Abstract
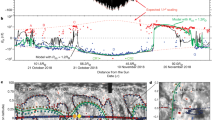
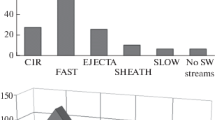
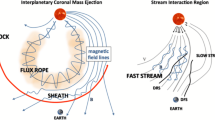
Analysis of the Interball-1 spacecraft data (1995 – 2000) has shown that the solar wind ion flux sometimes increases or decreases abruptly by more than 20% over a time period of several seconds or minutes. Typically, the amplitude of such sharp changes in the solar wind ion flux (SCIFs) is larger than 0.5×108 cm−2 s−1. These sudden changes of the ion flux were also observed by the Solar Wind Experiment (SWE), on board the Wind spacecraft, as the solar wind density increases and decreases with negligible changes in the solar wind velocity. SCIFs occur irregularly at 1 AU, when plasma flows with specific properties come to the Earth’s orbit. SCIFs are usually observed in slow, turbulent solar wind with increased density and interplanetary magnetic field strength. The number of times SCIFs occur during a day is simulated using the solar wind density, magnetic field, and their standard deviations as input parameters for a period of five years. A correlation coefficient of ∼0.7 is obtained between the modelled and the experimental data. It is found that SCIFs are not associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs), corotating interaction regions (CIRs), or interplanetary shocks; however, 85% of the sector boundaries are surrounded by SCIFs. The properties of the solar wind plasma for days with five or more SCIF observations are the same as those of the solar wind plasma at the sector boundaries. One possible explanation for the occurrence of SCIFs (near sector boundaries) is magnetic reconnection at the heliospheric current sheet or local current sheets. Other probable causes of SCIFs (inside sectors) are turbulent processes in the slow solar wind and at the crossings of flux tubes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCIF:
-
Sharp change of ion flux
- IMF:
-
Interplanetary magnetic field
- SBC:
-
Sector boundary crossing
- HCS:
-
Heliospheric current sheet
- CIR:
-
Corotating interaction region
- CME:
-
Coronal mass ejection
- ULF:
-
Ultra low frequency
- MC:
-
Magnetic cloud
References
Blanco, J.J., Rodriguez-Pacheco, J., Hidalgo, M.A., Sequeiros, J.: 2006, Analysis of the heliospheric current sheet fine structure: Single or multiple current sheets. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 68, 2173 – 2181.
Borodkova, N.L., Zastenker, G.N., Riazantseva, O., Richardson, J.D.: 2005, Large and sharp solar wind dynamic pressure variations as a source of geomagnetic field disturbances in the outer magnetosphere (at the geosynchronous orbits). Planet. Space Sci. 53, 25 – 32.
Borovsky, J.E.: 2008, Flux tube texture of the solar wind: Strands of the magnetic carpet at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A08110.
Borrini, G., Gosling, J., Bame, S., Feldman, W., Wilcox, J.: 1981, Solar wind helium and hydrogen structure near the heliospheric current sheet: A signal of coronal streamers at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4565 – 4573.
Briggs, P.R., Armstrong, T.P.: 1984, Observations of interplanetary energetic ion enhancements near magnetic sector boundaries. Geophys. Res. Lett. 11, 27 – 30.
Bruno, R., Carbone, V.: 2005, The solar wind as a turbulence laboratory. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2. http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2005-4 .
Crooker, N.U., Huang, C.-L., Lamassa, S.M., Larson, D.E., Kahler, S.W., Spence, H.E.: 2004, Heliospheric plasma sheets. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A03107.
Dalin, P.A., Zastenker, G.N., Nozdrachev, M.N., Veselovsky, I.S.: 2002a, Properties of large and sharp impulses in the solar wind. Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron. 3, 51 – 56.
Dalin, P.A., Zastenker, G.N., Paularena, K.I., Richardson, J.D.: 2002b, A survey of large, rapid solar wind dynamic pressure changes observed by Interball-1 and IMP 8. Ann. Geophys. 20, 293 – 299.
Gosling, J.T., McComas, D.J., Skoug, R.M., Smith, C.W.: 2006, Magnetic reconnection at the heliospheric current sheet and the formation of closed magnetic field lines in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L17102.
Hakamada, K.: 1980, Geomagnetic activity at the time of heliospheric current sheet crossings. Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, 653 – 656.
Hammond, C.M., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Goldstein, B.E., Balogh, A.: 1995, Solar wind double ion beams and the heliospheric current sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 7881 – 7889.
Hirshberg, J., Colburn, D.S.: 1973, Geomagnetic activity at sector boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 3952 – 3957.
Hollweg, J.V.: 1972, Supergranulation-driven Alfvén waves in the solar chromosphere, and related phenomena. Cosm. Electrodyn. 2, 423 – 444.
Hollweg, J.V.: 1986, Transition region, corona, and solar wind in coronal holes. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 4111 – 4125.
Khabarova, O.V., Zastenker, G.N.: 2008, Sharp and sizeable changes of solar wind ion flux as a feature of dense non-CIR turbulent regions. Geoph. Res. Abstracts, 10, EGU2008-A-09908.
Lacombe, C., Salem, C., Mangeney, A., Steinberg, J.-L., Macsimovic, M., Bosqued, J.M.: 2000, Latitudinal distribution of the solar wind properties in the low- and high-pressure regimes: Wind observations. Ann. Geophys. 18, 852 – 865.
Lavraud, B., Denton, M.H., Thomsen, M.F., Borovsky, J.E., Friedel, R.H.W.: 2005, Superposed epoch analysis of dense plasma access to geosynchronous orbit. Ann. Geophys. 23, 2519 – 2529.
Li, X.: 2003, Transition region, coronal heating and the fast solar wind. Astron. Astrophys. 406, 345 – 356.
Marsch, E.: 2006, Kinetic physics of the solar corona and solar wind. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 3, 1. http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2006-1 .
Marsch, E., Liu, S.: 1993, Structure functions and intermittency of velocity fluctuations in the inner solar wind. Ann. Geophys. 11, 227 – 238.
Murphy, N., Smith, E.J., Burton, M.E., Winterhalter, D., McComas, D.J.: 1993, Energetic ion beams near the heliospheric current sheet: Possible evidence for reconnection. Jet Propulsion Lab. (NASA) Technical Report. http://trs-new.jpl.nasa.gov/dspace/bitstream/2014/35959/1/93-1689.pdf .
Neugebauer, M., Liewer, P.C., Goldstein, B.E., Zhou, X., Steinberg, J.T.: 2004, Solar wind stream interaction regions without sector boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A10102.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Interscience, New York.
Parkhomov, V.A., Riazantseva, M.O., Zastenker, G.N.: 2005, Local amplification of auroral electrojet as response to sharp solar wind dynamic pressure change on June 26, 1998. Planet. Space Sci. 53, 265 – 274.
Phan, T.D., Gosling, J.T., Davis, M.S.: 2009, Prevalence of extended reconnection X-lines in the solar wind at 1 AU. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L09108.
Qin, G., Li, G.: 2008, Effect of flux tubes in the solar wind on the diffusion of energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 682, L129 – L132.
Riazantseva, M.O., Dalin, P.A., Zastenker, G.N.: 2002, Statistical analysis of fast and large impulses of solar wind ion flux (density) as measured by Interball-1. Soln.-zemn. fiz. 2, 89 – 92.
Riazantseva, M.O., Khabarova, O.V., Zastenker, G.N.: 2005, Sharp boundaries of solar wind plasma structures and an analysis of their pressure balance. Cosm. Res. 43, 157 – 164.
Riazantseva, M.O., Dalin, P.A., Zastenker, G.N., Parhomov, V.A., Eselevich, V.G., Eselevich, M.V., Richardson, J.: 2003a, Properties of sharp and large changes in the solar wind ion flux (density). Cosm. Res. 41, 395 – 404.
Riazantseva, M.O., Dalin, P.A., Zastenker, G.N., Richardson, J.: 2003b, Orientation of sharp fronts in the solar wind plasma. Cosm. Res. 41, 405 – 416.
Riazantseva, M.O., Zastenker, G.N., Richardson, J.D., Eiges, P.E.: 2005, Sharp boundaries of small- and middle-scale solar wind structures. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12110.
Riazantseva, M.O., Khabarova, O.V., Zastenker, G.N., Richardson, J.D.: 2007, Sharp boundaries of the solar wind plasma structures and their relationship to the solar wind turbulence. Adv. Space Res. 40, 1802 – 1806.
Roberts, D.A., Keiter, P.A., Goldstein, M.L.: 2005, Origin and dynamics of the heliospheric streamer belt and current sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A06102.
Romanova, N., Pilipenko, V., Crosby, N., Khabarova, O.: 2007, ULF wave index and its possible applications in space physics. Bulg. J. Phys. 34, 136 – 148. http://www.bjp-bg.com/papers/bjp2007_2_136-148.pdf .
Safrankova, J., Zastenker, G.N., Nemecek, Z., et al.: 1997, Small scale observations of magnetopause motion: Preliminary results of the INTERBALL project. Ann. Geophys. 15, 562 – 569.
Schwenn, R.: 1990, Large-scale structure of the interplanetary medium. In: Schewenn, R., Marsch, E. (eds.) Physics of the Inner Heliosphere I, Springer, Berlin, 99 – 181.
Smith, E.J.: 2001, The heliospheric current sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15819 – 15831.
Svalgaard, L.: 1973, Geomagnetic responses to the solar wind and solar activity, NASA, SUIPR report no. 555. http://www.leif.org/research/Geomagnetic-Response-to-Solar-Wind.pdf .
Svalgaard, L.: 1975, On the use of Godhavn H component as an indictor of the interplanetary sector polarity. J. Geophys. Res. 80, 2717 – 2722.
Svalgaard, L., Wilcox, J.M., Scherrer, P.H., Howard, R.: 1975, The Sun’s magnetic sector structure. Solar Phys. 45, 83 – 91.
Velli, M., Grappin, R.: 1993, Properties of the solar wind. Adv. Space Res. 13, 49 – 58.
von Steiger, R., Schwadron, N., Fisk, L., Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Hefti, S., et al.: 2000, Composition of quasi-stationary solar wind flows from Ulysses/Solar Wind Ion Composition Spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27217 – 27238.
Wang, Y.-M.: 1993, Flux-tube divergence, coronal heating, and the solar wind. Astrophys. J. Lett. 410, L123 – L126.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1990, Solar wind speed and coronal flux-tube expansion. Astrophys. J. 355, 726 – 732.
Watari, S., Watanabe, T.: 2006, Sector boundary crossings and geomagnetic activities. Adv. Geosi. 2(ST), 135 – 142.
Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1965, Quasi-stationary corotating structure in the interplanetary medium. J. Geophys. Res. 70, 5793 – 5805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khabarova, O., Zastenker, G. Sharp Changes of Solar Wind Ion Flux and Density Within and Outside Current Sheets. Sol Phys 270, 311–329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9719-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9719-4