Abstract
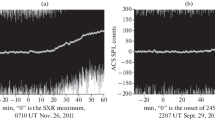
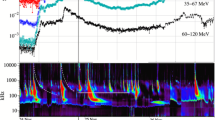
Solar energetic particles (SEPs) detected in space are statistically associated with flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). But it is not clear how these processes actually contribute to the acceleration and transport of the particles. The present work addresses the question why flares accompanied by intense soft X-ray bursts may not produce SEPs detected by observations with the GOES spacecraft. We consider all X-class X-ray bursts between 1996 and 2006 from the western solar hemisphere. 21 out of 69 have no signature in GOES proton intensities above 10 MeV, despite being significant accelerators of electrons, as shown by their radio emission at cm wavelengths. The majority (11/20) has no type III radio bursts from electron beams escaping towards interplanetary space during the impulsive flare phase. Together with other radio properties, this indicates that the electrons accelerated during the impulsive flare phase remain confined in the low corona. This occurs in flares with and without a CME. Although GOES saw no protons above 10 MeV at geosynchronous orbit, energetic particles were detected in some (4/11) confined events at Lagrangian point L1 aboard ACE or SoHO. These events have, besides the confined microwave emission, dm-m wave type II and type IV bursts indicating an independent accelerator in the corona. Three of them are accompanied by CMEs. We conclude that the principal reason why major solar flares in the western hemisphere are not associated with SEPs is the confinement of particles accelerated in the impulsive phase. A coronal shock wave or the restructuring of the magnetically stressed corona, indicated by the type II and IV bursts, can explain the detection of SEPs when flare-accelerated particles do not reach open magnetic field lines. But the mere presence of these radio signatures, especially of a metric type II burst, is not a sufficient condition for a major SEP event.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimov, V.V., Ambrož, P., Belov, A.V., Berlicki, A., Chertok, I.M., Karlický, M., et al.: 1996, Evidence for prolonged acceleration based on a detailed analysis of the long-duration solar gamma-ray flare of June 15, 1991. Solar Phys. 166, 107 – 134.
Aurass, H., Landini, F., Poletto, G.: 2009, Coronal current sheet signatures during the 17 May 2002 CME-flare. Astron. Astrophys. 506, 901 – 911.
Axisa, F.: 1974, On the role of the magnetic configuration of flares for production of type III solar radio bursts. Solar Phys. 35, 207 – 224.
Balch, C.C.: 2008, Updated verification of the Space Weather Prediction Center’s solar energetic particle prediction model. Space Weather 6, S01001.
Bastian, T.S., Benz, A.O., Gary, D.E.: 1998, Radio emission from solar flares. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 36, 131 – 188.
Belov, A., Kurt, V., Mavromichalaki, H., Gerontidou, M.: 2007, Peak-size distributions of proton fluxes and associated soft X-ray flares. Solar Phys. 246, 457 – 470.
Benz, A.O., Brajša, R., Magdalenić, J.: 2007, Are there radio-quiet solar flares? Solar Phys. 240, 263 – 270.
Benz, A.O., Grigis, P.C., Csillaghy, A., Saint-Hilaire, P.: 2005, Survey on solar X-ray flares and associated coherent radio emissions. Solar Phys. 226, 121 – 142.
Bougeret, J.L., Kaiser, M.L., Kellogg, P.J., Manning, R., Goetz, K., Monson, S.J., et al.: 1995, Waves: The radio and plasma wave investigation on the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 231 – 263.
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., et al.: 1995, The large angle spectroscopic coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357 – 402.
Bruggmann, G., Vilmer, N., Klein, K.L., Kane, S.R.: 1994, Electron trapping in evolving coronal structures during a large gradual hard X-ray/radio burst. Solar Phys. 149, 171 – 193.
Cane, H.V., Erickson, W.C., Prestage, N.P.: 2002, Solar flares, type III radio bursts, coronal mass ejections and energetic particles. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1315.
Cliver, E.W., McNamara, L.F., Gentile, L.C.: 1985, Peak flux density spectra of large solar radio bursts and proton emission from flares. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 6251 – 6266.
Cliver, E.W., Dennis, B.R., Kiplinger, A.L., Kane, S.R., Neidig, D.F., Sheeley, N.R., Koomen, M.J.: 1986, Solar gradual hard X-ray bursts and associated phenomena. Astrophys. J. 305, 920 – 935.
Delaboudinière, J.P., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., Hochedez, J.F., Millier, F., et al.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-ultraviolet imaging telescope for the SoHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, 291 – 312.
Démoulin, P., Klein, K.L., Goff, C.P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Culhane, J.L., Mandrini, C.H., Matthews, S.A., Harra, L.K.: 2007, Decametric N burst: A consequence of the interaction of two coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 240, 301 – 313.
Dröge, W.: 1996, Energetic solar electron spectra and gamma-ray observations. In: Ramaty, R., Mandzhavidze, N., Hua, X.M. (eds.) High Energy Solar Physics, AIP Conf. Ser. 374, 78 – 85.
Dryer, M., Andrews, M.D., Aurass, H., DeForest, C., Galvin, A.B., Garcia, H., et al.: 1998, The solar minimum active region 7978, its X2.6/1B flare, CME, and interplanetary shock propagation of 9 July 1996. Solar Phys. 181, 159 – 183.
Garcia, H.A.: 2004, Forecasting methods for occurrence and magnitude of proton storms with solar soft X-rays. Space Weather 2, S02002.
Gold, R.E., Krimigis, S.M., Hawkins, S.E., Haggerty, D.K., Lohr, D.A., Fiore, E., Armstrong, T.P., Holland, G., Lanzerotti, L.J.: 1998, Electron, proton, and alpha monitor on the advanced composition explorer spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 541 – 562.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009, Major solar flares without coronal mass ejections. In: Gopalswamy, N., Webb, D.F. (eds.) Universal Heliophysical Processes, IAU Symp. 257, 283 – 286.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12105.
Gosling, J.T., Birn, J., Hesse, M.: 1995, Three-dimensional magnetic reconnection and the magnetic topology of coronal mass ejection events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 869 – 872.
Guidice, D.A., Castelli, J.P.: 1975, Spectral distributions of microwave bursts. Solar Phys. 44, 155 – 172.
Haggerty, D.K., Roelof, E.C.: 2002, Impulsive near-relativistic solar electron events: delayed injection with respect to solar electromagnetic emission. Astrophys. J. 579, 841 – 853.
Hofmann, A., Ruždjak, V.: 2007, Favourable magnetic field configurations for generation of flare-associated meter-wave type III radio bursts. Solar Phys. 240, 107 – 119.
Ippolito, A., Pommois, P., Zimbardo, G., Veltri, P.: 2005, Magnetic connection from the Earth to the solar corona, flare positions and solar energetic particle observations. Astron. Astrophys. 438, 705 – 711.
Kahler, S.W.: 1982a, Radio burst characteristics of solar proton flares. Astrophys. J. 261, 710 – 719.
Kahler, S.W.: 1982b, The role of the big flare syndrome in correlations of solar energetic proton fluxes and associated microwave burst parameters. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 3439 – 3448.
Kahler, S.W., Hundhausen, A.J.: 1992, The magnetic topology of solar coronal structures following mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 1619 – 1631.
Kerdraon, A., Delouis, J.: 1997, The Nançay radioheliograph. In: Trottet, G. (ed.) Coronal Physics from Radio and Space Observations, Lecture Notes in Physics 483, Springer, Berlin, 192 – 201.
Klein, K.L., Trottet, G., Vilmer, N.: 2009, A search for solar energetic particle events with CME-less flares. Proc. 31st Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Paper 0634. http://icrc2009.uni.lodz.pl/proc/pdf/icrc0634.pdf .
Klein, K.L., Trottet, G., Klassen, A.: 2010, Energetic particle acceleration and propagation in strong CME-less flares. Solar Phys. 263, 185 – 208.
Klein, K.L., Schwartz, R.A., McTiernan, J.M., Trottet, G., Klassen, A., Lecacheux, A.: 2003, An upper limit of the number and energy of electrons accelerated at an extended coronal shock wave. Astron. Astrophys. 409, 317 – 324.
Klein, K.L., Krucker, S., Lointier, G., Kerdraon, A.: 2008, Open magnetic flux tubes in the corona and the transport of solar energetic particles. Astron. Astrophys. 486, 589 – 596.
Kocharov, L.G., Kovaltsov, G.A., Kocharov, G.E., Chuikin, E.I., Usoskin, I.G., Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F., Melnikov, V.F., Podstrigach, T.S., Armstrong, T.P.: 1994, Electromagnetic and corpuscular emission from the solar flare of 1991 June 15: continuous acceleration of relativistic particles. Solar Phys. 150, 267 – 283.
Krucker, S., Kontar, E.P., Christe, S., Lin, R.P.: 2007, Solar flare electron spectra at the Sun and near the Earth. Astrophys. J. Lett. 663, 109 – 112.
Laitinen, T., Klein, K.L., Kocharov, L., Torsti, J., Trottet, G., Bothmer, V., Kaiser, M.L., Rank, G., Reiner, M.J.: 2000, Solar energetic particle event and radio bursts associated with the 1996 July 9 flare and coronal mass ejection. Astron. Astrophys. 360, 729 – 741.
Laurenza, M., Cliver, E.W., Hewitt, J., Storini, M., Ling, A.G., Balch, C.C., Kaiser, M.L.: 2009, A technique for short-term warning of solar energetic particle events based on flare location, flare size, and evidence of particle escape. Space Weather 7, S04008.
Marqué, C., Posner, A., Klein, K.L.: 2006, Solar energetic particles and radio-silent fast coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 642, 1222 – 1235.
Masson, S., Klein, K.L., Bütikofer, R., Flückiger, E.O., Kurt, V., Yushkov, B., Krucker, S.: 2009, Acceleration of relativistic protons during the 20 January 2005 flare and CME. Solar Phys. 257, 305 – 322.
Melnikov, V.F., Gary, D.E., Nita, G.M.: 2008, Peak frequency dynamics in solar microwave bursts. Solar Phys. 253, 43 – 73.
Nakajima, H., Sekiguchi, H., Sawa, M., Kai, K., Kawashima, S.: 1985, The radiometer and polarimeters at 80, 35, and 17 GHz for solar observations at Nobeyama. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 37, 163 – 170.
Nindos, A., Aurass, H., Klein, K.L., Trottet, G.: 2008, Radio emission of flares and coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 253, 3 – 41.
Nita, G.M., Gary, D.E., Lee, J.: 2004, Statistical study of two years of solar flare radio spectra obtained with the Owens Valley Solar Array. Astrophys. J. 605, 528 – 545.
Nolte, J.T., Roelof, E.C.: 1973, Large-scale structure of the interplanetary medium, I: high coronal source longitude of the quiet-time solar wind. Solar Phys. 33, 241.
Pick, M.: 1986, Observations of radio continua and terminology. Solar Phys. 104, 19 – 32.
Pick, M., Vilmer, N.: 2008, Sixty-five years of solar radioastronomy: flares, coronal mass ejections and Sun Earth connection. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 16, 1 – 153.
Pick, M., Maia, D., Kerdraon, A., Howard, R., Brueckner, G.E., Michels, D.J., et al.: 1998, Joint Nancay Radioheliograph and LASCO observations of coronal mass ejections – II. The 9 July 1996 event. Solar Phys. 181, 455 – 468.
Rieger, E., Treumann, R.A., Karlický, M.: 1999, The radio-silent start of an intense solar gamma-ray flare. Solar Phys. 187, 59 – 75.
Simnett, G.M., Benz, A.O.: 1986, The role of metric and decimetric radio emission in the understanding of solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 165, 227 – 234.
Torsti, J., Valtonen, E., Lumme, M., Peltonen, P., Eronen, T., Louhola, M., et al.: 1995, Energetic particle experiment ERNE. Solar Phys. 162, 505 – 531.
Trottet, G.: 1986, Relative timing of hard X-rays and radio emissions during the different phases of solar flares – consequences for the electron acceleration. Solar Phys. 104, 145 – 163.
Trottet, G., Vilmer, N., Barat, C., Benz, A., Magun, A., Kuznetsov, A., Sunyaev, R., Terekhov, O.: 1998, A multiwavelength analysis of an electron-dominated gamma-ray event associated with a disk solar flare. Astron. Astrophys. 334, 1099 – 1111.
Veronig, A.M., Brown, J.C.: 2004, A coronal thick-target interpretation of two hard X-ray loop events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 603, 117 – 120.
Wang, Y., Zhang, J.: 2007, A comparative study between eruptive X-class flares associated with coronal mass ejections and confined X-class flares. Astrophys. J. 665, 1428 – 1438.
White, S.M., Kundu, M.R., Bastian, T.S., Gary, D.E., Hurford, G.J., Kucera, T., Bieging, J.H.: 1992, Multifrequency observations of a remarkable solar radio burst. Astrophys. J. 384, 656 – 664.
Zlobec, P., Messerotti, M., Ruzdjak, V., Vrsnak, B., Karlicky, M.: 1990, The role of the magnetic field intensity and geometry in the type III burst generation. Solar Phys. 130, 31 – 37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, KL., Trottet, G., Samwel, S. et al. Particle Acceleration and Propagation in Strong Flares without Major Solar Energetic Particle Events. Sol Phys 269, 309–333 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9710-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9710-0