Abstract
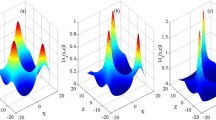
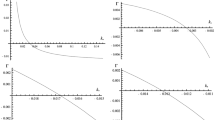
Remote observations of coronal holes have strongly suggested the resonant interactions of ion-cyclotron waves with ions as a principal mechanism for plasma heating and acceleration of the fast solar wind. In order to study these waves, a WKB (Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin) linear perturbation analysis is used in the frame work of a collisionless multi-fluid model where we consider in addition to protons a second ion component made of alpha particles. We consider a non-uniform background plasma describing a funnel region in the open coronal holes and we use the ray tracing Hamiltonian-type equations to compute the ray path of the waves and the spatial variation of their properties. At low frequency (smaller than the proton cyclotron frequency), the results showed a distinct behavior of the two ion-cyclotron modes found in our calculations, namely the first one propagates anisotropically guided along the magnetic field lines while the second one propagates isotropically with no preferred direction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axford, W.I., McKenzie, J.F.: 1997, The origin of the solar wind. In: Winterhalter, D., Gosling, J.T., Habbal, S.R., Kurth, W.S., Neugebauer, M. (eds.) Solar Wind Eight, American Institute of Physics, Woodbury, 31.
Bernstein, I.B., Friedland, L.: 1984, Geometric optics in space and time varying plasmas. In: Galeev, A.A., Sudan, R.N. (eds.) Basic Plasma Physics: Handbook of Plasma Physics 1, 367.
Bourouaine, S., Vocks, C., Marsch, E.: 2008, Multi-ion kinetic model for coronal loop. Astrophys. J. Lett. 680, L77.
Cranmer, S.R.: 2009, Coronal holes. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 6(3). http://solarphysics.livingreviews.org/Articles/lrsp-2009-3/ .
Fineschi, S., Naletto, G., Nicolosi, P., Noci, G., Pernechele, C., Romoli, M., Spadaro, D., Tondello, G.: 1994, Ultraviolet coronagraph spectrometer (UVCS) for the solar and heliospheric (SOHO) mission. In: Cerutti-Maori, M.G., Roussel, P. (eds.) Space Optics 1994: Earth Observation and Astronomy. Proc. SPIE 2209, 348.
Fleck, B., Domingo, V., Poland, A.I.: 1995, The SOHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, ix. doi: 10.1007/BF00733423 .
Fontenla, J.M., Avrett, E.H., Loeser, R.: 1993, Energy balance in the solar transition region. III – Helium emission in hydrostatic, constant-abundance models with diffusion. Astrophys. J. 406, 319.
Gabriel, A.H.: 1976, A magnetic model of the solar transition region. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A 281, 339.
Hackenberg, P., Marsch, E., Mann, G.: 2000, On the origin of the fast solar wind in polar coronal funnels. Astron. Astrophys. 360, 1139.
Hollweg, J.V.: 2000, Cyclotron resonance in coronal holes: 3. A five-beam turbulence-driven model. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 15699.
Hollweg, J.V., Isenberg, P.A.: 2002, Generation of the fast solar wind: A review with emphasis on the resonant cyclotron interaction. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1147.
Isenberg, P.A., Lee, M.A., Hollweg, J.V.: 2000, A kinetic model of coronal heating and acceleration by ion-cyclotron waves: Preliminary results. Solar Phys. 193, 247.
Kohl, J.L., Noci, G., Antonucci, E., Tondello, G., Huber, M.C.E., Gardner, L.D., et al.: 1997, First results from the SOHO Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer. Solar Phys. 175, 613.
Krauss-Varban, D., Omidi, N., Quest, K.B.: 1994, Mode properties of low-frequency waves: Kinetic theory versus Hall-MHD. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5987.
Li, X., Habbal, S.R., Hollweg, J.V., Esser, R.: 1999, Heating and cooling of protons by turbulence-driven ion cyclotron waves in the fast solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 2521.
Mann, G., Hackenberg, P., Marsch, E.: 1997, Linear mode analysis in multi-ion plasmas. J. Plasma Phys. 58, 205.
Markovskii, S.A.: 2001, Generation of ion cyclotron waves in coronal holes by a global resonant magnetohydrodynamic mode. Astrophys. J. 557, 337.
Marsch, E., Tu, C.-Y.: 2001, Heating and acceleration of coronal ions interacting with plasma waves through cyclotron and Landau resonance. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 227.
Mecheri, R., Marsch, E.: 2007, Coronal ion-cyclotron beam instabilities within the multi-fluid description. Astron. Astrophys. 474, 609.
Melrose, D.B.: 1986, Instabilities in Space and Laboratory Plasmas, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Chapter 12.
Ofman, L., Gary, S.P., Viñas, A.: 2002, Resonant heating and acceleration of ions in coronal holes driven by cyclotron resonant spectra. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1461.
Ofman, L., Davila, J.M., Nakariakov, V.M., Viñas, A.-F.: 2005, High-frequency Alfvén waves in multi-ion coronal plasma: Observational implications. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09102.
Shafranov, V.D.: 1967, Electromagnetic waves in a plasma. In: Leontovich, M.A. (ed.) Reviews of Plasma Physics 3, Consultant Bureau, New York, 1.
Stix, T.H.: 1992, Waves in Plasmas, American Institute of Physics, New York, Chapter 10.
Vocks, C., Marsch, E.: 2001, A semi-kinetic model of wave-ion interaction in the solar corona. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 1917.
Weinberg, S.: 1962, Eikonal method in magnetohydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 126, 1899.
Wilhelm, K.: 1995, SUMER – Solar Ultraviolet Measurements of Emitted Radiation. In: Benz, A.O., Krüger, A. (eds.) Coronal Magnetic Energy Releases, Lecture Notes in Physics 444, Springer, Berlin, 245.
Wilhelm, K., Marsch, E., Dwivedi, B.N., Hassler, D.M., Lemaire, P., Gabriel, A.H., Huber, M.C.E.: 1998, The solar corona above polar coronal holes as seen by SUMER on SOHO. Astrophys. J. 500, 1023.
Xie, H., Ofman, L., Viñas, A.: 2004, Multiple ions resonant heating and acceleration by Alfvén/cyclotron fluctuations in the corona and the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 8103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mecheri, R. Properties of Ion-Cyclotron Waves in the Open Solar Corona. Sol Phys 282, 133–146 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0134-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0134-2