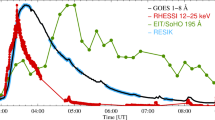
Abstract
We test the compatibility and biases of multi-thermal flare DEM (differential emission measure) peak temperatures determined with AIA with those determined by GOES and RHESSI using the isothermal assumption. In a set of 149 M- and X-class flares observed during the first two years of the SDO mission, AIA finds DEM peak temperatures at the time of the peak GOES 1 – 8 Å flux to have an average of T p=12.0±2.9 MK and Gaussian DEM widths of log10(σ T )=0.50±0.13. From GOES observations of the same 149 events, a mean temperature of T p=15.6±2.4 MK is inferred, which is systematically higher by a factor of T GOES/T AIA=1.4±0.4. We demonstrate that this discrepancy results from the isothermal assumption in the inversion of the GOES filter ratio. From isothermal fits to photon spectra at energies of ϵ≈6 – 12 keV of 61 of these events, RHESSI finds the temperature to be higher still by a factor of T RHESSI/T AIA=1.9±1.0. We find that this is partly a consequence of the isothermal assumption. However, RHESSI is not sensitive to the low-temperature range of the DEM peak, and thus RHESSI samples only the high-temperature tail of the DEM function. This can also contribute to the discrepancy between AIA and RHESSI temperatures. The higher flare temperatures found by GOES and RHESSI imply correspondingly lower emission measures. We conclude that self-consistent flare DEM temperatures and emission measures require simultaneous fitting of EUV (AIA) and soft X-ray (GOES and RHESSI) fluxes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschwanden, M.J.: 2007, RHESSI timing studies: multithermal delays. Astrophys. J. 661, 1242 – 1259. 10.1086/516814 .
Aschwanden, M.J.: 2012, The spatio-temporal evolution of solar flares observed with AIA/SDO: Fractal diffusion, sub-diffusion, or logistic growth? Astrophys. J. 757, 94. 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/94 .
Aschwanden, M.J., Alexander, D.: 2001, Flare plasma cooling from 30 MK down to 1 MK modeled from Yohkoh, GOES, and TRACE observations during the Bastille Day Event (14 July 2000). Solar Phys. 204, 91 – 120. 10.1023/A:1014257826116 .
Aschwanden, M.J., Shimizu, T.: 2013, Multi-wavelength observations of the spatio-temporal evolution of solar flares with AIA/SDO: II. Hydrodynamic scaling laws and thermal energies. Astrophys. J. 776, 132. 10.1088/0004-637X/776/2/132 .
Aschwanden, M.J., Stern, R.A., Güdel, M.: 2008, Scaling laws of solar and stellar flares. Astrophys. J. 672, 659 – 673. 10.1086/523926 .
Aschwanden, M.J., Zhang, J., Liu, K.: 2013, Multi-wavelength observations of the spatio-temporal evolution of solar flares with AIA/SDO. I. Universal scaling laws of space and time parameters. Astrophys. J. 775, 23. 10.1088/0004-637X/775/1/23 .
Aschwanden, M.J., Boerner, P., Schrijver, C.J., Malanushenko, A.: 2013, Automated temperature and emission measure analysis of coronal loops and active regions observed with the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO/AIA). Solar Phys. 283, 5 – 30. 10.1007/s11207-011-9876-5 .
Battaglia, M., Grigis, P.C., Benz, A.O.: 2005, Size dependence of solar X-ray flare properties. Astron. Astrophys. 439, 737 – 747. 10.1051/0004-6361:20053027 .
Brown, J.C.: 1974, On the thermal interpretation of hard X-ray bursts from solar flares. In: Newkirk, G.A. (ed.) Coronal Disturbances, IAU Symp. 57, 395 – 411.
Caspi, A., Lin, R.P.: 2010, RHESSI line and continuum observations of super-hot flare plasma. Astrophys. J. Lett. 725, L161 – L166. 10.1088/2041-8205/725/2/L161 .
Dulk, G.A., Dennis, B.R.: 1982, Microwaves and hard X-rays from solar flares – Multithermal and nonthermal interpretations. Astrophys. J. 260, 875 – 884. 10.1086/160306 .
Emslie, A.G., Dennis, B.R., Shih, A.Y., Chamberlin, P.C., Mewaldt, R.A., Moore, C.S., Share, G.H., Vourlidas, A., Welsch, B.T.: 2012, Global energetics of thirty-eight large solar eruptive events. Astrophys. J. 759, 71. 10.1088/0004-637X/759/1/71 .
Feldman, U., Mandelbaum, P., Seely, J.F., Doschek, G.A., Gursky, H.: 1992, The potential for plasma diagnostics from stellar extreme-ultraviolet observations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 81, 387 – 408. 10.1086/191698 .
Feldman, U., Doschek, G.A., Behring, W.E., Phillips, K.J.H.: 1996, Electron temperature, emission measure, and X-ray flux in A2 to X2 X-ray class solar flares. Astrophys. J. 460, 1034 – 1041. 10.1086/177030 .
Graham, D.R., Hannah, I.G., Fletcher, L., Milligan, R.O.: 2013, The emission measure distribution of impulsive phase flare footpoints. Astrophys. J. 767, 83. 10.1088/0004-637X/767/1/83 .
Hannah, I.G., Christe, S., Krucker, S., Hurford, G.J., Hudson, H.S., Lin, R.P.: 2008, RHESSI microflare statistics. II. X-ray imaging, spectroscopy, and energy distributions. Astrophys. J. 677, 704 – 718. 10.1086/529012 .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., et al.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17 – 40. 10.1007/s11207-011-9776-8 .
Lin, R.P., Schwartz, R.A., Pelling, R.M., Hurley, K.C.: 1981, A new component of hard X-rays in solar flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 251, L109 – L114. 10.1086/183704 .
Lin, R.P., Dennis, B.R., Hurford, G.J., Smith, D.M., Zehnder, A., Harvey, P.R., Curtis, D.W., Pankow, D., et al.: 2002, The Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). Solar Phys. 210, 3 – 32. 10.1023/A:1022428818870 .
Mazzotta, P., Mazzitelli, G., Colafrancesco, S., Vittorio, N.: 1998, Ionization balance for optically thin plasmas: rate coefficients for all atoms and ions of the elements H to NI. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 133, 403 – 409. 10.1051/aas:1998330 .
McTiernan, J.M.: 2009, RHESSI/GOES observations of the nonflaring Sun from 2002 to 2006. Astrophys. J. 697, 94 – 99. 10.1088/0004-637X/697/1/94 .
Raftery, C.L., Gallagher, P.T., Milligan, R.O., Klimchuk, J.A.: 2009, Multi-wavelength observations and modelling of a canonical solar flare. Astron. Astrophys. 494, 1127 – 1136. 10.1051/0004-6361:200810437 .
Rosner, R., Tucker, W.H., Vaiana, G.S.: 1978, Dynamics of the quiescent solar corona. Astrophys. J. 220, 643 – 645. 10.1086/155949 .
Ryan, D.F., Milligan, R.O., Gallagher, P.T., Dennis, B.R., Tolbert, A.K., Schwartz, R.A., Young, C.A.: 2012, The thermal properties of solar flares over three solar cycles using GOES X-ray observations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 202, 11. 10.1088/0067-0049/202/2/11 .
Ryan, D.F., Chamberlin, P.C., Milligan, R.O., Gallagher, P.T.: 2013, Decay-phase cooling and inferred heating of M- and X-class solar flares. Astrophys. J. 778, 68. 10.1088/0004-637X/778/1/68 .
Smith, D.M., Lin, R.P., Turin, P., Curtis, D.W., Primbsch, J.H., Campbell, R.D., Abiad, R., Schroeder, P., Cork, C.P., Hull, E.L., Landis, D.A., Madden, N.W., Malone, D., Pehl, R.H., Raudorf, T., Sangsingkeow, P., Boyle, R., Banks, I.S., Shirey, K., Schwartz, R.: 2002, The RHESSI spectrometer. Solar Phys. 210, 33 – 60. 10.1023/A:1022400716414 .
Thomas, R.J., Crannell, C.J., Starr, R.: 1985, Expressions to determine temperatures and emission measures for solar X-ray events from GOES measurements. Solar Phys. 95, 323 – 329. 10.1007/BF00152409 .
White, S.M., Thomas, R.J., Schwartz, R.A.: 2005, Updated expressions for determining temperatures and emission measures from GOES soft X-ray measurements. Solar Phys. 227, 231 – 248. 10.1007/s11207-005-2445-z .
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the following for supporting this research: NASA (contract NNG04EA00C of the SDO/AIA instrument to LMSAL), the Fulbright Association, Catholic University of America, and the Irish Research Council. Thanks must also go to Richard A. Schwartz for his helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryan, D.F., O’Flannagain, A.M., Aschwanden, M.J. et al. The Compatibility of Flare Temperatures Observed with AIA, GOES, and RHESSI. Sol Phys 289, 2547–2563 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0492-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0492-z