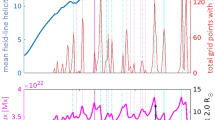
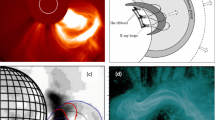
Abstract
A flare and fast coronal mass ejection originated between solar active regions NOAA 11514 and 11515 on 2012 July 1 (SOL2012-07-01) in response to flux emergence in front of the leading sunspot of the trailing region 11515. Analyzing the evolution of the photospheric magnetic flux and the coronal structure, we find that the flux emergence triggered the eruption by interaction with overlying flux in a non-standard way. The new flux neither had the opposite orientation nor a location near the polarity inversion line, which are favorable for strong reconnection with the arcade flux under which it emerged. Moreover, its flux content remained significantly smaller than that of the arcade (\({\approx}\,40~\%\)). However, a loop system rooted in the trailing active region ran in part under the arcade between the active regions, passing over the site of flux emergence. The reconnection with the emerging flux, leading to a series of jet emissions into the loop system, caused a strong but confined rise of the loop system. This lifted the arcade between the two active regions, weakening its downward tension force and thus destabilizing the considerably sheared flux under the arcade. The complex event was also associated with supporting precursor activity in an enhanced network near the active regions, acting on the large-scale overlying flux, and with two simultaneous confined flares within the active regions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F., Aly, J.J., Tagger, M.: 1996, Plasmoid formation in a single sheared arcade and application to coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 306, 913. ADS .
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F., Aly, J.J., Mikic, Z., Linker, J.: 2003, Coronal mass ejection: Initiation, magnetic helicity, and flux ropes. II. Turbulent diffusion-driven evolution. Astrophys. J. 595, 1231. DOI . ADS .
Amari, T., Aly, J.-J., Luciani, J.-F., Mikic, Z., Linker, J.: 2011, Coronal mass ejection initiation by converging photospheric flows: Toward a realistic model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 742, L27. DOI . ADS .
Archontis, V., Hood, A.W.: 2010, Flux emergence and coronal eruption. Astron. Astrophys. 514, A56. DOI . ADS .
Archontis, V., Hood, A.W.: 2012, Magnetic flux emergence: A precursor of solar plasma expulsion. Astron. Astrophys. 537, A62. DOI . ADS .
Archontis, V., Török, T.: 2008, Eruption of magnetic flux ropes during flux emergence. Astron. Astrophys. 492, L35. DOI . ADS .
Aulanier, G., Démoulin, P., Grappin, R.: 2005, Equilibrium and observational properties of line-tied twisted flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 430, 1067. DOI . ADS .
Aulanier, G., Török, T., Démoulin, P., DeLuca, E.E.: 2010, Formation of torus-unstable flux ropes and electric currents in erupting sigmoids. Astrophys. J. 708, 314. DOI . ADS .
Burtseva, O., Petrie, G.: 2013, Magnetic flux changes and cancellation associated with X-class and M-class flares. Solar Phys. 283, 429. DOI . ADS .
Chen, P.F., Shibata, K.: 2000, An emerging flux trigger mechanism for coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 545, 524. DOI . ADS .
Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Schmieder, B., Hémoux, J.C., Csepura, G., Hagyard, M.J.: 1993, Evidence for magnetic reconnection in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 271, 292. ADS .
Feynman, J., Martin, S.F.: 1995, The initiation of coronal mass ejections by newly emerging magnetic flux. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 3355. DOI . ADS .
Forbes, T.G., Priest, E.R.: 1995, Photospheric magnetic field evolution and eruptive flares. Astrophys. J. 446, 377. DOI . ADS .
Gibson, S.E., Fan, Y.: 2006, The partial expulsion of a magnetic flux rope. Astrophys. J. Lett. 637, L65. DOI . ADS .
Green, L.M., Kliem, B., Wallace, A.J.: 2011, Photospheric flux cancellation and associated flux rope formation and eruption. Astron. Astrophys. 526, A2. DOI . ADS .
Hagyard, M.J., Venkatakrishnan, P., Smith, J.B. Jr.: 1990, Nonpotential magnetic fields at sites of gamma-ray flares. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 73, 159. DOI . ADS .
Harvey, J.W., Hill, F., Hubbard, R.P., Kennedy, J.R., Leibacher, J.W., Pintar, J.A., Gilman, P.A., Noyes, R.W., Title, A.M., Toomre, J., Ulrich, R.K., Bhatnagar, A., Kennewell, J.A., Marquette, W., Patron, J., Saa, O., Yasukawa, E.: 1996, The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) project. Science 272, 1284. DOI . ADS .
Harvey, J.W., Bolding, J., Clark, R., Hauth, D., Hill, F., Kroll, R., Luis, G., Mills, N., Purdy, T., Henney, C., Holland, D., Winter, J.: 2011, Full-disk solar H-alpha images from GONG. In: AAS/Solar Physics Division Abstracts #42, 1745. ADS .
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., Thompson, W.T., St Cyr, O.C., Mentzell, E., Mehalick, K., Lemen, J.R., Wuelser, J.P., Duncan, D.W., Tarbell, T.D., Wolfson, C.J., Moore, A., Harrison, R.A., Waltham, N.R., Lang, J., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Mapson-Menard, H., Simnett, G.M., Halain, J.P., Defise, J.M., Mazy, E., Rochus, P., Mercier, R., Ravet, M.F., Delmotte, F., Auchere, F., Delaboudiniere, J.P., Bothmer, V., Deutsch, W., Wang, D., Rich, N., Cooper, S., Stephens, V., Maahs, G., Baugh, R., McMullin, D., Carter, T.: 2008, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67. DOI . ADS .
Kaneko, T., Yokoyama, T.: 2014, Simulation study of solar plasma eruptions caused by interactions between emerging flux and coronal arcade fields. Astrophys. J. 796, 44. DOI . ADS .
Karpen, J.T., Antiochos, S.K., DeVore, C.R.: 2012, The mechanisms for the onset and explosive eruption of coronal mass ejections and eruptive flares. Astrophys. J. 760, 81. DOI . ADS .
Kliem, B., Török, T.: 2006, Torus instability. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(25), 255002. DOI . ADS .
Kusano, K., Bamba, Y., Yamamoto, T.T., Iida, Y., Toriumi, S., Asai, A.: 2012, Magnetic field structures triggering solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 760, 31. DOI . ADS .
Leake, J.E., Linton, M.G., Antiochos, S.K.: 2014, Simulations of emerging magnetic flux. II. The formation of unstable coronal flux ropes and the initiation of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 787, 46. DOI . ADS .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Friedlaender, F.M., Heyman, G.F., Hurlburt, N.E., Katz, N.L., Kushner, G.D., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., McFeaters, E.L., Mitchell, S., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Springer, L.A., Stern, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Wuelser, J.-P., Wolfson, C.J., Yanari, C., Bookbinder, J.A., Cheimets, P.N., Caldwell, D., Deluca, E.E., Gates, R., Golub, L., Park, S., Podgorski, W.A., Bush, R.I., Scherrer, P.H., Gummin, M.A., Smith, P., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Soufli, R., Windt, D.L., Beardsley, S., Clapp, M., Lang, J., Waltham, N.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI . ADS .
Li, H., Sakurai, T., Ichimoto, K., UeNo, S.: 2000, Magnetic field evolution leading to solar flares I. Cases with low magnetic shear and flux emergence. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 52, 465. ADS .
Lin, J., Forbes, T.G.: 2000, Effects of reconnection on the coronal mass ejection process. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 2375. DOI . ADS .
Lin, J., Forbes, T.G., Isenberg, P.A.: 2001, Prominence eruptions and coronal mass ejections triggered by newly emerging flux. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25053. DOI . ADS .
Lites, B.W.: 2005, Magnetic flux ropes in the solar photosphere: The vector magnetic field under active region filaments. Astrophys. J. 622, 1275. DOI . ADS .
Livi, S.H.B., Martin, S., Wang, H., Ai, G.: 1989, The association of flares to cancelling magnetic features on the Sun. Solar Phys. 121, 197. DOI . ADS .
Louis, R.E., Puschmann, K.G., Kliem, B., Balthasar, H., Denker, C.: 2014, Sunspot splitting triggering an eruptive flare. Astron. Astrophys. 562, A110. DOI . ADS .
Low, B.C.: 1996, Solar activity and the corona. Solar Phys. 167, 217. DOI . ADS .
Lynch, B.J., Antiochos, S.K., DeVore, C.R., Luhmann, J.G., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2008, Topological evolution of a fast magnetic breakout CME in three dimensions. Astrophys. J. 683, 1192. DOI . ADS .
Mackay, D.H., van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2006, Models of the large-scale corona. I. Formation, evolution, and liftoff of magnetic flux ropes. Astrophys. J. 641, 577. DOI . ADS .
Mackay, D.H., Karpen, J.T., Ballester, J.L., Schmieder, B., Aulanier, G.: 2010, Physics of solar prominences: II – Magnetic structure and dynamics. Space Sci. Rev. 151, 333. DOI . ADS .
Manchester, W. IV, Gombosi, T., DeZeeuw, D., Fan, Y.: 2004, Eruption of a buoyantly emerging magnetic flux rope. Astrophys. J. 610, 588. DOI . ADS .
Martin, S.F.: 1998, Conditions for the formation and maintenance of filaments (invited review). Solar Phys. 182, 107. DOI . ADS .
Martin, S.F., Dezso, L., Antalova, A., Kucera, A., Harvey, K.L.: 1982, Emerging magnetic flux, flares and filaments – FBS interval 16 – 23 June 1980. Adv. Space Res. 2, 39. DOI . ADS .
Martres, M.-J., Michard, R., Soru-Iscovici, I., Tsap, T.T.: 1968, Étude de la localisation des éruptions dans la structure magnétique évolutive des régions actives solaires. Solar Phys. 5, 187. DOI . ADS .
Mikic, Z., Linker, J.A.: 1994, Disruption of coronal magnetic field arcades. Astrophys. J. 430, 898. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI . ADS .
Roumeliotis, G., Sturrock, P.A., Antiochos, S.K.: 1994, A numerical study of the sudden eruption of sheared magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 423, 847. DOI . ADS .
Rust, D.M.: 1972, Flares and changing magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 25, 141. DOI . ADS .
Sakajiri, T., Brooks, D.H., Yamamoto, T., Shiota, D., Isobe, H., Akiyama, S., Ueno, S., Kitai, R., Shibata, K.: 2004, A study of a tiny two-ribbon flare driven by emerging flux. Astrophys. J. 616, 578. DOI . ADS .
Savcheva, A.S., Green, L.M., van Ballegooijen, A.A., DeLuca, E.E.: 2012, Photospheric flux cancellation and the build-up of sigmoidal flux ropes on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 759, 105. DOI . ADS .
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., Wachter, R., Couvidat, S., Rabello-Soares, M.C., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Akin, D.J., Allard, B.A., Miles, J.W., Rairden, R., Shine, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J., Elmore, D.F., Norton, A.A., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 229. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2009, Driving major solar flares and eruptions: A review. Adv. Space Res. 43, 739. DOI . ADS .
Schuck, P.W.: 2006, Tracking magnetic footpoints with the magnetic induction equation. Astrophys. J. 646, 1358. DOI . ADS .
Sterling, A.C., Chifor, C., Mason, H.E., Moore, R.L., Young, P.R.: 2010, Evidence for magnetic flux cancelation leading to an ejective solar eruption observed by Hinode, TRACE, STEREO, and SoHO/MDI. Astron. Astrophys. 521, A49. DOI . ADS .
Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Wiegelmann, T., Hayashi, K., Chen, Q., Thalmann, J.: 2012, Evolution of magnetic field and energy in a major eruptive active region based on SDO/HMI observation. Astrophys. J. 748, 77. DOI . ADS .
Titov, V.S., Démoulin, P.: 1999, Basic topology of twisted magnetic configurations in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 351, 707. ADS .
Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2003, The evolution of twisting coronal magnetic flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 406, 1043. DOI . ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Martens, P.C.H.: 1989, Formation and eruption of solar prominences. Astrophys. J. 343, 971. DOI . ADS .
van Tend, W., Kuperus, M.: 1978, The development of coronal electric current systems in active regions and their relation to filaments and flares. Solar Phys. 59, 115. DOI . ADS .
Wang, H.: 2006, Rapid changes of photospheric magnetic fields around flaring magnetic neutral lines. Astrophys. J. 649, 490. DOI . ADS .
Wang, J., Shi, Z.: 1993, The flare-associated magnetic changes in an active region. II – Flux emergence and cancellation. Solar Phys. 143, 119. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1999, Filament eruptions near emerging bipoles. Astrophys. J. Lett. 510, L157. DOI . ADS .
Xu, X.-Y., Chen, P.-F., Fang, C.: 2005, A parametric survey of the CME triggering process by numerical simulations. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 5, 636. DOI . ADS .
Xu, X.-Y., Fang, C., Chen, P.-F.: 2008, A statistical study on the filament eruption caused by new emerging flux. Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 32, 56. DOI . ADS .
Zhang, J., Cheng, X., Ding, M.-D.: 2012, Observation of an evolving magnetic flux rope before and during a solar eruption. Nat. Commun. 3, 747. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, Prediction of the interplanetary magnetic field strength. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 19. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge constructive comments by the referee, which were helpful in improving the clarity of this article. R.E.L. is grateful for the financial assistance from the German Science Foundation (DFG) under grant DE 787/3-1 and the European Commission’s FP7 Capacities Programme under the Grant Agreement number 312495. G.C. and B.K. acknowledge support by the NSF under Grant No. 1249270. B.K. also acknowledges support by the DFG. HMI data are courtesy of NASA/SDO and the HMI science team. They are provided by the Joint Science Operations Center – Science Data Processing at Stanford University. EUVI-B and COR1-B images are supplied courtesy of the STEREO Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) team. This work utilizes data obtained by the Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) Program, managed by the National Solar Observatory, which is operated by AURA, Inc. under a cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. The data were acquired by instruments operated by the Big Bear Solar Observatory, High Altitude Observatory, Learmonth Solar Observatory, Udaipur Solar Observatory, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, and Cerro Tololo Interamerican Observatory. We have used the SOHO/LASCO CME catalog, generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Solar and Stellar Flares: Observations, Simulations, and Synergies
Guest Editors: Lyndsay Fletcher and Petr Heinzel
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louis, R.E., Kliem, B., Ravindra, B. et al. Triggering an Eruptive Flare by Emerging Flux in a Solar Active-Region Complex. Sol Phys 290, 3641–3662 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0726-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0726-8