K., Koleva, K.: 2016, Bulg. Astron. J. 25, 78.
Komm, R.W., Howard, R.F., Harvey, J.W.: 1993, Solar Phys. 143, 19. DOI.
LaBonte, B.J., Howard, R.: 1982, Solar Phys. 75, 161. DOI.
Li, K.J., Feng, W., Shi, X.J., Xie, J.L., Gao, P.X., Liang, H.F.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 759. DOI.
Makarov, V.I., Tlatov, A.G., Callebaut, D.K.: 1997, Solar Phys. 170, 373. DOI.
Mendoza, B.: 1999, Solar Phys. 188, 237. DOI.
Obridko, V.N., Shelting, B.D.: 2016, Astron. Lett. 42, 631. DOI.
Ogurtsov, M.G., Nagovitsyn, Y.A., Kocharov, G.E., Jungner, H.: 2002, Solar Phys. 211, 371. DOI.
Olemskoy, S.V., Kitchatinov, L.L.: 2005, Astron. Lett. 31, 706. DOI.
Pesnell, W.D.: 2018, Space Weather 16, 1997. DOI.
Roudier, Th., Švanda, M., Ballot, J., Malherbe, J.M., Rieutord, M.: 2018, Astron. Astrophys. 611, A92. DOI.
Rozelot, J.P.: 1994, Solar Phys. 149, 149. DOI.
Ruždjak, D., Brajša, R., Sudar, D., Skokić, I., Poljančić-Beljan, I.: 2017, Solar Phys. 292, 179. DOI.
Singh, J., Prabhu, T.P.: 1985, Solar Phys. 97, 203. DOI.
Sivaraman, K.R., Sivaraman, H., Gupta, S.S., Howard, R.: 2003, Solar Phys. 214, 65. DOI.
Snodgrass, H.B.: 1992, In: Harvey, K.L. (ed.) The Solar Cycle CS-27, Astron. Soc. Pac, San Francisco, 205.
Snodgrass, H.B., Howard, R.: 1985, Solar Phys. 95, 221. DOI.
Sudar, D., Skokć Ruždjak, D., Brajsa, R., Wöhl, H.: 2014, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 439, 1471. DOI.
Suzuki, M.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 4021. DOI.
Švanda, M., Klvǎna, M., Sobotka, M., Bumba, V.: 2008, Astron. Astrophys. 477, 285. DOI.
Tan, B.: 2011, Astrophys. Space Sci. 332, 65. DOI.
Temmer, M., Rybák, J., Bendík, P., Veronig, A., Vogler, F., Otruba, W., Pötzi, W., Hanslmeier, A.: 2006, Astron. Astrophys. 447, 735. DOI.
Ward, F.: 1965, Astrophys. J. 141, 534. DOI.
Ward, F.: 1966, Astrophys. J. 145, 416. DOI.
Wood, R.M., Wood, K.D.: 1965, Nature 208, 129. DOI.
Yoshimura, H., Kambry, M.A.: 1993, Solar Phys. 143, 205. DOI.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the anonymous referee for the critical review and for useful comments and suggestions. The author acknowledges the work of all the people contribute and maintain the GPR and DPD sunspot databases. The sunspot-number data are provided by WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The author declares to have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The author formerly worked at Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru-560 034, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javaraiah, J. Long–Term Variations in Solar Differential Rotation and Sunspot Activity, II: Differential Rotation Around the Maxima and Minima of Solar Cycles 12 – 24. Sol Phys 295, 170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01740-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01740-x