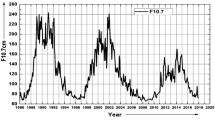
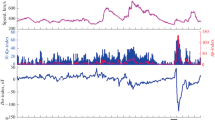
Abstract
In this study we compared the temporal and periodic variations of the Maximum CME Speed Index (MCMESI) and the the number of different class (C, M, and X) solar X-ray flares for the last two solar cycles (Solar Cycles 23 and 24). To obtain the correlation between the MCMESI and solar flare numbers the cross-correlation analysis was applied to monthly data sets. Also to investigate the periodic behavior of all data sets the Multi Taper Method (MTM) and the Morlet wavelet analysis method were performed with daily data from 2009 to 2018. To evaluate our wavelet analysis Cross Wavelet Transform (XWT) and Wavelet Transform Coherence (WTC) methods were performed. Causal relationship between data sets were further examined by Convergence Cross Mapping (CCM) method. As results of our analysis we found the following: i) The C class X-ray flare numbers increased about 16% during the Solar Cycle 24 compared to Cycle 23, while all other data sets decreased; the MCMESI decreased about 16% and the number of M and X class flares decreased about 32%. ii) All the X-ray solar flare classes show remarkable positive correlation with the MCMESI. While the correlation between the MCMESI and C class flares comes from the general solar cycle trend, it mainly results from the fluctuations in the data in case of the X class flares. iii) In general, all class flare numbers and the MCMESI show similar periodic behavior. iv) The 546-day periodicity detected in the MCMESI may not be of solar origin or at least the solar flares are not the source of this periodicity. v) C and M class solar flares have a stronger causative effect on the MCMESI compared to X class solar flares. However, the only bidirectional causal relationship is obtained between the MCMESI and C class flare numbers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, M.D., Hovard, R.A..: 2001, A two-type classification of Lasco Coronal Mass Ejection. Space Sci. Rev. 95, 147. DOI.
Ballester, J.L., Oliver, R., Carbonell, M.: 2002, The near 160 day periodicity in the photospheric magnetic flux. Astrophys. J. 566, 505. DOI.
Barlyaeva, T., Wojak, J., Lamy, P., Boclet, B., Toth, I.: 2018, Periodic behaviour of coronal mass ejections, eruptive events, and solar activity proxies during solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 177, 12. DOI.
Byrne, J.P., Morgan, H., Habbal, S.R., Gallagher, P.T.: 2012, Automatic detection and tracking of Coronal Mass Ejections. II. Multiscale filtering of coronagraph images. Astrophys. J. 752(2), 145. DOI.
Chang, C., Glover, G.H.: 2010, Time–frequency dynamics of resting-state brain connectivity measured with fMRI. NeuroImage 50(1), 81. DOI.
Chen, P.F.: 2011, Coronal Mass Ejections: models and their observational basis. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 8(1), 1. DOI.
Chowdhury, P., Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V., Obridko, V.N., Rozelot, J.P.: 2019, Analysis of the hemispheric sunspot number time series for the Solar Cycles 18 to 24. Solar Phys. 294(10), 142. DOI.
Cliver, E.W., Ling, A.G., Wise, J.E., Lanzerotti, L..J.: 1999, A prediction of geomagnetic activity for Solar Cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. 104(A4), 6871. DOI.
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V.: 2004, On the three-dimensional configuration of coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 422, 307. DOI.
Emslie, A.G., Kucharek, H., Dennis, B.R., Gopalswamy, N., Holman, G.D., Share, G.H., Vourlidas, A., Forbes, T.G., Gallagher, P.T., Mason, G.M., Metcalf, T.R., Mewaldt, R.A., Murphy, R.J., Schwartz, R.A., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2004, Energy partition in two solar flare/CME events. J. Geophys. Res. 109(A10), 10104. DOI.
Escudier, R., Mignot, J., Swingedouw, D.: 2013, A 20-year coupled ocean-sea ice-atmosphere variability mode in the North Atlantic in an AOGCM. Clim. Dyn. 40(3–4), 619. DOI.
Fang, K., Gou, X., Chen, F., Liu, C., Davi, N., Li, J., Zhao, Z., Li, Y.: 2012, Tree-ring based reconstruction of drought variability (1615-2009) in the Kongtong Mountain area, northern China. Glob. Planet. Change 80, 190. DOI.
Ghil, M., Allen, M.R., Dettinger, M.D., Ide, K., Kondrashov, D., Mann, M.E., Robertson, A.W., Saunders, A., Tian, Y., Varadi, F., Yiou, P.: 2002, Advanced spectral methods for climatic time series. Rev. Geophys. 40(1), 1003. DOI.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104(1–4), 295. DOI.
Gosling, J.T., Bame, S..J., McComas, D..J., Phillips, J.L.: 1990, Coronal mass ejections and large geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 17(7), 901. DOI.
Grinsted, A., Moore, J.C., Jevrejeva, S.: 2004, Application of cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 11, 561. DOI.
Gurgenashvili, E., Zaqarashvili, T.V., Kukhianidze, V., Oliver, R., Ballester, J.L., Ramishvili, G., Shergelashvili, B., Hanslmeier, A., Poedts, S.: 2016, Rieger-type periodicity during Solar Cycles 14-24: estimation of dynamo magnetic field strength in the solar interior. Astrophys. J. 826(1), 55. DOI.
Hudson, H.S., Cliver, E.W.: 2001, Observing coronal mass ejections without coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A11), 25199. DOI.
Inceoglu, F., Simoniello, R., Arlt, R., Rempel, M.: 2019, Constraining non-linear dynamo models using quasi-biennial oscillations from sunspot area data. Astron. Astrophys. 625, A117. DOI.
Kilcik, A., Ozguc, A., Rozelot, J.P.: 2010, Latitude dependency of solar flare index–temperature relation occuring over middle and high latitudes of Atlantic–Eurasian region. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 72(18), 1379. DOI.
Kilcik, A., Anderson, C..N.K., Rozelot, J.P., Ye, H., Sugihara, G., Ozguc, A.: 2009, Nonlinear prediction of Solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 693(2), 1173. DOI.
Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V.B., Abramenko, V., Goode, P.R., Gopalswamy, N., Ozguc, A., Rozelot, J.P.: 2011, Maximum coronal mass ejection speed as an indicator of solar and geomagnetic activities. Astrophys. J. 727(1), 44. DOI.
Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V., Sahin, S., Sarp, V., Obridko, V., Ozguc, A., Rozelot, J.P.: 2018, The evolution of flaring and non-flaring active regions. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 477(1), 293. DOI.
Kundu, M.R., White, S.M., Garaimov, V.I., Manoharan, P.K., Subramanian, P., Ananthakrishnan, S., Janardhan, P.: 2004, Radio observations of rapid acceleration in a slow filament eruption/fast coronal mass ejection event. Astrophys. J. 607(1), 530. DOI.
Lamy, P.L., Floyd, O., Boclet, B., Wojak, J., Gilardy, H., Barlyaeva, T.: 2019, Coronal mass ejections over Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Space Sci. Rev. 215(5), 39. DOI.
Lau, K.M., Weng, H.: 1995, Climate signal detection using wavelet transform: how to make a time series sing. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 76(12), 2391. DOI.
Lou, Y.Q., Wang, Y.M. Fan, Z., Wang, S., Wang, J.X.: 2003, Periodicities in solar coronal mass ejections. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 345(3), 809. DOI.
MacQueen, R.M., Fisher, R.R.: 1983, The kinematics of solar inner coronal transients. Solar Phys. 89(1), 89. DOI.
Maraun, D., Kurths, J.: 2004, Cross wavelet analysis: significance testing and pitfalls. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 11(4), 505. DOI.
Marullo, S., Artale, V., Santoleri, R.: 2011, The SST multidecadal variability in the Atlantic–Mediterranean region and its relation to AMO. J. Climate 24(16), 4385. DOI.
Oliver, R., Carbonell, M., Ballester, J.L.: 1992, Intermediate-term periodicities in solar activity. Solar Phys. 137, 141. DOI.
Oloketuyi, J., Liu, Y., Zhao, M.: 2019, The periodic and temporal behaviors of solar X-ray flares in Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Astrophys. J. 874(1), 20. DOI.
Papaioannou, A., Sandberg, I., Anastasiadis, A., Kouloumvakos, A., Georgoulis, M.K., Tziotziou, K., Tsiropoula, G., Jiggens, P., Hilgers, A.: 2016, Solar flares, coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particle event characteristics. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 6, A42. DOI.
Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2018, EUHFORIA: European heliospheric forecasting information asset. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 8, A35. DOI.
Sarp, V., Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V., Rozelot, J.P., Ozguc, A.: 2018, Prediction of Solar Cycle 25: a non-linear approach. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 481(3), 2981. DOI.
Slemzin, V.A., Goryaev, F.F., Rodkin, D.G., Shugay, Y.S., Kuzin, S.V.: 2019, Formation of coronal mass ejections in the solar corona and propagation of the resulting plasma streams in the heliosphere. Plasma Phys. Rep. 45(10), 889. DOI.
Sugihara, G., May, R.M.: 1990, Nonlinear forecasting as a way of distinguishing chaos from measurement error in time series. Nature 344(6268), 734. DOI.
Sugihara, G., May, R., Ye, H., Hsieh, C.-h., Deyle, E., Fogarty, M., Munch, S.: 2012, Detecting causality in complex ecosystems. Science 338(6106), 496. DOI.
Takens, F.: 1981, Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In: Lecture Notes in Mathematics 898, 366. DOI.
Thomson, D.J.: 1982, Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Proc. IEEE 70, 1055.
Torrence, C., Compo, G.P.: 1998, A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79, 61.
Webb, D.F., Howard, T.A.: 2012, Coronal mass ejections: observations. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 9(1), 3. DOI.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. DOI.
Zaqarashvili, T.V., Gurgenashvili, E.: 2018, Magneto-Rossby waves and seismology of solar interior. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 5, 7. DOI.
Zaqarashvili, T.V., Carbonell, M., Oliver, R., Ballester, J.L.: 2010, Quasi-biennial oscillations in the solar tachocline caused by magnetic Rossby wave instabilities. Astrophys. J. Lett. 724(1), L85. DOI.
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, On the temporal relationship between coronal mass ejections and flares. Astrophys. J. 559(1), 452. DOI.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the referee for his/her valuable comments and suggestions, which improved the manuscript. The CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. This study was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) by the Project of 115F031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilcik, A., Chowdhury, P., Sarp, V. et al. Temporal and Periodic Variation of the MCMESI for the Last Two Solar Cycles; Comparison with the Number of Different Class X-ray Solar Flares. Sol Phys 295, 159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01711-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01711-2