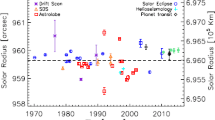
Abstract
The total solar irradiance varies over a solar cycle of 11 years and maybe over cycles of longer periods. Is the solar diameter variable over time too? A discussion of the solar diameter and its variations must be linked to the limb darkening function (LDF). We introduce a new method to perform high-resolution astrometry of the solar diameter from the ground, through the observations of eclipses, using the luminosity evolution of Baily’s bead and the profile of the lunar edge available from satellite data. This approach unifies the definition of the solar limb with the inflection point of LDF for eclipses and drift-scan or heliometric methods. The method proposed is applied for the videos of the eclipse on 15 January 2010 recorded in Uganda and in India. The result suggests reconsidering the evaluations of the historical eclipses observed with the naked eye.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Dealing with the radius is equivalent to dealing with the diameter, but in this work we refer to the former or to the latter depending on the context.
References
Adassuriya, J., Gunasekera, S., Samarasinha, N.: 2012, Determination of the solar radius based on the annular solar eclipse of 15 January 2010. Sun Geophys. 6, 13.
Antia, H.M., Basu, S., Pintar, J., Pohl, B.: 2000, Solar cycle variation in solar f-mode frequencies and radius. Solar Phys. 192, 459.
Araki, H., Tazawa, S., Noda, H., Tsubokawa, T., Kawano, N., Sasaki, S.: 2008, Observation of the lunar topography by the laser altimeter LALT on board Japanese lunar explorer SELENE. Adv. Space Res. 42, 317.
Auwers, A.: 1891, Der Sonnendurchmesser und der Venusdurchmesser nach den Beobachtungen an den Heliometern der deutschen Venus-Expeditionen. Astron. Nachr. 128, 361.
Baily, F.: 1836, On a remarkable phenomenon that occurs in total and annular eclipses of the sun. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 4, 15.
Bush, R.I., Emilio, M., Kuhn, J.R.: 2010, On the constancy of the solar radius. III. Astrophys. J. 716, 1381.
Clavius, C.: 1593, In Sphaeram Ioannis de Sacro Bosco Commentarius.
Djafer, D., Thuillier, G., Sofia, S.: 2008, A comparison among solar diameter measurements carried out from the ground and outside Earth’s atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 676, 651.
Dziembowski, W.A., Goode, P.R., Schou, J.: 2001, Does the Sun shrink with increasing magnetic activity? Astrophys. J. 553, 897.
Eddy, J., Boornazian, A.A., Clavius, C., Shapiro, I.I., Morrison, L.V., Sofia, S.: 1980, Shrinking Sun. Sky Telesc. 60, 10.
Egidi, A., Caccin, B., Sofia, S., Heaps, W., Hoegy, W., Twigg, L.: 2006, High-precision measurements of the solar diameter and oblateness by the Solar Disk Sextant (SDS) experiment. Solar Phys. 235, 407.
Emilio, M., Kuhn, J.R., Bush, R.I., Scholl, I.F.: 2012, Measuring the solar radius from space during the 2003 and 2006 Mercury transits. Astrophys. J., in press.
Haberreiter, M., Schmutz, W., Hubeny, I.: 2008, NLTE model calculations for the solar atmosphere with an iterative treatment of opacity distribution functions. Astron. Astrophys. 492, 833.
Krivova, V.I., Solanki, S.K., Fligge, M., Unruh, Y.C.: 2003, Reconstruction of solar irradiance variations in cycle 23: Is solar surface magnetism the cause? Astron. Astrophys. 399, 1.
Kuhn, J.R., Bush, R.I., Emilio, M., Scherrer, P.H.: 2004, On the constancy of the solar diameter. II. Astrophys. J. 613, 1241.
Livingston, W., Wallace, L.: 2003, The Sun’s immutable basal quiet atmosphere. Solar Phys. 212, 227.
Pap, J.M.: 2003, Total solar and spectral irradiance variations from near-UV to infrared. In: Rozelot, J.-P. (ed.) The Sun’s Surface and Subsurface: Investigating Shape, Lecture Notes in Physics 599, Springer, Berlin, 129.
Pouillet, C.S.M.: 1838, Memoire sur le chaleur solaire, Bachelier, Paris.
Ribes, J.C., Nesme-Ribes, E.: 1993, The solar sunspot cycle in the Maunder minimum AD1645 to AD1715. Astron. Astrophys. 76, 549.
Rogerson, J.B.: 1959, The solar limb intensity profile. Astrophys. J. 130, 985.
Rozelot, J.P., Lefebvre, S., Pireaux, S., Ajabshirizadeh, A.: 2004, Are non-magnetic mechanisms such as temporal solar diameter variations conceivable for an irradiance variability? Solar Phys. 224, 229.
Shapiro, A.I., Schmutz, W., Schoell, M., Haberreiter, M., Rozanov, E.: 2010, NLTE solar irradiance modeling with the COSI code. Astron. Astrophys. 517, A48.
Sigismondi, C.: 2009, Guidelines for measuring solar radius with Baily beads analysis. Sci. China Ser. G 52, 1773.
Sigismondi, C.: 2011, High precision ground-based measurements of solar diameter in support of Picard mission. arXiv:1112.5878 .
Sigismondi, C., Oliva, P.: 2005, Solar oblateness from Archimedes to Dicke. Nuovo Cimento B 120, 1181.
Sofia, S., Heaps, W., Twigg, L.W.: 1994, The solar diameter and oblateness measured by the solar disk sextant on the 1992 September 30 balloon flight. Astrophys. J. 427, 1048.
Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A.: 2005, Solar irradiance variations: From current measurements to long-term estimates. Solar Phys. 224, 197.
Thuillier, G., Claudel, J., Djafer, D., Haberreiter, M., Mein, N., Melo, S.M.L., Schmutz, W., Shapiro, A., Short, C.I., Sofia, S.: 2011, The shape of the solar limb: Models and observations. Solar Phys. 268, 125.
Acknowledgements
This research has made use of the data taken with the LALT instrument on board the lunar orbiter Kaguya of JAXA/SELENE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raponi, A., Sigismondi, C., Guhl, K. et al. The Measurement of Solar Diameter and Limb Darkening Function with the Eclipse Observations. Sol Phys 278, 269–283 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-9947-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-9947-2