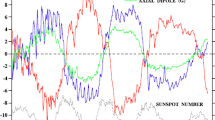Abstract
Synoptic magnetograms and relevant proxy data were analyzed to study the evolution of the Sun’s polar magnetic fields. The time-latitude analysis of large-scale magnetic fields demonstrates cyclic changes in their zonal structure and the polar field buildup. The time-latitude distributions of the emergent and remnant magnetic flux enable us to examine individual features of recent cycles. The poleward transport of predominantly following polarities contributed much of the polar flux and led to polar field reversals. Multiple reversals of dominant polarities at the Sun’s poles were identified in Cycles 20 and 21. Triple reversals were caused by remnant flux surges of following and leading polarities. The time-latitude analysis of solar magnetic fields in Cycles 20 – 24 revealed zones that are characterized by a predominance of negative (non-Joy) tilts and by the appearance of active regions that violate Hale’s polarity law. The decay of non-Joy and anti-Hale active regions results in remnant flux surges that disturb the usual order in magnetic flux transport and sometimes lead to multiple reversals of polar fields. The analysis of local and large-scale magnetic fields and their causal relation improved our understanding of the Sun’s polar field weakening.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H.W.: 1961, The topology of the Sun’s magnetic field and the 22-year cycle. Astrophys. J. 133, 572.
Baranyi, T.: 2015, Comparison of Debrecen and Mount Wilson/Kodaikanal sunspot group tilt angles and the Joy’s law. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 447, 1857.
Baumann, I., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M., Solanki, S.K.: 2004, Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field on the solar surface: A parameter study. Astron. Astrophys. 426, 1075.
Cameron, R.H., Duvall, T.L., Schüssler, M., Schunker, H.: 2018, Observing and modeling the poloidal and toroidal fields of the solar dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 609, A56.
Choudhuri, A.R., Karak, B.B.: 2012, Origin of grand minima in sunspot cycles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109(17), 171103.
Choudhuri, A.R., Schüssler, M., Dikpati, M.: 1995, The solar dynamo with meridional circulation. Astron. Astrophys. 303, L29.
Dasi-Espuig, M., Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A., Cameron, R., Peñuela, T.: 2010, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 518, A7.
Dasi-Espuig, M., Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A., Cameron, R., Peñuela, T.: 2013, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle (Corrigendum). Astron. Astrophys. 556, C3.
DeVore, C.R., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Boris, J.P., Young, T.R. Jr., Harvey, K.L.: 1985, Simulations of magnetic-flux transport in solar active regions. Solar Phys. 102, 41.
Durney, B.R.: 1995, On a Babcock–Leighton dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field. Solar Phys. 160, 213.
Duvall, T.L. Jr., Wilcox, J.M., Svalgaard, L., Scherrer, P.H., McIntosh, P.S.: 1977, Comparison of H alpha synoptic charts with the large-scale solar magnetic field as observed at Stanford. NASA STI/Recon Technical Report N 77.
Erofeev, D.V.: 2004, An observational evidence for the Babcock–Leighton dynamo scenario. In: Stepanov, A.V., Benevolenskaya, E.E., Kosovichev, A.G. (eds.) Multi-Wavelength Investigations of Solar Activity, IAU Symposium 223, 97.
Gaizauskas, V., Harvey, K.L., Harvey, J.W., Zwaan, C.: 1983, Large-scale patterns formed by solar active regions during the ascending phase of Cycle 21. Astrophys. J. 265, 1056.
Golubeva, E.M., Mordvinov, A.V.: 2016, Decay of activity complexes, formation of unipolar magnetic regions, and coronal holes in their causal relation. Solar Phys. 291, 3605.
Golubeva, E.M., Mordvinov, A.V.: 2017, Rearrangements of open magnetic flux and formation of polar coronal holes in Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 292, 175.
Györi, L., Baranyi, T., Ludmány, A., Gerlei, O., Csepura, G., Mezö, G.: 2004, Debrecen photoheliographic data for the years 1993 – 1995. Publ. Debr. Heliophys. Obs. 17, 1.
Hathaway, D.H., Rightmire, L.: 2011, Variations in the axisymmetric transport of magnetic elements on the Sun: 1996 – 2010. Astrophys. J. 729, 80.
Hoeksema, J.T.: 2010, Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field over three solar cycles. In: Kosovichev, A.G., Andrei, A.H., Rozelot, J.-P. (eds.) Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets, IAU Symposium 264, 222.
Howard, R.F.: 1991, Axial tilt angles of sunspot groups. Solar Phys. 136, 251.
Jiang, J., Cameron, R.H., Schüssler, M.: 2015, The cause of the weak solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. Lett. 808, L28.
Jiang, J., Işik, E., Cameron, R.H., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M.: 2010, The effect of activity-related meridional flow modulation on the strength of the solar polar magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 717, 597.
Jiang, J., Cameron, R.H., Schmitt, D., Işık, E.: 2013, Modeling solar cycles 15 to 21 using a flux transport dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 553, A128.
Jiang, J., Hathaway, D.H., Cameron, R.H., Solanki, S.K., Gizon, L., Upton, L.: 2014, Magnetic flux transport at the solar surface. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 491.
Jones, H.P., Duvall, T.L. Jr., Harvey, J.W., Mahaffey, C.T., Schwitters, J.D., Simmons, J.E.: 1992, The NASA/NSO spectromagnetograph. Solar Phys. 139, 211.
Kitchatinov, L.L., Mordvinov, A.V., Nepomnyashchikh, A.A.: 2018, Modelling variability of solar activity cycles. Astron. Astrophys. 615, A38.
Kosovichev, A.G., Stenflo, J.O.: 2008, Tilt of emerging bipolar magnetic regions on the Sun. Astrophys. J. Lett. 688, L115.
Leighton, R.B.: 1969, A magneto-kinematic model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 156, 1.
Li, J.: 2018, A systematic study of Hale and anti-Hale sunspot physical parameters. Astrophys. J. 867(2), 89. http://stacks.iop.org/0004-637X/867/i=2/a=89 .
Li, J., Ulrich, R.K.: 2012, Long-term measurements of sunspot magnetic tilt angles. Astrophys. J. 758(2), 115.
Lockwood, M., Owens, M.J., Imber, S.M., James, M.K., Bunce, E.J., Yeoman, T.K.: 2017, Coronal and heliospheric magnetic flux circulation and its relation to open solar flux evolution. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 5870.
Makarov, V.I., Fatianov, M.P., Sivaraman, K.R.: 1983, Poleward migration of the magnetic neutral line and the reversal of the polar fields on the Sun. I – Period 1945 – 1981. Solar Phys. 85, 215.
Makarov, V.I., Sivaraman, K.R.: 1986, Atlas of H-alpha synoptic charts for solar cycle 19 (1955 – 1964). Carrington solar rotations 1355 to 1486. Kodaikanal Obs. Bull. 7, 138.
McClintock, B.H., Norton, A.A.: 2013, Recovering Joy’s law as a function of solar cycle, hemisphere, and longitude. Solar Phys. 287, 215.
McClintock, B.H., Norton, A.A.: 2016, Tilt angle and footpoint separation of small and large bipolar sunspot regions observed with HMI. Astrophys. J. 818, 7.
McIntosh, P.S.: 1979, Annotated atlas of H-alpha synoptic charts for solar Cycle 20 (1964 – 1974) Carrington solar rotations 1487 – 1616. NASA STI/Recon Technical Report N 79.
Mordvinov, A.V., Yazev, S.A.: 2014, Reversals of the Sun’s polar magnetic fields in relation to activity complexes and coronal holes. Solar Phys. 289, 1971.
Mordvinov, A.V., Grigoryev, V.M., Erofeev, D.V.: 2015, Evolution of sunspot activity and inversion of the Sun’s polar magnetic field in the current cycle. Adv. Space Res. 55, 2739.
Mordvinov, A., Pevtsov, A., Bertello, L., Petri, G.: 2016, The reversal of the Sun’s magnetic field in Cycle 24. J. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2(1), 3.
Muñoz-Jaramillo, A., Dasi-Espuig, M., Balmaceda, L.A., DeLuca, E.E.: 2013, Solar cycle propagation, memory prediction: insights from a century of magnetic proxies. Astrophys. Lett. 767, L25.
Olemskoy, S.V., Kitchatinov, L.L.: 2013, Grand minima and North–South asymmetry of solar activity. Astrophys. J. 777, 71.
Petrie, G.J.D.: 2015, Solar magnetism in the polar regions. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12, 5.
Petrie, G., Ettinger, S.: 2017, Polar field reversals and active region decay. Space Sci. Rev. 210, 77.
Pevtsov, A.A., Berger, M.A., Nindos, A., Norton, A.A., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2014, Magnetic helicity, tilt, and twist. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 285.
Schrijver, C.J., Zwaan, C.: 2000, Solar and Stellar Magnetic Activity, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Wang, Y.-M.: 2016, Bipolar magnetic regions determined from Kitt Peak vacuum telescope magnetograms. DOI .
Snodgrass, H.B., Kress, J.M., Wilson, P.R.: 2000, Observations of the polar magnetic fields during the polarity reversals of Cycle 22. Solar Phys. 191, 1.
Sokoloff, D., Khlystova, A., Abramenko, V.: 2015, Solar small-scale dynamo and polarity of sunspot groups. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 451, 1522.
Starck, J.-L., Murtagh, F.: 2006, Astronomical Image and Data Analysis, Springer, Berlin, 360.
Stenflo, J.O., Kosovichev, A.G.: 2012, Bipolar magnetic regions on the Sun: Global analysis of the SOHO/MDI data set. Astrophys. J. 745(2), 129.
Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Zhao, J.: 2015, On polar magnetic field reversal and surface flux transport during Solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 798, 114.
Tlatova, K., Tlatov, A., Pevtsov, A., Mursula, K., Vasil’eva, V., Heikkinen, E., Bertello, L., Pevtsov, A., Virtanen, I., Karachik, N.: 2018, Tilt of sunspot bipoles in Solar Cycles 15 to 24. Solar Phys. 293, 118.
Upton, L., Hathaway, D.H.: 2014, Effects of meridional flow variations on Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Astrophys. J. 792(2), 142.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1989, Average properties of bipolar magnetic regions during sunspot Cycle 21. Solar Phys. 124(1), 81.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1991, Magnetic flux transport and the Sun’s dipole moment – New twists to the Babcock–Leighton model. Astrophys. J. 375, 761.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 2004, Footpoint switching and the evolution of coronal holes. Astrophys. J. 612(2), 1196.
Webb, D.F., Gibson, S.E., Hewins, I., McFadden, R., Emery, B.A., Malanushenko, A.V.: 2017, Studies of global solar magnetic field patterns using a newly digitized archive. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts.
Yeates, A.R., Baker, D., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2015, Source of a prominent poleward surge during Solar Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 290, 3189.
Acknowledgements
This research uses synoptic magnetograms from the WSO and Kitt Peak observatories. We also used sunspot group tilt data from the Mount Wilson and Debrecen observatories. The synoptic maps from the McIntosh archive were also used in this research. We are grateful to A.I. Khlystova for preparing data on anti-Hale active regions, and J. Sutton for improving the English version of the manuscript. The work was supported by Basic Research program II.16 and the RFBR project 17-02-00016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mordvinov, A.V., Kitchatinov, L.L. Evolution of the Sun’s Polar Fields and the Poleward Transport of Remnant Magnetic Flux. Sol Phys 294, 21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1410-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1410-1