Abstract
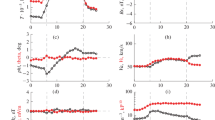
Forecasting space weather more accurately from solar observations requires an understanding of the variations in physical properties of interplanetary (IP) shocks as solar activity changes. We examined the characteristics (occurrence rate, physical parameters, and types of shock driver) of IP shocks. During the period of 1995 – 2001, a total of 249 forward IP shocks were observed. In calculating the shock parameters, we used the solar wind data from Wind at the solar minimum period (1995 – 1997) and from ACE since 1998 including the solar maximum period (1999 – 2001). Most of IP shocks (68%) are concentrated in the solar maximum period. The values of physical quantities of IP shocks, such as the shock speed, the sonic Mach number, and the ratio of plasma density compression, are larger at solar maximum than at solar minimum. However, the ratio of IMF compression is larger at solar minimum. The IP shock drivers are classified into four groups: magnetic clouds (MCs), ejecta, high speed streams (HSSs), and unidentified drivers. The MC is the most dominant and strong shock driver and 150 out of total 249 IP shocks are driven by MCs. The MC is a principal and very effective shock driver not only at solar maximum but also at solar minimum, in contrast to results from previous studies, where the HSS is considered as the dominant IP shock driver.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdichevsky, D.B., Szabo, A., Lepping, R.P., Vinas, A.F.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27289.
Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, Interplanetary Magnetohydrodynamics, Oxford University Press, London, 89.
Burlaga, L.F., Slittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673.
Cane, H.V., White, S.M.: 1989, Solar Phys. 120, 137.
Cho, K.-S., Moon, Y.-J., Dryer, M., Fry, C.D., Park, Y.-D., Kim, K.-S.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, SSH 8-1.
Dryer, M.: 1994, Space Sci. Rev. 67, 363.
Dryer, M., Smart, D.F.: 1984, Adv. Space Res. 4, 291.
Dryer, M., Smith, Z.K., Wu, S.T., Wang, J.F., Gislason, G., Han, S.M., Smart, D.F., Shea, M.A.: 1984, Astrophys. Space Sci. 105, 187.
Foukal, P.V.: 2004, Solar Astrophysics, Wiley, New York, 413.
Fry, C.D., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Sun, W., Deehr, C.S., Akasofu, S.-I.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1070.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29207.
Hewish, A., Tappin, S.J., Gapper, G.R.: 1985, Nature 314, 14.
Kahler, S.W., Reames, D.V.: 1991, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 9419.
Kahler, S.W., Crooker, N.U., Gosling, J.T.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 9919.
Kallendrode, M.-B.: 2001, Space Physics, 2nd edn., Springer, Berlin, 143.
Kim, R.-S., Cho, K.-S., Moon, Y.-J., Kim, Y.-H., Yi, Y., Dryer, M., Bong, S.-C., Park, Y.-D.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A11104.
Lazarus, A.J., Ogilvie, K.W., Burlaga, L.F.: 1970, Solar Phys. 13, 232.
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Burlaga, L.F., Lazarus, A.J., Kasper, J., Desch, M.D., Wu, C.-C., Reames, D.V., Singer, H.J., Smith, C.W., Ackerson, K.L.: 2001, Solar Phys. 204, 285.
Lindsay, G.M., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Gazid, P.: 1994, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 11.
Lindsay, G.M., Luhmann, J.G., Russell, C.T., Gosling, J.T.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12515.
Oh, S.Y., Yi, Y., Nah, J.-K., Cho, K.-S.: 2002, J. Korean Astron. Soc. 35, 151.
Robinson, R.D., Stewart, R.T.: 1985, Solar Phys. 97, 145.
Russell, C.T., Shinde, A.A.: 2005, Solar Phys. 229, 323.
Smith, Z., Dryer, M.: 1990, Solar Phys. 129, 387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S.Y., Yi, Y. & Kim, Y.H. Solar Cycle Variation of the Interplanetary Forward Shock Drivers Observed at 1 AU. Sol Phys 245, 391–410 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-007-9042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-007-9042-2