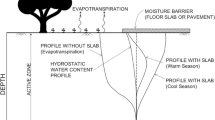
Expansive soil, also called swelling soil can cause severe damage to buildings and foundations due to the high swell-shrink behavior corresponding to moisture content changes. Slag, which is defined as the by-product of the iron and steel-making process, has been widely used as a stabilizer agent for developing clay soil mechanical characteristics. This review paper highlighted the findings of previous studies on treating expansive soils utilizing several types of slag. The effect of mixing slag with other additives such as Portland cement and lime on expansive soil swelling properties was reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. P. Krohn and J. E. Slosson, “Assessment of expansive soils in the United States,” Proc. 4th International Conference on expansive soils, Denver (1980).
A. K. Sharma and P. Sivapullaiah, “Ground granulated blast furnace slag amended fly ash as an expansive soil stabilizer,” Soils Found., 56(2), 205-212 (2016).
L. Jones and I. Jefferson, Expansive Soils, ICE Manual of Geotechnical Engineering, ICE Publishing, London (2012).
F. H. Chen, Foundations on Expansive Soils, Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co., Amsterdam (1975).
B. M. Das and K. Sobhan, Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, Cengage learning (2014).
A. K. Mishra, S. Dhawan, and S. M. Rao, “Analysis of swelling and shrinkage behavior of compacted clays,” Geotech. Geol. Eng., 26(3), 289-298 (2008).
M. Dixit, “Damage mechanism in problematic soils,” Int. J. Civ. Eng. Techn., 7(5), 232-241 (2016).
S. Asuri and P. Keshavamurthy, “Expansive soil characterisation: an appraisal,” INAE Letters, 1(1), 29-33 (2016).
Y. N. Yaseen and J. K. Abbas, “An experimental study on swelling properties of expansive soil treated with iron furnace slag,” Tikrit J. Eng. Scie., 27(3), 61-66 (2020).
Z. Nalbantoğlu, “Effectiveness of class C fly ash as an expansive soil stabilizer,” Constr. Build. Mat., 18(6), 377-381 (2004).
Z. Nalbantoglu and E. Gucbilmez, “Improvement of calcareous expansive soils in semi-arid environments,” J. Arid Environ., 47(4), 453-463 (2001).
R. D. Holtz, W. D. Kovacs, and T. C. Sheahan, An Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering, 2nd ed., Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1981).
A. J. Chen, J. S. Zhang, and H. B. Zou, “Experimental study on CBR swelling characteristics of remolded expansive soil,” Adv. Mat. Res., 287, 1267-1270 (2011).
A. S. Muntohar, “Prediction and classification of expansive clay soils,” Expansive Soils: Recent Advances in Characterization and Treatment, 8, 25-35 (2006).
D. R. Snethen, L. D. Johnson, and D. M. Patrick, An Evaluation of Expedient Methodology for Identification of Potentially Expansive Soils, United States. Federal HIghway Administration (1977).
W. G Holtz and H. J. Gibbs, “Engineering Properties of Expansive Clays,” Transact.Am. Soc. Civ. Eng., 121(1), 641-663 (1956).
Indian Standard IS:1498, Classification and Identification of Soils for General Engineering Purposes, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi (1970).
J. James and P. K. Pandian, “Effect of micro ceramic dust on the plasticity and swell index of lime stabilized expansive soil,” Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 10(42), 30647-30650 (2015).
J. James and P. K. Pandian, “Development of early strength of lime stabilized expansive soil: effect of red mud and egg shell ash,” Acta Technica Corviniensis-Bulletin of Engineering, 9(1), 93 (2016).
A. K. Sabat and S. Pati, “A review of literature on stabilization of expansive soil using solid wastes,” Electron. J. Geotech. Eng., 19 (6), 6251-6267 (2014).
L. Yadu and R. Tripathi, “Effects of granulated blast furnace slag in the engineering behaviour of stabilized soft soil,”Procedia Engineer., 51, 125-131 (2013).
M. Tiza and V. T. Iorver, “A review of literature on effect of agricultural solid wastes on stabilization of expansive soil,” Int. J. Innovative Research in Multidisciplinary Field, 2(7), 121-132 (2016).
T. M. Petry and D. N. Little, “Review of stabilization of clays and expansive soils in pavements and lightly loaded structures—history, practice, and future,” J. Mat. Civ. Eng., 14(6), 447-460 (2002).
A. A. Al-Rawas et al., “A comparative evaluation of various additives used in the stabilization of expansive soils,” Geotech. Test. J., 25(2), 199-209 (2002).
I. Akinwumi, Utilization of Steel Slag for Stabilization of a Lateritic Soil, LAP Lambert Academic Publishing (2013).
M. M. Zumrawi and F. O. Khalill, “Experimental study of steel slag used as aggregate in asphalt mixture,” Am. J. Constr. Build. Mat., 2(1), 26-32 (2017).
I. Z. Yildirim and M. Prezzi, “Chemical, mineralogical, and morphological properties of steel slag,” Adv. Civ. Eng. (2011).
G. Veith, “Essay competition: green, ground and great: soil stabilization with slag,” Build. Res. Inf., 28(1), 70-72 (2000).
Y. Yi M. Liska and A. Al-Tabbaa, “Properties of two model soils stabilized with different blends and contents of GGBS, MgO, lime, and PC,” J. Mat. Civ. Eng., 26(2), 267-274 (2013).
M. E. Ouf, Stabilisation of Clay Subgrade Soils Using Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag, University of Leeds (2001).
H. Matsuda, et al., “Application of granulated blast furnace slag to the earthquake resistant earth structure as a geomaterial,” Proc. 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering (2008).
K. Narendra and A. Prasad, “Effect of ground granulated blast furnace slag on expansive soils under static loading,” VFSTR J. STEM, 3(1), 61-65 (2017).
A. M. Chand, et al., “Behavior of black cotton soil with addition of copper slag and steel slag,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Techn. (IRJET), 4(1), 752-758 (2017).
S. More et al., “Stabilization of black cotton soil by using steel slag,” Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci., Engineering and Technology, 7(5), 6300-6305 (2018).
B. M. Patil, “Effect of steel slag on CBR value of black cotton soil,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Techn. (IRJET), 5(5), 3315 – 3318 (2018).
F. I. Shalabi, I. M. Asi, and H. Y. Qasrawi, “Effect of by-product steel slag on the engineering properties of clay soils,” J. King Saud University-Engineering Sciences, 29(4), 394-399 (2017).
J. V. Chandra and P. M. Lavanya, “Effect of granulated blast furnace slag in the stabilization of expansive soil for the pavement sub-grades,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Techn., 4(5), 1735-1739 (2017).
T. Oormila and T. Preethi, “Effect of stabilization using flyash and GGBS in soil characteristics,” Int. J. Eng. Trends Techn., 11(6), 284-289 (2014).
E. Cokca, V. Yazici, and V. Ozaydin, “Stabilization of expansive clays using granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS) and GBFS-cement,” Geotech. Geol. Eng., 27(4), 489- 499 (2009).
T. P. Thombre and S. S. Koranne, “Stabilization of black cotton soil by using steel slag powder,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Techn., 5(9), 508-512 (2018).
A. Rawat and R. Jain, “Effect of blast furnace slag on index properties of black cotton soil,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Techn. (IRJET), 4(1) (2017).
G. Darwish, and A.P. Tangri, “Effects of ground granulated blast furnace slag and lime on the strength and durability of clayey soil,” Int. J. Eng. Adv. Techn., 8(5), 920-926 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Osnovaniya, Fundamenty i Mekhanika Gruntov, No. 6, November-December, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Saedi, M., Sabbar, A.S. Treatment of Expansive Soils with Slag: A Review Study. Soil Mech Found Eng 60, 574–580 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-024-09931-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-024-09931-5