Abstract
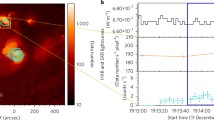
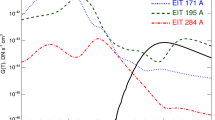
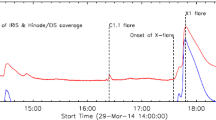
One of the key processes associated with the “standard” flare model is chromospheric evaporation, a process during which plasma heated to high temperatures by energy deposition at the flare footpoints is driven upwards into the corona. Despite several decades of study, a number of open questions remain, including the relationship between plasma produced during this process and observations of earlier “superhot” plasma. The Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer (EIS) onboard Hinode has a wide slot, which is often used as a flare trigger in the He ii emission-line band. Once the intensity passes a threshold level, the study will switch to one focussed on the flaring region. However, when the intensity is not high enough to reach the flare trigger threshold, these datasets are then available during the entire flare period and provide high-cadence spectroscopic observations over a large field of view. We make use of data from two such studies of a C4.7 flare and a C1.6 flare to probe the relationship between hot Fe xxiv plasma and plasmas observed by the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI) and the X-ray Telescope (XRT) to track where the emission comes from and when it begins. The flare trigger slot data used in our analysis has one-minute cadence. Although the spatial and spectral information are merged in the wide-slot data, it is still possible to extract when the hot plasma appears, through the appearance of the Fe xxiv spectral image. It is also possible to derive spectrally pure Fe xxiv light curves from the EIS data, and compare them with those derived from hard X-rays, enabling a full exploration of the evolution of hot emission. The Fe xxiv emission peaks just after the peak in the hard X-ray lightcurve; consistent with an origin in the evaporation of heated plasma following the transfer of energy to the lower atmosphere. A peak was also found for the C4.7 flare in the RHESSI peak temperature, which occurred before the hard X-rays peaked. This suggests that the first peak in hot-plasma emission is likely to be directly related to the energy-release process.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battaglia, M., Kontar, E.P.: 2011, Hard X-ray footpoint sizes and positions as diagnostics of flare accelerated energetic electrons in the low solar atmosphere. Astrophys. J.735, 42. DOI . ADS .
Caspi, A., Krucker, S., Lin, R.P.: 2014, Statistical properties of super-hot solar flares. Astrophys. J.781, 43. DOI . ADS .
Caspi, A., Lin, R.P.: 2010, RHESSI line and continuum observations of super-hot flare plasma. Astrophys. J. Lett.725, L161. DOI . ADS .
Culhane, J.L., Phillips, A.T., Inda-Koide, M., Kosugi, T., Fludra, A., Kurokawa, H., Makishima, K., Pike, C.D., Sakao, T., Sakurai, T., Doschek, G.A., Bentley, R.D.: 1994, Yohkoh observations of the creation of high-temperature plasma in the flare of 16 December 1991. Solar Phys.153, 307. DOI . ADS .
Culhane, J.L., Harra, L.K., James, A.M., Al-Janabi, K., Bradley, L.J., Chaudry, R.A., Rees, K., Tandy, J.A., Thomas, P., Whillock, M.C.R., Winter, B., Doschek, G.A., Korendyke, C.M., Brown, C.M., Myers, S., Mariska, J., Seely, J., Lang, J., Kent, B.J., Shaughnessy, B.M., Young, P.R., Simnett, G.M., Castelli, C.M., Mahmoud, S., Mapson-Menard, H., Probyn, B.J., Thomas, R.J., Davila, J., Dere, K., Windt, D., Shea, J., Hagood, R., Moye, R., Hara, H., Watanabe, T., Matsuzaki, K., Kosugi, T., Hansteen, V., Wikstol, Ø.: 2007, The EUV imaging spectrometer for Hinode. Solar Phys.243, 19. DOI . ADS .
De Pontieu, B., Title, A.M., Lemen, J.R., Kushner, G.D., Akin, D.J., Allard, B., Berger, T., Boerner, P., Cheung, M., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Freeland, S., Heyman, G.F., Hoffman, C., Hurlburt, N.E., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D., Rehse, R., Sabolish, D., Seguin, R., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Wülser, J.-P., Wolfson, C.J., Yanari, C., Mudge, J., Nguyen-Phuc, N., Timmons, R., van Bezooijen, R., Weingrod, I., Brookner, R., Butcher, G., Dougherty, B., Eder, J., Knagenhjelm, V., Larsen, S., Mansir, D., Phan, L., Boyle, P., Cheimets, P.N., DeLuca, E.E., Golub, L., Gates, R., Hertz, E., McKillop, S., Park, S., Perry, T., Podgorski, W.A., Reeves, K., Saar, S., Testa, P., Tian, H., Weber, M., Dunn, C., Eccles, S., Jaeggli, S.A., Kankelborg, C.C., Mashburn, K., Pust, N., Springer, L., Carvalho, R., Kleint, L., Marmie, J., Mazmanian, E., Pereira, T.M.D., Sawyer, S., Strong, J., Worden, S.P., Carlsson, M., Hansteen, V.H., Leenaarts, J., Wiesmann, M., Aloise, J., Chu, K.-C., Bush, R.I., Scherrer, P.H., Brekke, P., Martinez-Sykora, J., Lites, B.W., McIntosh, S.W., Uitenbroek, H., Okamoto, T.J., Gummin, M.A., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Waltham, N.: 2014, The Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS). Solar Phys.289, 2733. DOI . ADS .
Fivian, M., Hemmeck, R., McHedlishvili, A., Zehnder, A.: 2002, RHESSI aspect reconstruction. Solar Phys.210, 87. DOI . ADS .
Fletcher, L., Dennis, B.R., Hudson, H.S., Krucker, S., Phillips, K., Veronig, A., Battaglia, M., Bone, L., Caspi, A., Chen, Q., Gallagher, P., Grigis, P.T., Ji, H., Liu, W., Milligan, R.O., Temmer, M.: 2011, An observational overview of solar flares. Space Sci. Rev.159, 19. DOI . ADS .
Golub, L., Deluca, E., Austin, G., Bookbinder, J., Caldwell, D., Cheimets, P., Cirtain, J., Cosmo, M., Reid, P., Sette, A., Weber, M., Sakao, T., Kano, R., Shibasaki, K., Hara, H., Tsuneta, S., Kumagai, K., Tamura, T., Shimojo, M., McCracken, J., Carpenter, J., Haight, H., Siler, R., Wright, E., Tucker, J., Rutledge, H., Barbera, M., Peres, G., Varisco, S.: 2007, The X-Ray Telescope (XRT) for the Hinode mission. Solar Phys.243, 63. DOI . ADS .
Harra, L.K., Hara, H., Doschek, G.A., Matthews, S., Warren, H., Culhane, J.L., Woods, M.M.: 2017, Measuring velocities in the early stage of an eruption. Astrophys. J.842, 58. DOI . ADS .
Kobelski, A.R., Saar, S.H., Weber, M.A., McKenzie, D.E., Reeves, K.K.: 2014, Calibrating data from the Hinode/X-Ray Telescope and associated uncertainties. Solar Phys.289, 2781. DOI . ADS .
Kosugi, T., Matsuzaki, K., Sakao, T., Shimizu, T., Sone, Y., Tachikawa, S., Hashimoto, T., Minesugi, K., Ohnishi, A., Yamada, T., Tsuneta, S., Hara, H., Ichimoto, K., Suematsu, Y., Shimojo, M., Watanabe, T., Shimada, S., Davis, J.M., Hill, L.D., Owens, J.K., Title, A.M., Culhane, J.L., Harra, L.K., Doschek, G.A., Golub, L.: 2007, The Hinode (Solar-B) mission: an overview. Solar Phys.243, 3. DOI . ADS .
Lee, K.-S., Imada, S., Watanabe, K., Bamba, Y., Brooks, D.H.: 2017, IRIS, Hinode, SDO, and RHESSI observations of a white light flare produced directly by nonthermal electrons. Astrophys. J.836, 150. DOI . ADS .
Lin, R.P., Dennis, B.R., Hurford, G.J., Smith, D.M., Zehnder, A., Harvey, P.R., Curtis, D.W., Pankow, D., Turin, P., Bester, M., Csillaghy, A., Lewis, M., Madden, N., van Beek, H.F., Appleby, M., Raudorf, T., McTiernan, J., Ramaty, R., Schmahl, E., Schwartz, R., Krucker, S., Abiad, R., Quinn, T., Berg, P., Hashii, M., Sterling, R., Jackson, R., Pratt, R., Campbell, R.D., Malone, D., Landis, D., Barrington-Leigh, C.P., Slassi-Sennou, S., Cork, C., Clark, D., Amato, D., Orwig, L., Boyle, R., Banks, I.S., Shirey, K., Tolbert, A.K., Zarro, D., Snow, F., Thomsen, K., Henneck, R., McHedlishvili, A., Ming, P., Fivian, M., Jordan, J., Wanner, R., Crubb, J., Preble, J., Matranga, M., Benz, A., Hudson, H., Canfield, R.C., Holman, G.D., Crannell, C., Kosugi, T., Emslie, A.G., Vilmer, N., Brown, J.C., Johns-Krull, C., Aschwanden, M., Metcalf, T., Conway, A.: 2002, The Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). Solar Phys.210, 3. DOI . ADS .
Milligan, R.O., Dennis, B.R.: 2009, Velocity characteristics of evaporated plasma using Hinode/EUV imaging spectrometer. Astrophys. J.699, 968. DOI . ADS .
Narukage, N., Sakao, T., Kano, R., Shimojo, M., Winebarger, A., Weber, M., Reeves, K.K.: 2014, Coronal-temperature-diagnostic capability of the Hinode/ X-ray telescope based on self-consistent calibration. II. Calibration with on-orbit data. Solar Phys.289, 1029. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys.275, 3. DOI . ADS .
Pike, C.D., Phillips, K.J.H., Lang, J., Sterling, A., Watanabe, T., Hiei, E., Culhane, J.L., Cornille, M., Dubau, J.: 1996, YOHKOH observations of Fe XXVI X-ray line emission from solar flares. Astrophys. J.464, 487. DOI . ADS .
Polito, V., Reep, J.W., Reeves, K.K., Simões, P.J.A., Dudík, J., Del Zanna, G., Mason, H.E., Golub, L.: 2016, Simultaneous IRIS and Hinode/EIS observations and modelling of the 2014 October 27 X2.0 class flare. Astrophys. J.816, 89. DOI . ADS .
Polito, V., Del Zanna, G., Valori, G., Pariat, E., Mason, H.E., Dudík, J., Janvier, M.: 2017, Analysis and modelling of recurrent solar flares observed with Hinode/EIS on March 9, 2012. Astron. Astrophys.601, A39. DOI . ADS .
Tanaka, K.: 1986, Solar flare X-ray spectra of Fe XXVI and Fe XXV from the Hinotori satellite. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan38, 225. ADS .
Warmuth, A., Mann, G.: 2016, Constraints on energy release in solar flares from RHESSI and GOES X-ray observations. II. Energetics and energy partition. Astron. Astrophys.588, A116. DOI . ADS .
Widing, K.G., Dere, K.P.: 1977, Multiple loop activation and continuous energy release in the solar flare of June 15, 1973. Solar Phys.55, 431. DOI . ADS .
Wu, C.-C., Liou, K., Lepping, R.P., Hutting, L., Plunkett, S., Howard, R.A., Socker, D.: 2016, The first super geomagnetic storm of solar cycle 24: “The St. Patrick’s day event (17 March 2015)”. Earth Planets Space68, 151. DOI . ADS .
Young, P.R., Tian, H., Jaeggli, S.: 2015, The 2014 March 29 X-flare: subarcsecond resolution observations of Fe XXI \(\lambda\)1354.1. Astrophys. J.799, 218. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
This project has been funded through the award of the Daiwa-Adrian Prize through the Daiwa Anglo–Japanese foundation. Hinode is a Japanese mission developed and launched by ISAS/JAXA, collaborating with NAOJ as a domestic partner, and NASA and STFC (UK) as international partners. Scientific operation of Hinode is performed by the Hinode science team organized at ISAS/JAXA. This team mainly consists of scientists from institutes in the partner countries. Support for the post-launch operation is provided by JAXA and NAOJ (Japan), STFC (UK), NASA, ESA, and NSC (Norway). SDO data were obtained courtesy of NASA/SDO and the AIA and HMI science teams. D.M. Long acknowledges support from the European Commission’s H2020 Programme under the following Grant Agreements: GREST (no. 653982) and Pre-EST (no. 739500) as well as support from the Leverhulme Trust for an Early-Career Fellowship (ECF-2014-792) and is grateful to the Science Technology and Facilities Council for the award of an Ernest Rutherford Fellowship (ST/R003246/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harra, L., Matthews, S., Long, D. et al. Locating Hot Plasma in Small Flares using Spectroscopic Overlappogram Data from the Hinode EUV Imaging Spectrometer. Sol Phys 295, 34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01602-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01602-6